- You are here: Home
- Services
- Disease Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) & High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Streptozotocin (STZ) & High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
Creative Bioarray has extensive experience in researching nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and provides clients worldwide with comprehensive preclinical services for NAFLD. Our team will work closely with you, assisting in the selection of appropriate models, designing study plans, and conducting final data analysis and reporting.
NAFLD is increasingly recognized as a significant liver manifestation of metabolic syndrome, which is closely linked to diabetes. Due to this strong association, there is widespread speculation that the connection between diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) may be intricately related to the progression of NAFLD. In order to delve deeper into this hypothesis and explore the potential role of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in the causal association between diabetes and HCC, we have meticulously established a NAFLD model induced by STZ in conjunction with a high-fat diet. This model allows us to simulate the metabolic disturbances observed in patients with diabetes and NAFLD, providing a robust platform for investigating the potential mechanisms underlying the progression from diabetes to HCC through the lens of NASH, as well as evaluating new therapies.
Our Streptozotocin (STZ) & High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Available Animal
Mouse
- Modeling Method
Neonatal C57BL/6 mice receive a single low-dose STZ injection two days after birth followed by administration of a high-fat diet after four weeks of age.
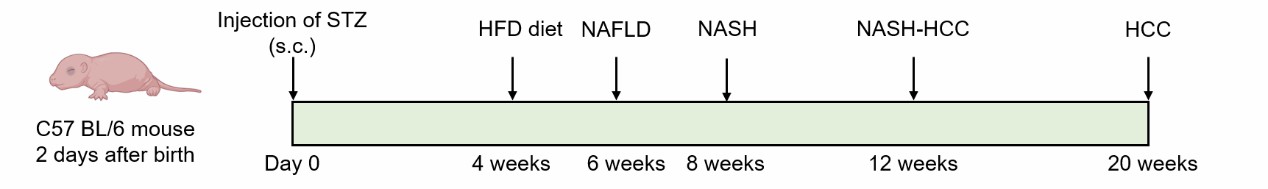 Fig. 1 Modeling method of streptozotocin (STZ) & high-fat diet -induced NAFLD model.
Fig. 1 Modeling method of streptozotocin (STZ) & high-fat diet -induced NAFLD model.
- Endpoints
- Body weight
- Liver weight
- Serum analysis: AST, ALT, TG, TC
- Histology analysis: H&E staining, Oil red O staining
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
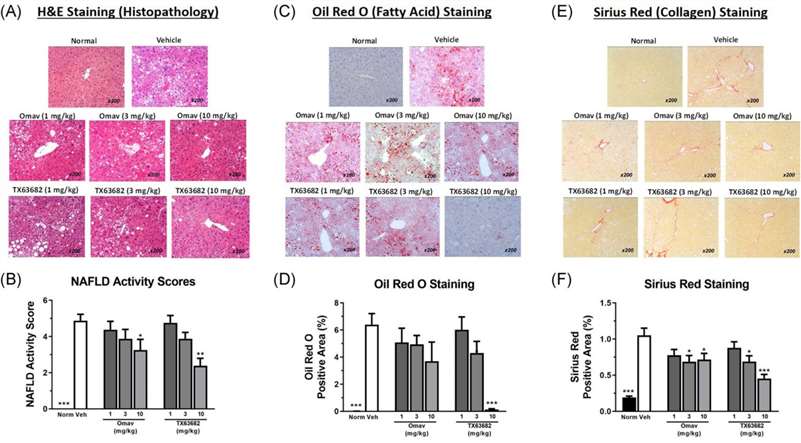 Fig. 2 Omaveloxolone and analog TX63682 protect liver in the model of NASH. Representative photomicrographs are presented for histopathology (A), Oil Red O staining of fatty acids (C), and Sirius Red staining of collagen (E). NAFLD activity scores (B) and percent positive area for Oil Red O (D) and Sirius Red (F) are also presented. (Reisman et al. 2020)
Fig. 2 Omaveloxolone and analog TX63682 protect liver in the model of NASH. Representative photomicrographs are presented for histopathology (A), Oil Red O staining of fatty acids (C), and Sirius Red staining of collagen (E). NAFLD activity scores (B) and percent positive area for Oil Red O (D) and Sirius Red (F) are also presented. (Reisman et al. 2020)
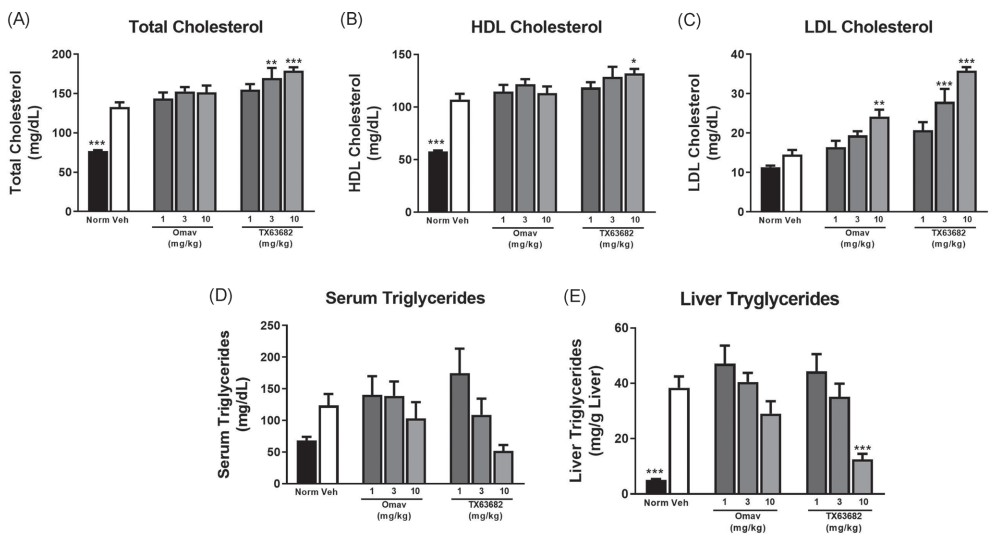 Fig. 3 Effect of omaveloxolone and analog TX63682 on lipids. Serum total cholesterol (A), HDL cholesterol (B), LDL cholesterol (C), and triglycerides (D) were analyzed by HPLC. E, Liver triglycerides were quantified with the commercially available Triglyceride E‐test Kit. (Reisman et al. 2020)
Fig. 3 Effect of omaveloxolone and analog TX63682 on lipids. Serum total cholesterol (A), HDL cholesterol (B), LDL cholesterol (C), and triglycerides (D) were analyzed by HPLC. E, Liver triglycerides were quantified with the commercially available Triglyceride E‐test Kit. (Reisman et al. 2020)
Furthermore, we also provide other NAFLD models that maybe you are interested in:
- High-fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray has a group of seasoned experts who are not only specialized in establishing disease models but also experienced in data interpretation. With our rich experiences and cutting-edge techniques, we are confident to provide you with the first-class services to meet your exact research needs. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
Reference
- Reisman, S.A., et al. Omaveloxolone and TX63682 are hepatoprotective in the STAM mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 2020, 34(9): e22526.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

