- You are here: Home
- Disease Models
- Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- EAE Models
- Proteolipid Protein (PLP)-Induced Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) Model
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Pain Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
Proteolipid Protein (PLP)-Induced Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) Model
Creative Bioarray offers a robust and stable model of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) induced through Proteolipid Protein (PLP). This model is designed to closely mimic human multiple sclerosis (MS), providing a reliable platform for the evaluation of potential therapeutic interventions. We provide a comprehensive range of assessments and support various administration routes tailored to specific needs, ensuring flexibility and precision in preclinical testing.
Our Proteolipid Protein (PLP)-Induced Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) Model
- Model Description (Relapsing EAE)
PLP is a major protein component of CNS myelin. Sections of PLP, such as 139-151 peptide, are encephalitogenic to certain mouse strains. The PLP-induced EAE model is commonly used to study MS due to its similarity to the human disease. In this model, female SJL mice are immunized with the PLP139-151 peptide, followed by administration of pertussis toxin (PTX). This leads to a relapsing-remitting disease course characterized by ascending flaccid paralysis, starting from the tail and progressing to hind and forelimb paralysis. The disease involves CNS inflammation, demyelination, and axonal cell death, with autoreactive T cells migrating into and re-activating within the CNS. This model is valuable for studying the effects of potential treatments on disease relapses and overall disease progression.
- Features of PLP-induced EAE Model in Creative Bioarray
- Relapsing-Remitting Disease Course: This model is a relapsing-remitting demyelinating disease.
- Therapeutic Treatment Evaluation: Ideal for studying the development and treatment of EAE relapses.
- Available Animal
Swiss Jim Lambert (SJL) mouse (female)
- Modeling Method
Relapsing EAE is induced in female SJL mice by immunization with PLP139-151 in CFA emulsion followed by two-time administration of PTX.
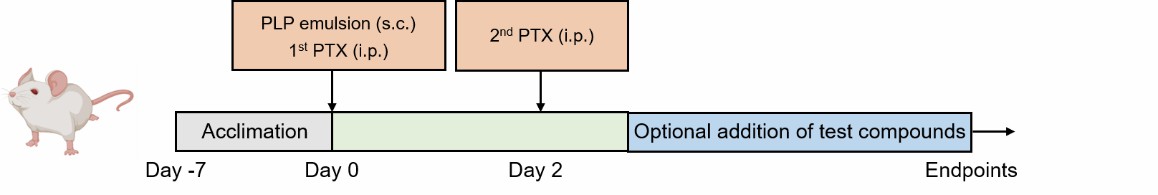 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the PLP-induced EAE model
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the PLP-induced EAE model
- Endpoints
- Body weight
- Clinical score
- Histology analysis
- Cytokine analysis
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
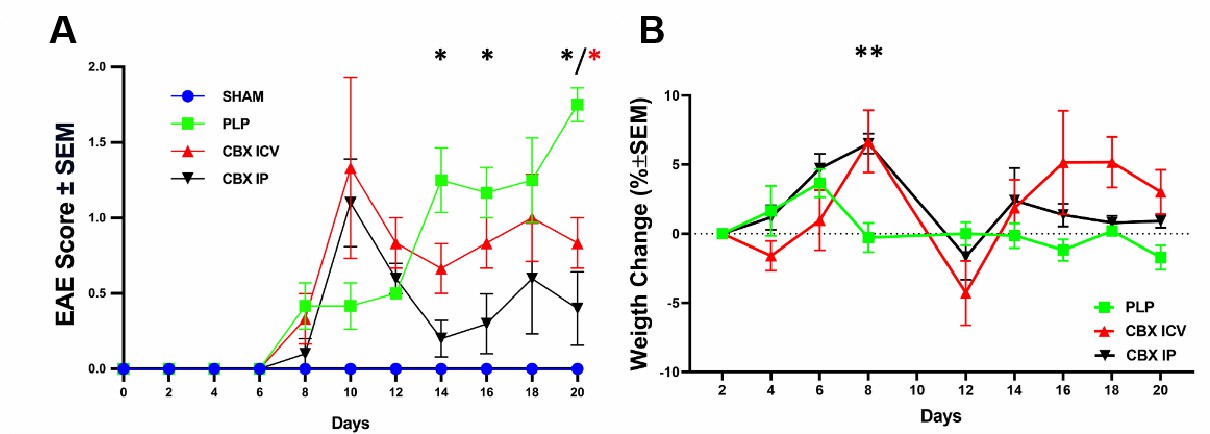 Fig. 2 Validation of PLP-EAE model. (A) The neurological scores deteriorated quickly at day 8 and entered remission from day 12 to the end of the experiment for CBX-treated groups but increased gradually and were maximum on the last day of the investigation for the PLP-EAE group. (B) Weight gain followed a similar trend with the neurological scores, and the worst day (the maximum weight loss) was observed after the day with top neurological scores. (Ucar et al. 2024)
Fig. 2 Validation of PLP-EAE model. (A) The neurological scores deteriorated quickly at day 8 and entered remission from day 12 to the end of the experiment for CBX-treated groups but increased gradually and were maximum on the last day of the investigation for the PLP-EAE group. (B) Weight gain followed a similar trend with the neurological scores, and the worst day (the maximum weight loss) was observed after the day with top neurological scores. (Ucar et al. 2024)
In addition, we also provide other EAE models that maybe you are interested in:
- MOG35-55-Induced Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) Model
- Myelin Basic Protein (MBP)-Induced Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) Model
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray stands as a premier research partner, providing an extensive array of rodent disease models and associated services. Our dedicated team of skilled experts and scientists works in close partnership with you to identify the most suitable disease model and develop a comprehensive research plan tailored to your project's needs. If you are interested in our services, please contact us or submit an inquiry.
Reference
- Ucar, E.A., et al. Carbenoxolone mitigates extensive fibrosis formation in PLP-induced EAE model and multiple sclerosis serum-exposed pericyte culture. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 2024, 18: 1403974.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

