
Immortalized Human Cardiomyocytes-SV40
Cat.No.: CSC-I9071L
Species: homo sapiens
Source: Ventricle Tissue
Morphology: Multipolar
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20 °C.
CIK-HT003 HT® Lenti-SV40T Immortalization Kit
The adult mammalian heart is composed of a variety of cell types, including cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, vascular and perivascular cells. The composition of the heart varies greatly between species, but in humans, cardiomyocytes are the largest cell type by volume, accounting for 70%-85% of the entire heart. Cardiomyocytes give rise to specialized cells such as atrial myocytes, ventricular myocytes and Purkinje cells, and are responsible for generating contractility.
Primary cells and immortalized cell lines derived from human tissues are two commonly used experimental models. Primary cells reflect disease biology most faithfully since they are directly isolated from the tissue of interest, and they maintain the morphology, function and protein markers in culture dishes as they possess in vivo, but they are relatively delicate cells that are difficult to maintain in culture and have a finite lifespan with limited potential for expansion.
Immortalized cardiomyocytes, which are generated from primary cells, are feasible alternatives to both primary cultures and in vivo experiments using laboratory animals. These cells exhibit rapid proliferation and homogeneous response to stimuli in culture, which allows them to be used in high-throughput drug screening experiment and even to model various cardiovascular diseases such as cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic response, cardiac adverse remodeling, metabolic alternations or ischemia-reperfusion injury. In addition, their culturing protocols are simple, and their maintenance costs are low.
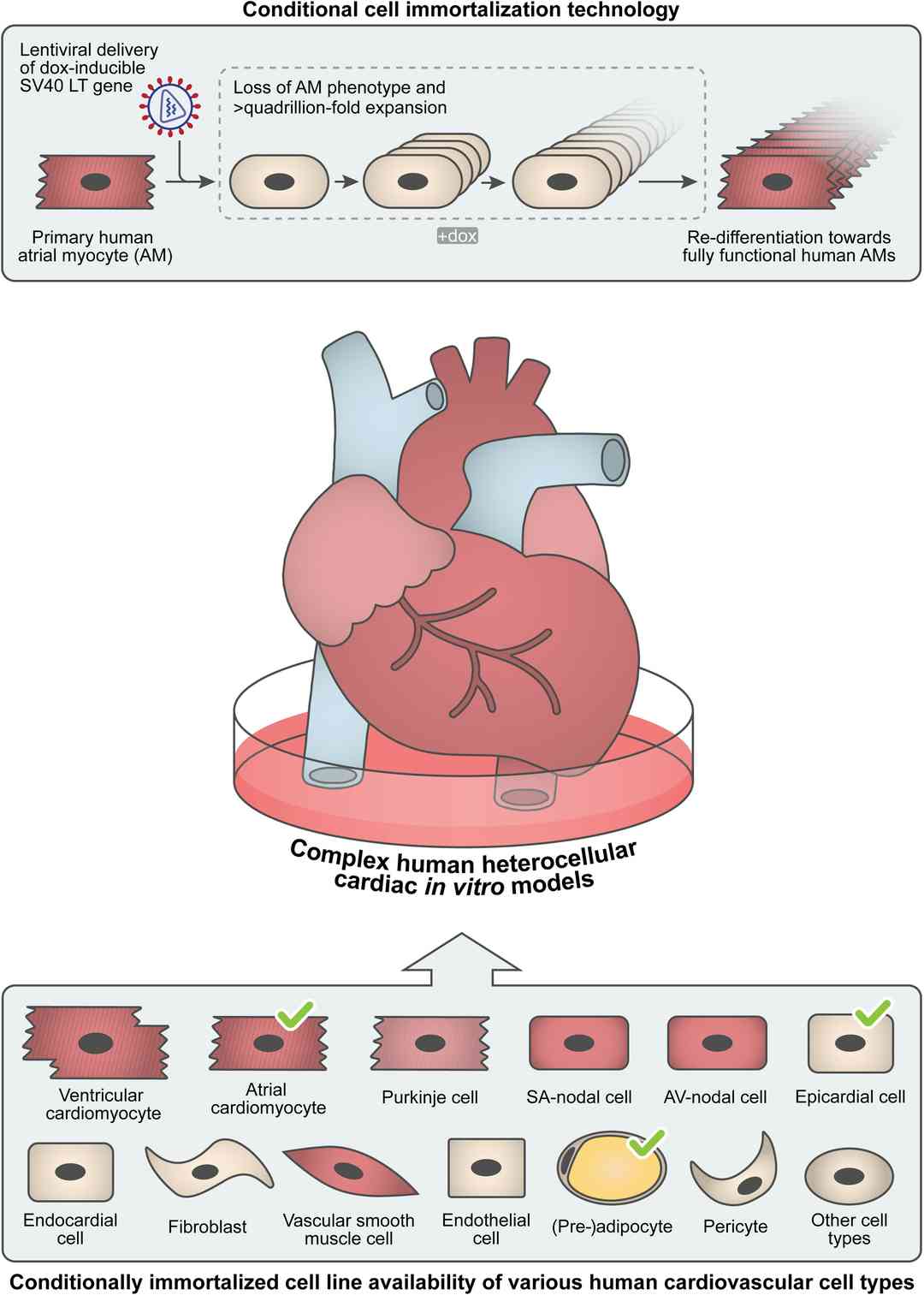 Fig. 1. Schematic overview of the generation of conditionally immortalized human atrial myocytes (AMs). Generation of human cardiovascular cell types using conditional immortalization technology (Harlaar, Niels, Daniël A. Pijnappels, and Antoine AF de Vries. 2022).
Fig. 1. Schematic overview of the generation of conditionally immortalized human atrial myocytes (AMs). Generation of human cardiovascular cell types using conditional immortalization technology (Harlaar, Niels, Daniël A. Pijnappels, and Antoine AF de Vries. 2022).
Diclofenac Affects Cell Viability in A Dose-Dependent Way
The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of Ketoprofen (K) in comparison with Diclofenac (Dic) in immortalized human cardiomyocytes. K shows no toxic effects at any time and concentration considered (Fig. 1A, B). A significant dose-dependent reduction of cell viability was found upon Dic treatment without any correlation with time exposure (Fig. 1C, D). Based on these results, the concentrations of 100 and 200 μM were selected for all the subsequent experiments, to avoid high cellular mortality. Moreover, to get more insight in the decrease of cell viability observed in the MTS assay, live-imaging cytotoxicity assay with both compounds was performed (Fig. 1E, F). The increase of green fluorescence, proportional to cytotoxicity, was displayed in cells exposed to both concentration of Dic compared to the untreated cells (Ctr), mainly after 24 h of treatment. Conversely, K-treated cells showed a slight increase of green fluorescence, at both the concentrations tested, compared to the untreated cells, thus indicating the cytotoxic effect of Dic only.
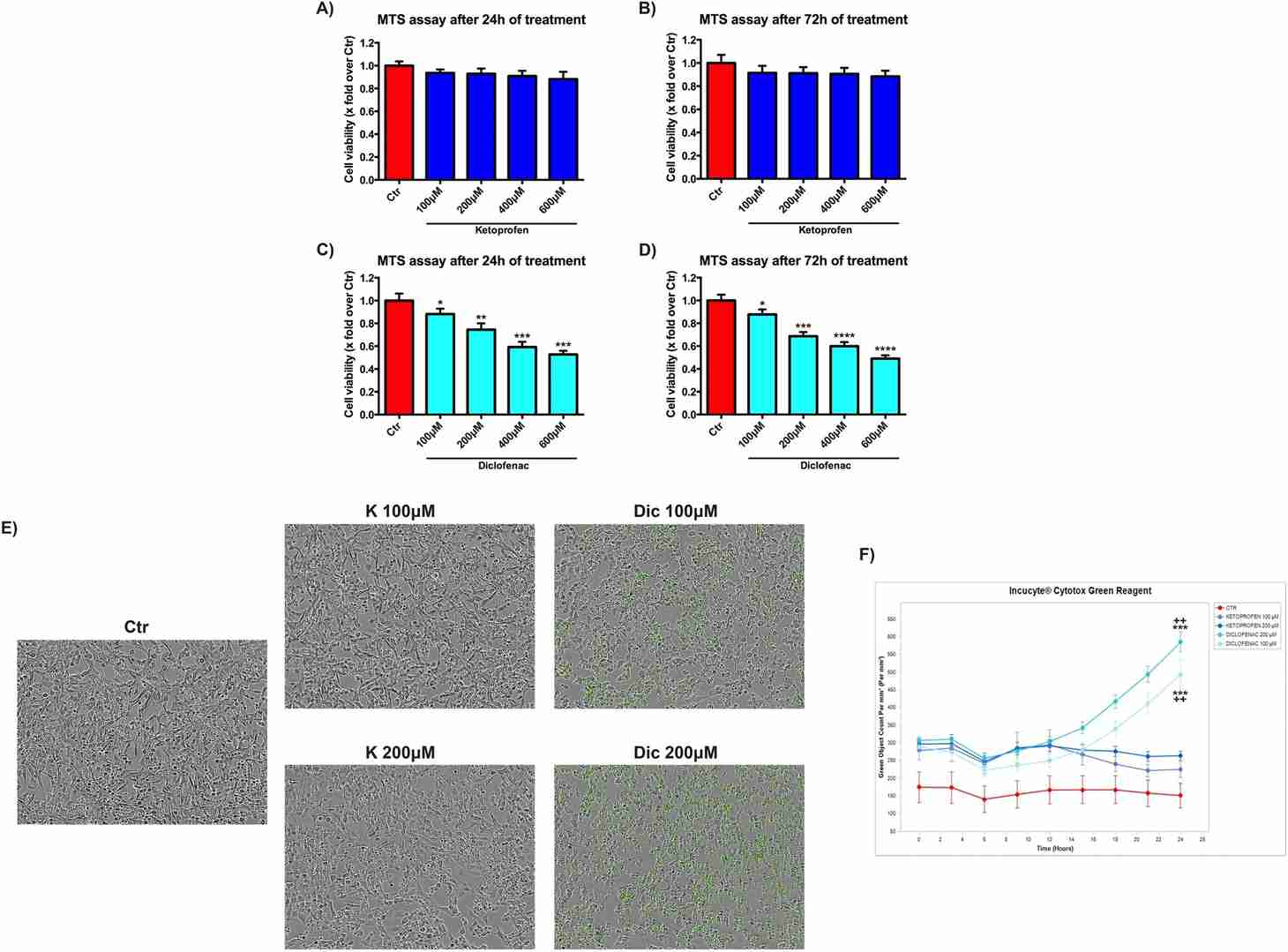 Fig. 1. Diclofenac affects cell viability in a dose-dependent way (Brandolini, Laura, et al. 2020).
Fig. 1. Diclofenac affects cell viability in a dose-dependent way (Brandolini, Laura, et al. 2020).
Cell Index Analysis, Ketoprofen versus Diclofenac
Cell Index (CI) was performed to provide a more sensitive and real-time analysis of cell health state compared to MTS, which only assays the cell metabolic activity. Delta cell index (DCI) related to 100 and 200 μM treatments are reported in Fig. 2A, B. K treated cells show a profile similar to the untreated cells. On the contrary Dic, at both concentrations, shows a significant reduction of DCI compared to untreated cells, as well as to K-treated cells. Furthermore, the cardiomyocytes morphological alterations due to Dic exposure, compared to K-treated and untreated cells, were also observed by contrast phase microscopy (Fig. 2C).
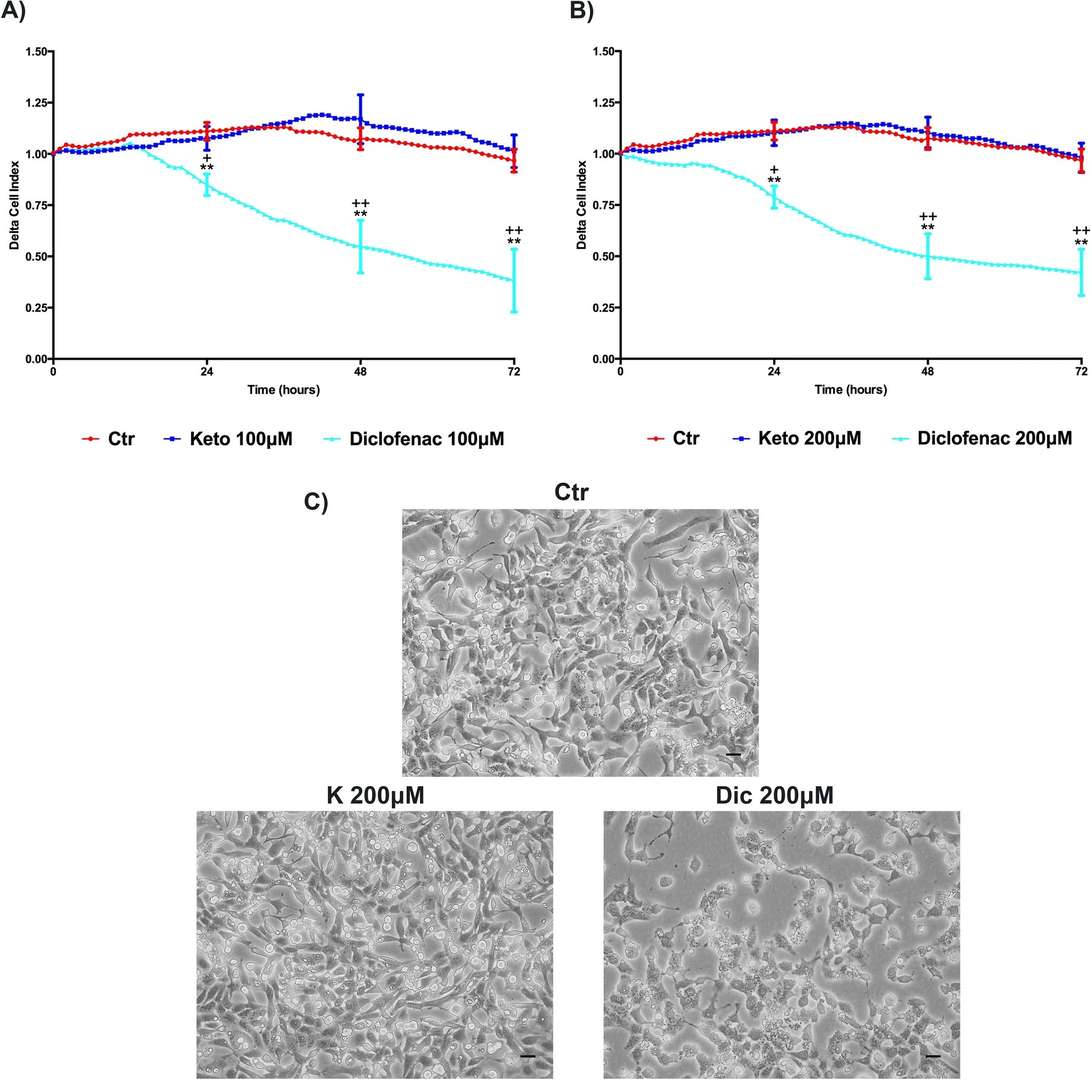 Fig. 2. Delta Cell index (DCI) evaluation, K versus Dic, in immortalized human cardiomyocytes (Brandolini, Laura, et al. 2020).
Fig. 2. Delta Cell index (DCI) evaluation, K versus Dic, in immortalized human cardiomyocytes (Brandolini, Laura, et al. 2020).
Immortalized Human Cardiomyocytes-SV40 are suitable for a variety of research applications, including:
- Cardiac physiology and pathophysiology studies.
- Investigating mechanisms of cardiac diseases and disorders.
- Drug development and cardiotoxicity screening.
- Research on ion channel function and cardiac electrophysiology.
- Studies of cardiomyocyte response to mechanical or biochemical stimuli.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells

