- You are here: Home
- Services
- Disease Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
- Fructose and Potassium Oxonate-Induced Hyperuricemia Model
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Fructose and Potassium Oxonate-Induced Hyperuricemia Model
Creative Bioarray is renowned for its expertise in establishing innovative animal models that accurately replicate human diseases. Our commitment to excellence is evident in our meticulously developed hyperuricemia model, which is induced through a combination of fructose and potassium oxonate. This model has been carefully designed to not only simulate the pathophysiological conditions of hyperuricemia but also to be adaptable to your specific research needs. Whether you are exploring the intricacies of disease mechanisms, evaluating novel therapeutic interventions, or validating diagnostic tools, our hyperuricemia model offers a robust platform to advance your research endeavors.
The fructose and potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia model offers a compelling approach to studying the mechanisms and treatments of hyperuricemia, leveraging the distinct metabolic pathways influenced by fructose and potassium oxonate. Fructose, predominantly metabolized in the liver by ketohexokinase (fructokinase C, KHK-C, or KHK), leads to the rapid generation of fructose-1-phosphate. This swift reaction depletes ATP and lowers phosphorylation levels, prompting an increase in AMP deaminase activity under conditions of reduced intracellular phosphate. Consequently, AMP is converted to IMP, intensifying the production of uric acid.
In tandem, potassium oxonate, a triazabenzene compound, inhibits uricase activity, further elevating uric acid levels. This dual mechanism--fructose metabolism and uricase inhibition--creates a robust model for hyperuricemia that closely mimics the human condition.
Our Fructose and Potassium Oxonate-Induced Hyperuricemia Model
- Available Animal
Rat
- Modeling Method
Animals are administered a daily regimen of fructose dissolved in drinking water, supplemented with intragastric potassium oxonate, over a period of 10 weeks to induce hyperuricemia.
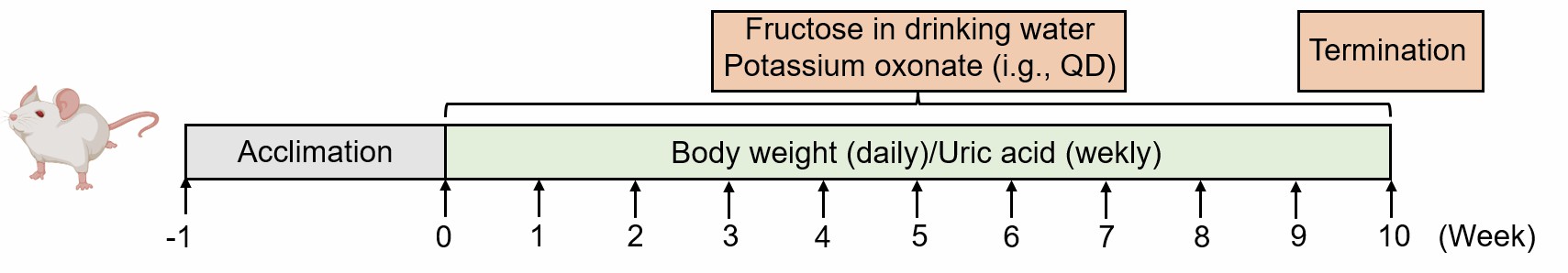 Fig. 1 Modeling method of fructose and potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia model.
Fig. 1 Modeling method of fructose and potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia model.
- Endpoints
- Serum biomarkers: uric acid (UA), creatinine, BUN, etc
- Kidney observation
- Histology analysis of kidney: H&E staining, Masson staining
- qPCR or Western blot
- Body weight
- Other customized endpoints: available upon request
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray is willing to share our state-of-the-art platforms and sufficient expertise with our clients to boost their drug development. If you are interested in our services, please do not hesitate to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
Reference
- Xu, Z., et al. Comparison of 3 hyperuricemia mouse models and evaluation of food-derived anti-hyperuricemia compound with spontaneous hyperuricemia mouse model. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2022, 630: 41-49.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

