Immortalized Human Astrocytes-SV40T
Cat.No.: CSC-C12025Z
Species: Homo sapiens
Morphology: Polygonal
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20°C.
Astrocytes are the major glial cells in the central nervous system (CNS) and actively participates in neuronal branching, neuronal network formation, synapse formation, and overall homeostasis of the CNS. Moreover, abnormal astrocytic functions have been reported with tight association to a variety of neurodegenerative diseases.
Culturing primary astrocytes is an in vitro tool widely used in the studies of astrocyte biology, astrocyte-neuron interaction and astrocyte-related drug discoveries. Primary cells closely match their in vivo properties and serve as good indicators for their in vivo functions. However, even though these advantages exist, the isolation of primary astrocyte cultures is a laborious process, both in terms of time consumption and high maintenance costs. Besides, it generates variable results since astrocytes are highly heterogeneous cells, making it difficult to compare results among different research groups. An alternative is the use of immortalized astrocytes, which are genetically transformed cells with a higher proliferative rate. Two of the greatest advantages of using immortalized cell lines are that they greatly reduce the frequency with which stock cultures need to be replenished, and they may also minimize some of the phenotypic drift that tends to occur in cells maintained in cell culture for extended periods of time. Furthermore, they are faster and easier to manipulate than primary cultures once they can be stocked and thawed.
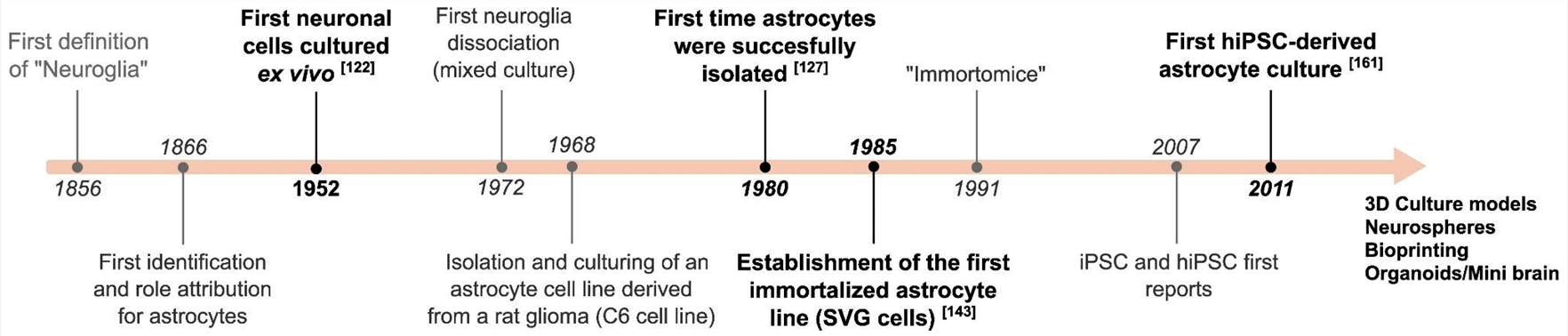 Fig. 1. Timeline of major developments in astrocytic cell culture (Preato, André Maciel, et al. 2024).
Fig. 1. Timeline of major developments in astrocytic cell culture (Preato, André Maciel, et al. 2024).
Downregulation of CLU Suppresses Proliferation of Human Astrocytes
The glycoprotein clusterin (CLU) is important for cell proliferation and cell cycle regulation, DNA repair signaling pathways, membrane recycling, and immune system regulation. Here, we aimed to investigate the effects of CLU dysregulation on two human astrocytic cell lines: CCF-STTG1 astrocytoma cells and SV-40 immortalized human astrocytes (INHA).
Cells were reverse transfected with siRNA directed against mRNAs encoding CLU. First, we examined CLU expression by indirect immunofluorescence analysis and observed a decrease in CLU levels in knockdown cells (Fig. 1A). To further assess the efficacy of CLU downregulation, Western blotting analysis was performed using samples of cells transfected with siCLU siRNA or siNC (negative control). Compared with the control group, there was a significant decrease in CLU in both CCF and INHA cells in the siCLU groups (Fig. 1B and C). The MTT assay showed significantly decreased metabolic activity in the siCLU groups, indicating an effect of CLU downregulation on cell growth (Fig. 1D), which was further confirmed by the crystal violet assay in combination with bright-field imaging (Fig. 1E and F). To investigate the effects of CLU downregulation on Ki-67 protein, a key marker for mitotic division, we quantified Ki-67 immunofluorescence in the nucleus using Olympus ScanR imaging. Our results demonstrated a significant reduction of Ki-67 expression in siCLU cells compared to siNC cells, indicating a cell cycle arrest (Fig. 1G and 1H). These findings indicate a loss of cell proliferation in astrocytes when CLU is downregulated, suggesting a crucial role of CLU in cell cycle regulation.
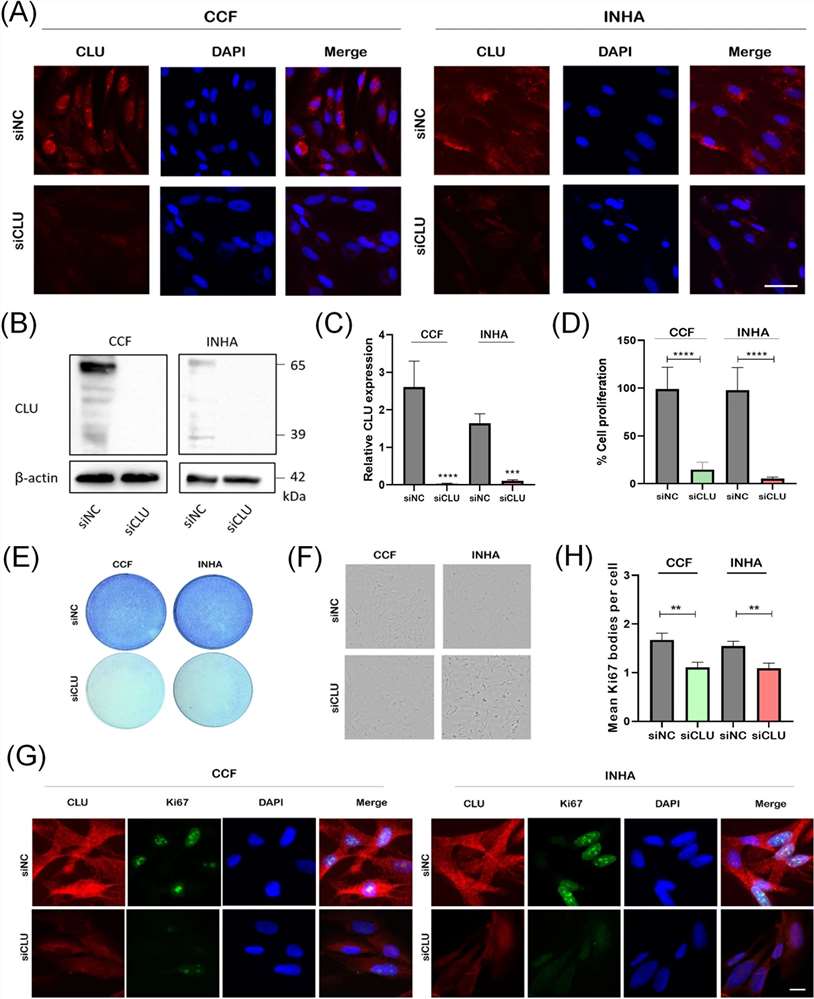 Fig. 1. Downregulation of CLU inhibits proliferation of human astrocytes (Sultana, Pinky, et al. 2024).
Fig. 1. Downregulation of CLU inhibits proliferation of human astrocytes (Sultana, Pinky, et al. 2024).
IHAs and GBM Cells Exhibit Similar Viscoelastic Properties
In this study, we utilized fluid shear stress assay to investigate and compare the viscoelastic properties of normal immortalized human astrocytes (IHAs, Creative Bioarray, CSC-C12025Z, Shirley, NY, USA) and invasive human glioblastoma (GBM) cells when subjected to physiological levels of shear stress that are present in the brain microenvironment.
The strain-time behavior of cells reflects their ability to withstand deformation under applied stress and reveals characteristic creep deformation regimes that are significant for viscoelastic material responses. The primary (elastic), secondary (steady state), and tertiary (failure) regimes, represent the different phases of viscoelastic deformation. Fig. 2 shows the deformation behavior of IHAs and GBM cells when subjected to 4 Pa of fluid shear stress for 8 minutes.
We next compared the mechanical properties of the IHAs to those of GBM cells. Surprisingly, IHAs and GBM cells exhibit similar viscoelastic properties. As seen in Fig. 3, there are no distinguishable mechanical differences in the nuclei or cytoplasm between the normal and malignant brain cells. This unique similarity between healthy and cancerous brain cells may be a relationship that distinguishes glioblastoma from other cancer types and could highlight a distinct mechanical cancer-host interaction than what is found elsewhere.
 Fig. 2. IHAs and GBM cells have similar strain-time deformation profiles (Onwudiwe, Killian, et al. 2023).
Fig. 2. IHAs and GBM cells have similar strain-time deformation profiles (Onwudiwe, Killian, et al. 2023).
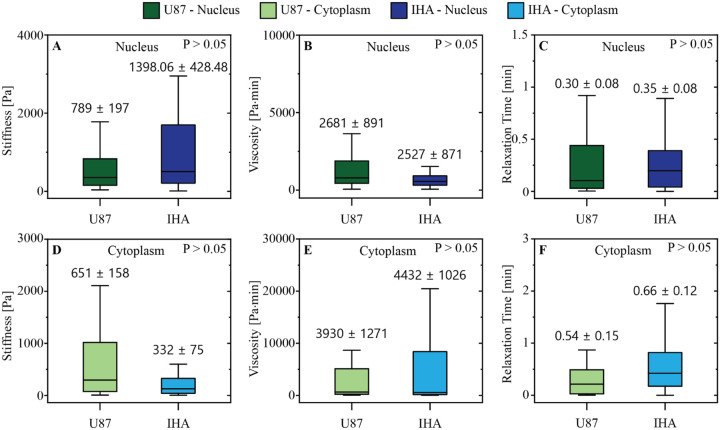 Fig. 3. GBM cells and IHAs have similar viscoelastic properties (Onwudiwe, Killian, et al. 2023).
Fig. 3. GBM cells and IHAs have similar viscoelastic properties (Onwudiwe, Killian, et al. 2023).
Immortalized Human Astrocytes (SV40T) are human astrocyte cells that have been genetically modified with the SV40 large T antigen to go beyond 30 passages. This allows them to be used continuously in research without the limitations associated with primary astrocyte cultures.
These cells are ideal for various research applications, including neurobiology, neurodegenerative disease studies, toxicity testing, neuroinflammation research, and drug discovery targeting central nervous system (CNS) disorders.
Absolutely. These astrocytes are suitable for co-culture with other cell types, such as neurons or microglia, to simulate the complex cellular environments of the CNS and study cell-cell interactions.
GFAP positive
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells