Exosomal Delivery of miR-410-3p Reverses Trophoblast EMT, Migration and Invasion
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 2024 Feb; 28 (3): e18097
Authors: Chen ZY, Li Z, Zong Y, Xia B, Luo SP, Deng GP, Gao J
INTRODUCTION
Current studies have indicated that insufficient trophoblast epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), migration, and invasion are crucial for spontaneous abortion (SA) occurrence and development. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous, non-coding, 22-nucleotide, single-stranded protein RNAs, widely present in eukaryotic cells. Exosomes are membranous vesicles released outside the cell after the fusion of intracellular multivesicular body and cell membrane, with a diameter of about 30 to 150 nm. Exosomes contain miRNAs, mRNAs, and DNA sequences that can be transferred to receptor cells to modulate their behavior. Exosomal miRNAs play significant roles in embryonic development and cellular communication.
METHODS
- The human trophoblast cell line HTR-8/SVneo (HTR-8) was cultured in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) at 37°C and 5% CO2. The miRNA mimic and inhibitor for miR-410-3p and the siRNA for TRAF6 were synthesized. HTR-8 cells were seeded on 6-well plates 24 hours before transfection. When cells reached 40%–50% confluence, mimic and inhibitor miRNAs, or siRNA, were transfected following the instructions. Cells were harvested 48 h after transfection.
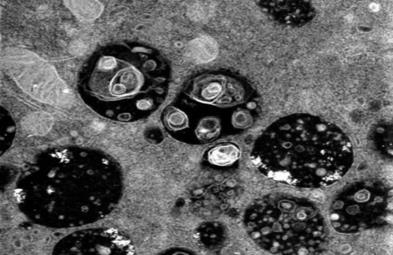
- Serum exosomes were isolated using cell culture media and the exosome isolation kit. After isolation, exosomes were stored at -80°C immediately for further analysis. Exosome morphology was determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Exosome particle size and concentration were measured by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). The NC and SA serum exosomes were labeled with PKH26 fluorescent dye. Stained exosomes were co-cultured with HTR-8 cells. After 48 h of incubation, the nuclei of each group were stained DAPI.
- Browse our recommendations
| Product/Service Types | Description |
| Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Service | Creative Bioarray has scientists and imaging laboratories to perform the full comprehensive TEM and Scanning TEM (STEM) service for the biological sciences and clinical research including plant samples, animal samples, bacteria, and pathology specimens. |
| Exosome Isolation Tools | Creative Bioarray aims to develop the best quality exosome isolation tools with optimized conditions to help our customers obtain pure exosomes with a higher yield. |
| Exosome DNA-RNA Extraction Kits | Creative Bioarray aims to develop the best quality exosome extraction kits with optimized conditions to help our customers obtain pure exosomes with higher yields. |
| Exosome Quantification | Exosome quantification mainly depends on their characteristic physical properties, such as size, mass, and density, or membrane proteins present on their surface. Creative Bioarray offers a range of options to meet most exosome quantitation demands. |
RESULTS
- miRNAs from normal control (NC) and SA serum exosomes were sequenced to determine how they affected trophoblast EMT, migration, and invasion. The heatmap showed that miR-371a-5p (log2(foldchange) = 8.0579, p-value = 0.004751), miR-3607-3p (log2(foldchange) = 6.2209, p-value = 0.010145), miR-147b (log2(foldchange) = 5.9556, p-value = 0.000715), miR-373-3p (log2(foldchange) = 5.9193, p-value = 0.013759), miR-6859-5p (log2(foldchange) = 5.6017, p-value = 0.004176), miR-410-3p (log2(foldchange) = 5.4236, p-value = 0.009131), miR-1275 (log2(foldchange) = 5.3395, p-value = 0.039169), miR-1270 (log2(foldchange) = 5.3295, p-value = 0.005300), miR-382-3p (log2(foldchange) = 5.128, p-value = 0.028083) and miR-6087 (log2(foldchange) = 4.9745, p-value = 0.012158) were the top 10 differentially expressed miRNAs. Since only miR-410-3p is a human-mouse homologous, we detected its expression in dependent samples by RT-PCR. We demonstrated that miR-410-3p was highly expressed in SA serum exosome. Hence, we selected miR-410-3p as the pivotal miRNA to study.
- We treated HTR-8 cells with NC or SA serum exosomes to elucidate whether the exosomes regulated SA serum inhibitory activity. The RT-PCR showed that SA serum exosomes increased miR-410-3p levels. The miR-410-3p level was reduced in SA serum exosomes after RNase A and Triton X-100 treatment but not after RNase A treatment alone, suggesting that extracellular miR-410-3p was encapsulated in the cell membrane rather than released directly. Furthermore, preliminary RNA polymerase II inhibitor treatment did not impact the level of miR-410-3p in recipient HTR-8 cells treated with SA serum exosomes, indicating that the increased miR-410-3p levels in trophoblasts might be due to SA serum exosomes-mediated miRNA transfer rather than endogenous miR-410-3p induction. These findings revealed that SA serum exosomes are enriched with miR-410-3p and increase miR-410-3p levels in trophoblasts.
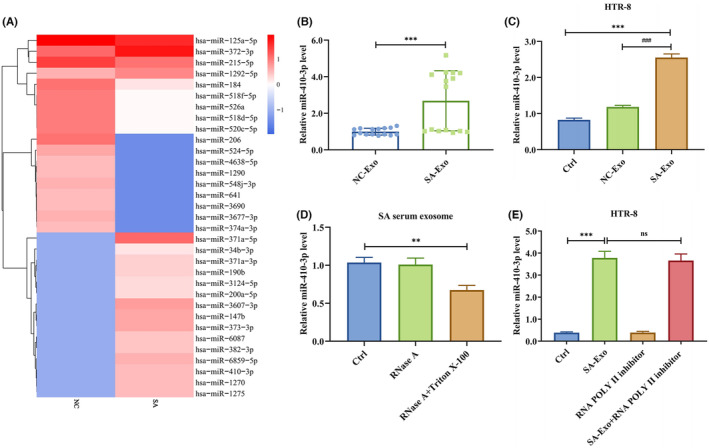 Fig. 1 SA serum exosomes are enriched with miR-410-3p.
Fig. 1 SA serum exosomes are enriched with miR-410-3p.
- To study the role of miR-410-3p on trophoblast migration and invasion, HTR-8 cells were transfected with miR-410-3p mimic or inhibitor. The miR-410-3p mimic facilitated miR-410-3p expression in HTR-8 cells, the opposite of its inhibitor. Additionally, the miR-410-3p mimic induced E-cadherin and inhibited N-cadherin and vimentin protein levels in HTR-8 cells in contrast to the miR-410-3p inhibitor. In the CCK-8 assay, the miR-410-3p mimic significantly inhibited HTR-8 cell proliferation, while the miR-410-3p inhibitor stimulated it. The wound healing and transwell assays showed that the miR-410-3p mimic slowed the scratch closure and weakened the invasion of HTR-8 cells, the opposite of the miR-410-3p inhibitor. These results indicated that SA serum exosomes restrict trophoblast proliferation, migration, and invasion via miR-410-3p transferring.
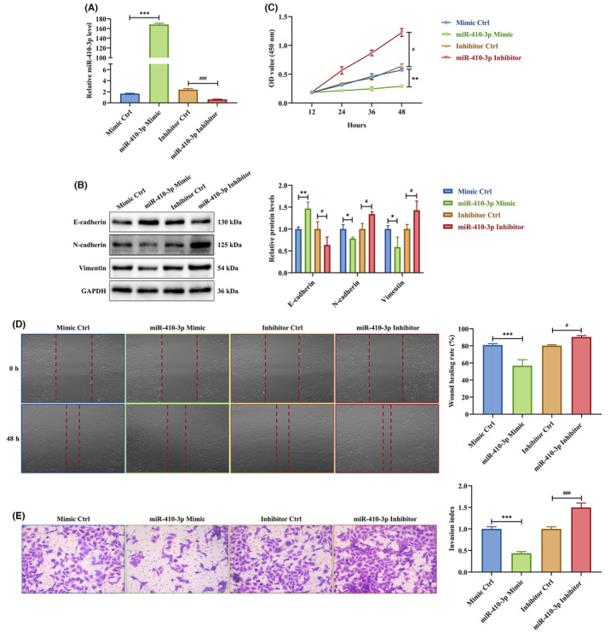 Fig. 2 miR-410-3p is responsible for the effects of SA serum exosomes on trophoblasts.
Fig. 2 miR-410-3p is responsible for the effects of SA serum exosomes on trophoblasts.
SUMMARY
The serum exosomes from SA patients inhibited trophoblast EMT and reduced their migration and invasion ability in vitro. The miRNA sequencing showed that miR-410-3p was upregulated in SA serum exosomes. The functional experiments showed that SA serum exosomes restrained trophoblast EMT, migration, and invasion by releasing miR-410-3p.
RELATED PRODUCTS & SERVICES
Reference
- Chen ZY, et al. (2024). "Exosome-delivered miR-410-3p reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of trophoblasts in spontaneous abortion." J Cell Mol Med. 28 (3): e18097.