Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
NUGC-4
Cat.No.: CSC-C6343J
Species: Human
Morphology: epithelial-like
Culture Properties: Adherent cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Store in liquid nitrogen.
The NUGC-4 cell line is a valuable model system derived from a signet ring cell carcinoma of the stomach. Signet ring cell carcinoma is a rare and highly aggressive subtype of gastric cancer, characterized by the presence of distinct mucin-producing tumor cells with a characteristic "signet ring" appearance.
The NUGC-4 cell line provides researchers with a unique opportunity to study the underlying molecular mechanisms and cellular behaviors that drive the development and progression of signet ring cell carcinoma of the stomach. As a human-derived model system, NUGC-4 cells retain the genetic and phenotypic characteristics of the original tumor, enabling more clinically relevant investigations compared to animal models or other gastric cancer cell lines.
Secretion of IL-1α and VEGF Protein by Gastric Cancer Cell Lines
Interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1α) plays an important role in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis of gastric cancer. The interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) inhibits IL-1 selectively, specifically through IL-1R type I (IL-1RI). The results of the reverse transcription (RT)-PCR analysis revealed that IL-1α mRNA was expressed only in the MKN45 cell line; no expression of IL-1α mRNA was detected in the NUGC-4 and AGS cell lines (Fig. 1a). Relative expression of IL-1α mRNA was determined by semi-quantitative RT-PCR, with the results agreeing with those of the RT-PCR experiment (Fig. 1b).
IL-1α protein was detected in the supernatants of cultured MKN45 and HUVEC cells (7.922 ± 0.525 and 5.231 ± 0.367 pg/mL/2 × 105cells, respectively), but not in those of cultured NUGC-4 and AGS cells (Fig. 2a). IL-1α significantly enhanced VEGF secretion by HUVECs in a dose-dependent manner (*P < 0.01, **P < 0.05), while VEGF secretion by HUVECs was blocked by rIL-1RA (*P < 0.01; Fig. 2c). The secretion of VEGF protein by MKN45 cells was higher than that by NUGC-4 and AGS cells (*P < 0.01). RIL-1RA blocked VEGF secretion by MKN45 cells in a dose-dependent manner (compared with control, *P < 0.01, **P < 0.05), but that by NUGC-4 and AGS was not affected (Fig. 2b).
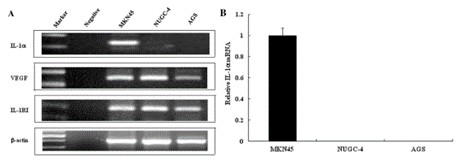 Fig. 1 Expression levels of interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1α), interleukin 1 receptor type I (IL-1RI), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA in gastric cancer cell lines MKN45, NUGC-4, and AGS. (Gong Z, et al., 2018)
Fig. 1 Expression levels of interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1α), interleukin 1 receptor type I (IL-1RI), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA in gastric cancer cell lines MKN45, NUGC-4, and AGS. (Gong Z, et al., 2018)
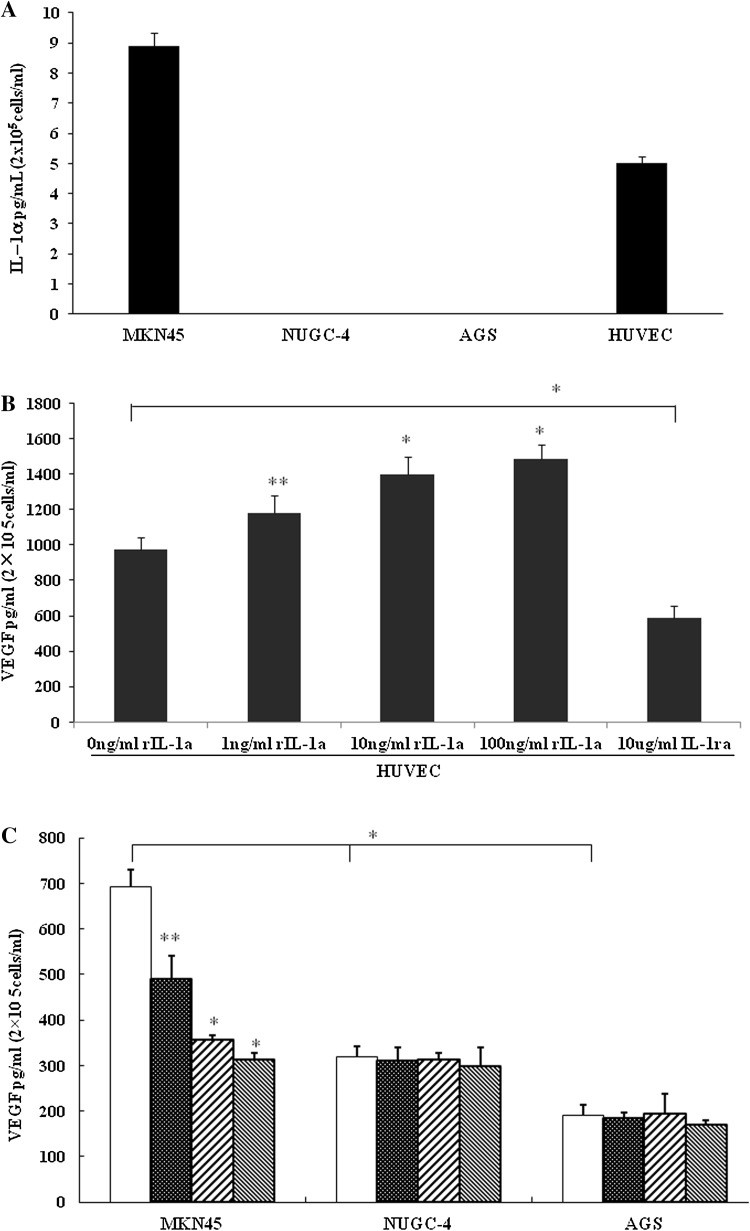 Fig. 2 (a) Secreted IL-1α levels in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and gastric cancer cell lines MKN45, NUGC-4, and AGS. (b) Effect of IL-1α and IL-1RA on the level of VEGF secreted by HUVECs. (c) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) influences the secretion of VEGF in gastric cancer cell lines. (Gong Z, et al., 2018)
Fig. 2 (a) Secreted IL-1α levels in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and gastric cancer cell lines MKN45, NUGC-4, and AGS. (b) Effect of IL-1α and IL-1RA on the level of VEGF secreted by HUVECs. (c) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) influences the secretion of VEGF in gastric cancer cell lines. (Gong Z, et al., 2018)
Anti-cancer Activity of iPS-ML Expressing Anti-HER2 scFv in Vitro
iPS-ML (iPS-cell-derived myeloid/macrophage line), generated by introducing proliferation and anti-senescence factors into iPS-cell-derived myeloid cells, grew continuously in an M-CSF-dependent manner. A cancer-related antigen, HER2/neu, is expressed in various human cancers, including breast and gastric cancers. The anti-cancer effect of iPS-ML expressing anti-HER2 single chain variable region fragment (scFv) was examined against a HER2-expressing gastric cancer cell line, NUGC-4 (Fig. 3A). iPS-ML stably expressing anti-HER2 scFv (iPS-ML/anti-HER2) was generated (Fig. 3B). iPS-ML/anti-HER2 were generated from iPS-MC derived from an iPS cell clone introduced with an expression vector for anti-HER2 scFv by a previously described method. The expression of the scFv by iPS-ML/anti-HER2 was examined and confirmed.
At first, the effect of iPS-ML/anti-HER2 against NUGC-4 cells was evaluated in vitro. Firefly luciferase-introduced NUGC-4 cells were co-cultured with iPS-ML with or without anti-HER2 scFv expression. iPS-ML reduced live NUGC-4 cells, and the expression of anti-HER2 scFv in iPS-ML enhanced the inhibitory effect against the growth of NUGC-4 cells (Fig. 3C).
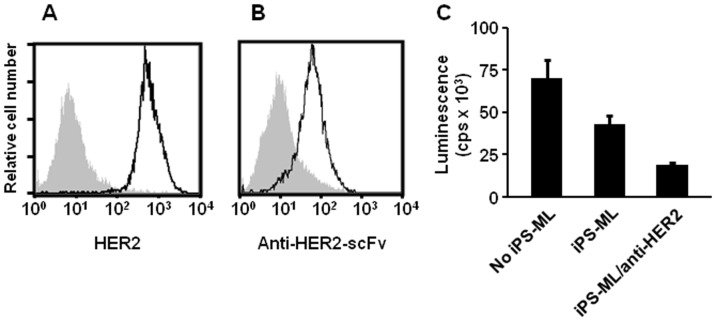 Fig. 3 Effect of trypsin treatment on adhesion of MKN-1 cells to fibronectin. (Miyata S, et al., 2000)
Fig. 3 Effect of trypsin treatment on adhesion of MKN-1 cells to fibronectin. (Miyata S, et al., 2000)
The most common is called adenocarcinoma, which accounts for about 90-95% of people with stomach cancer. Other types include primary gastric lymphoma, gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), and neuroendocrine (carcinoid) tumors in the stomach.
NUGC-4 cells are derived from signet ring cell carcinoma of the stomach, a subtype of gastric cancer known for its aggressive nature and distinct cellular morphology.
NUGC-4 cells are characterized by their signet ring appearance. This morphology is due to the presence of abundant intracytoplasmic mucin that pushes the nucleus to the periphery of the cell, giving it a ring-like appearance.
NUGC-4 cells are typically cultured in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). They should be maintained at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Proper adherence to these conditions is essential for optimal cell growth and viability.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 4.7 | 3 Scientist has reviewed this product
Timely replies
During the experiment, I asked many times for advice on cell culture methods and precautions, and Creative Bioarray's technicians always replied to my emails promptly.
23 Mar 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Good growth
The cells were delivered promptly and in perfect condition. They have performed exceptionally well in our assays, maintaining consistent morphology and growth rates.
13 Jan 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Outstanding technical support
The technical support from Creative Bioarray was outstanding, providing detailed protocols and troubleshooting assistance.
11 Dec 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need