- You are here: Home
- Services
- Disease Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
Creative Bioarray stands at the forefront of providing the most comprehensive animal model services tailored for the methionine and choline deficient (MCD) diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) model in mice. We can deliver robust results at highly competitive prices, ensuring that our clients can significantly accelerate their drug development processes. At Creative Bioarray, we are not just service providers; we are your partners in innovation, dedicated to propelling your research forward and bringing your discoveries to the market faster.
The MCD diet, which is commonly used in NAFLD animal studies, is characterized by a high sucrose content (40%) and a moderate amount of fat (10%). However, it lacks sufficient methionine and choline. Methionine is an essential amino acid that cannot be produced by the body and plays a crucial role in the synthesis of various compounds such as cysteine, lecithin, phosphatidylcholine, and others. Similarly, choline is an important component of cell and mitochondrial membranes and serves as a precursor for acetylcholine. The deficiency of these two components leads to impaired synthesis of phosphatidylcholine, resulting in reduced assembly and secretion of VLDL. Consequently, there is a decrease in triglyceride (TG) clearance, leading to the accumulation of lipids in the liver. This model also exhibits other pathological features, including impaired mitochondrial β-oxidation, increased oxidative stress from CYP2E1, and depletion of hepatic antioxidants. These factors contribute to the development of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and steatohepatitis.
Our Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Available Animal
Mouse
- Modeling Method
Animals are fed a MCD diet for 3-4 weeks to induce NAFLD.
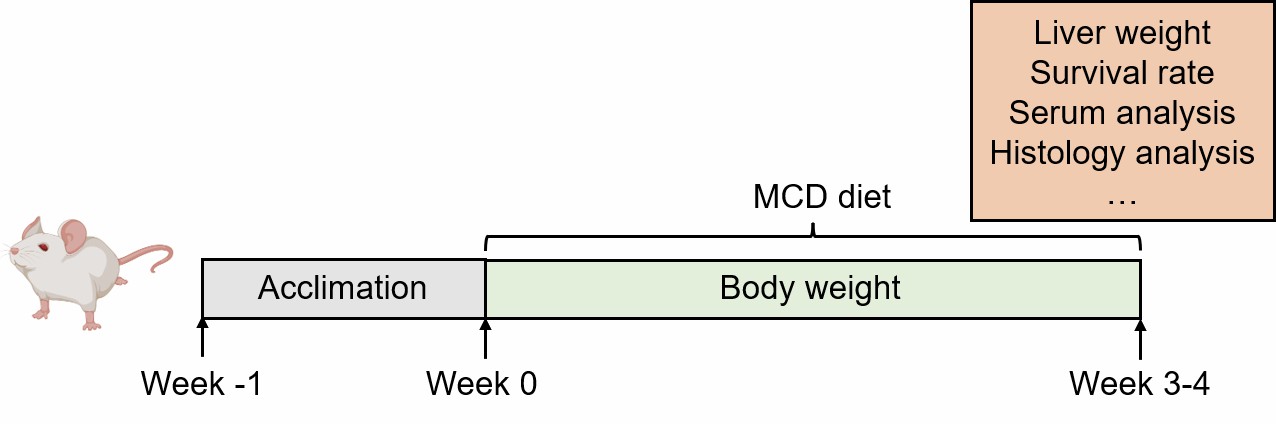 Fig. 1 Modeling method for the MCD diet-induced NAFLD model.
Fig. 1 Modeling method for the MCD diet-induced NAFLD model.
- Endpoints
- Body weight
- Liver weight
- Survival rate
- Serum analysis: ALT, AST, TG, TC
- Histology analysis: H&E staining, Oil red O staining
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
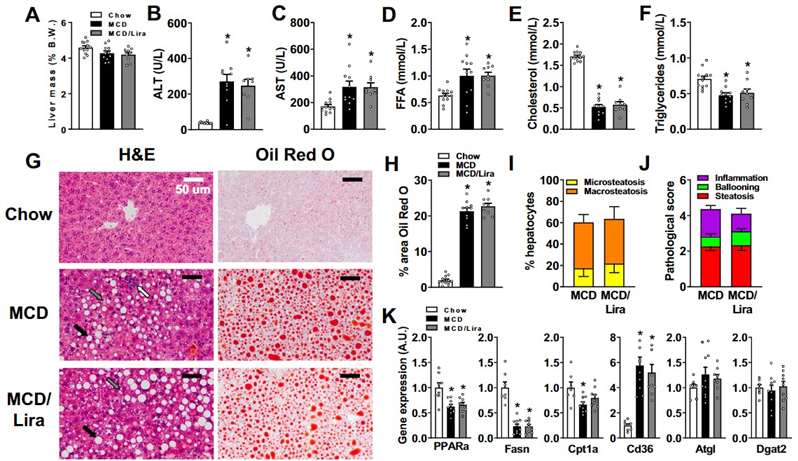 Fig. 2 Liraglutide infusion does not quantitatively change hepatic lipid accumulation in MCD diet-fed mice. (A) Relative liver mass. (B) Circulating alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels. (C) Circulating aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels. (D) Circulating free fatty acid (FFA) levels. (E) Circulating total cholesterol levels. (F) Circulating triglyceride levels. (G) Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Oil-red O staining of liver sections. (H) Quantification of lipids expressed as percent of area of liver sections stained with Oil red O. (I) Evaluation of the percent of hepatocyte containing micro- and macrosteatosis. (J) Pathological score with steatosis and activity. (K) Hepatic gene expression of lipids enzymes and transporters. (Somm et al. 2021)
Fig. 2 Liraglutide infusion does not quantitatively change hepatic lipid accumulation in MCD diet-fed mice. (A) Relative liver mass. (B) Circulating alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels. (C) Circulating aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels. (D) Circulating free fatty acid (FFA) levels. (E) Circulating total cholesterol levels. (F) Circulating triglyceride levels. (G) Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Oil-red O staining of liver sections. (H) Quantification of lipids expressed as percent of area of liver sections stained with Oil red O. (I) Evaluation of the percent of hepatocyte containing micro- and macrosteatosis. (J) Pathological score with steatosis and activity. (K) Hepatic gene expression of lipids enzymes and transporters. (Somm et al. 2021)
Meanwhile, we also provide other NAFLD models that maybe you are interested in:
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) & High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray is a leading research partner that specializes in offering a wide range of rodent disease models and comprehensive services with expertise in the field. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
References
- Nevzorova, Y.A., et al. Animal models for liver disease–a practical approach for translational research. Journal of hepatology, 2020, 73(2): 423-440.
- Somm, E., et al. The GLP-1R agonist liraglutide limits hepatic lipotoxicity and inflammatory response in mice fed a methionine-choline deficient diet. Translational research, 2021, 227: 75-88.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

