Tumor Stem Cells: Identification, Isolation and Therapeutic Interventions
Tumor stem cells, also known as cancer stem cells (CSCs), represent a subpopulation of cells within tumors that possess self-renewal capabilities and the ability to give rise to diverse progeny. These cells, often identified by their distinctive surface markers or functional properties, have been implicated in tumor initiation, progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance. The presence of tumor stem cells contributes to the intra-tumoral heterogeneity observed in various cancers, posing significant challenges for effective clinical management.
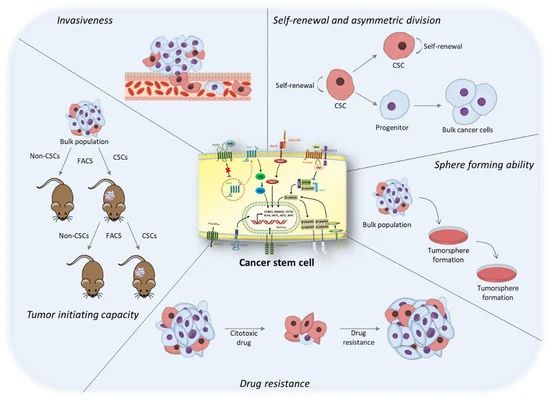 Fig. 1 Main characteristics of cancer stem cells. (Herreros-Pomares A, 2022)
Fig. 1 Main characteristics of cancer stem cells. (Herreros-Pomares A, 2022)
Identification and Isolation of Tumor Stem Cells
The identification and isolation of tumor stem cells comprise a complex and multifaceted endeavor in the field of cancer research. Researchers employ a combination of methodologies, such as cell surface marker profiling, functional assays, and genetic characterization, to delineate the unique attributes of tumor stem cell populations. Through these approaches, the remarkable heterogeneity and plasticity of tumor stem cells have been elucidated, shedding light on their dynamic roles in driving tumorigenesis and disease progression.
- Cell surface marker profiling. Tumor stem cells are often identified based on their distinct expression of cell surface markers. By utilizing techniques such as flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry, researchers can delineate specific antigenic profiles that distinguish tumor stem cells from differentiated tumor cells and normal tissue counterparts. This enables the selective isolation and enrichment of tumor stem cell populations for further analysis and functional studies.
- Functional assays. Functional assays play a critical role in validating the stem-like properties of tumor cells, including self-renewal capacity and multilineage differentiation potential. Sphere formation assays, clonogenic assays, and xenotransplantation into immunocompromised mice are commonly utilized to assess the tumorigenic potential of putative tumor stem cell populations, thereby verifying their ability to propagate tumor growth and maintain cellular heterogeneity.
- Genetic and transcriptomic characterization. The application of high-throughput sequencing technologies and single-cell transcriptomic profiling has revolutionized the molecular characterization of tumor stem cells. These approaches enable the comprehensive analysis of genetic alterations, signaling pathways, and gene expression patterns that underpin the stemness phenotype, providing invaluable insights into the regulatory networks governing tumor stem cell behavior.
Targeting Tumor Stem Cells for Therapeutic Intervention
Efforts to develop therapeutic strategies targeting tumor stem cells have gained momentum in recent years. By understanding the distinct molecular and metabolic vulnerabilities of tumor stem cells, researchers seek to devise precision-targeted therapies that selectively eradicate this critical cell population while preserving normal tissues' integrity. Innovative modalities, including stem cell-directed therapies, combination regimens, and immunotherapeutic approaches, hold promise in dismantling the foundations of tumor stem cell-driven malignancies.
- Stem cell-directed therapies. Designing therapeutics that exploit the vulnerabilities and distinct features of tumor stem cells represents an active area of research. By identifying molecular pathways and signaling cascades that are preferentially active in tumor stem cells, novel small molecule inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, or other targeted agents can be developed to selectively disrupt key regulatory mechanisms driving the stemness phenotype.
- Combination therapies. Combining conventional cytotoxic treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, with agents specifically targeting tumor stem cells is a strategy aimed at comprehensively addressing tumor cell populations. By leveraging the differential sensitivities of tumor stem cells and their differentiated progeny to distinct treatment modalities, combination regimens seek to disrupt the tumor hierarchy and minimize the emergence of therapy-resistant cell populations.
- Immunotherapeutic modalities. Immunotherapies have emerged as a potent approach with the potential to target tumor stem cells through immune-mediated mechanisms. Therapeutic vaccines, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and adoptive cell therapies hold the potential to engage the immune system in recognizing and eliminating tumor stem cells, leveraging the complex interplay between the tumor microenvironment and immune surveillance.
Creative Bioarray Relevant Recommendations
Creative Bioarray provides optimized solutions for cancer stem cell research—from identification and culturing to genomic and functional analysis.
View our full range of tumor stem cells and find what you need!
Reference
- Herreros-Pomares A. (2022). "Identification, Culture and Targeting of Cancer Stem Cells." Life (Basel). 12 (2), 184.

