Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
EoL-1 cell
Cat.No.: CSC-C6473J
Species: Human
Morphology: lymphocyte-like
Culture Properties: Suspension cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Store in liquid nitrogen.
EoL-1 cells were originally derived from the peripheral blood of a patient with acute myeloid leukemia that had transformed into a more aggressive eosinophilic leukemia. This transformation is a challenging clinical scenario, as eosinophilic leukemias are often resistant to standard chemotherapeutic approaches.
One of the defining features of the EoL-1 cell line is its ability to differentiate in response to treatment with n-butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid. Exposure to n-butyrate induces the EoL-1 cells to undergo morphological and functional changes characteristic of mature eosinophils, including the upregulation of eosinophil-specific surface markers and the acquisition of eosinophilic granules.
This inducible differentiation capability of EoL-1 cells has made them a valuable tool for researchers investigating the mechanisms underlying eosinophil development and the pathogenesis of eosinophilic leukemias. By studying the changes in gene expression and signaling pathways triggered by n-butyrate treatment, scientists can gain insights into the molecular drivers of this rare hematological malignancy.
EoL-1 Cell Lines as in Vitro Models for Studying Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia
The chimeric kinase FIP1L1-platelet-derived growth factor receptor α (PDGFRα) was identified as a cause of hypereosinophilic syndrome and chronic eosinophilic leukemia. To investigate the role of FIP1L1-PDGFRA in the pathogenesis of acute leukemia, 87 leukemia cell lines were screened for the presence of FIP1L1-PDGFRA. In 1 AML cell line, EoL-1 (and derivative EoL-3), a fusion between FIP1L1 and PDGFRA was detected (Fig. 1).
Dose-dependent inhibition of the growth of EoL-1 cells was tested for the kinase inhibitors imatinib and PKC412, both known to inhibit FIP1L1-PDGFRα, and SU5614, known to inhibit FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3). The growth of EoL-1 cells was inhibited by these drugs, with cellular IC50 of approximately 0.8 nM for imatinib, 20 nM for PKC412, and 50 nM for SU5614 (Fig. 2A). Twenty-four hours after drug treatment, most EoL-1 cells were apoptotic (Fig. 2B), indicating that growth inhibition by these 3 drugs was caused by apoptosis.
FIP1L1-PDGFRα has recently been identified as the major phosphorylated protein in EoL-1 cells. All 3 inhibitors directly affect FIP1L1-PDGFRα activity, as indicated by the dose-dependent decrease of phosphorylation of FIP1L1-PDGFRα and STAT5, a downstream effector of FIP1L1-PDGFRα-mediated signal transduction. A 50% reduction of phosphorylation of FIP1L1-PDGFRα was reached at approximately 5 nM imatinib, 100 nM PKC412, and 50 nM SU5614 (Fig. 2C).
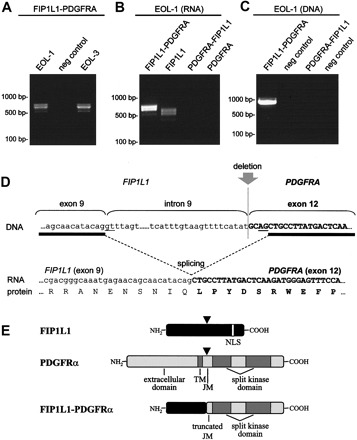 Fig. 1 Fusion of FIP1L1 to PDGFRA in the EoL-1 cell line. (Cools J, et al.,2004)
Fig. 1 Fusion of FIP1L1 to PDGFRA in the EoL-1 cell line. (Cools J, et al.,2004)
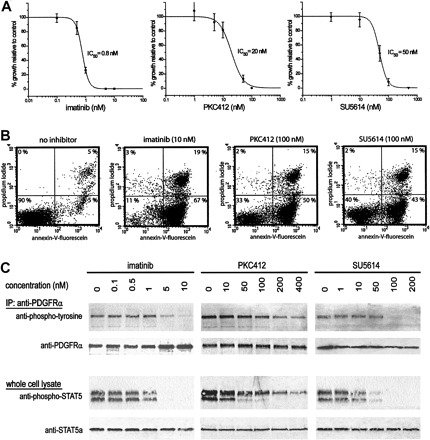 Fig. 2 Inhibition of cell growth, induction of apoptosis, and inhibition of FIP1L1-PDGFRα kinase activity in EoL-1 cells treated with various kinase inhibitors. (Cools J, et al.,2004)
Fig. 2 Inhibition of cell growth, induction of apoptosis, and inhibition of FIP1L1-PDGFRα kinase activity in EoL-1 cells treated with various kinase inhibitors. (Cools J, et al.,2004)
Docosahexaenoic Acid Inhibits Proliferation of EoL-1 Leukemia Cells
The effect of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid) upon the proliferation of the EoL-1 (Eosinophilic leukemia) cell line was assessed. As shown in Fig. 3A, in the presence of DHA, an inhibitory effect on the proliferation of EoL-1 cells was observed in a significant dose-dependent manner. Significant inhibition upon the proliferation of EoL-1 cells was observed on days 3 and 4 (Fig. 3A). n-Butyrate was used as a positive control because it is known that it comprises a differentiating agent that inhibits the proliferation of EoL-1 cells. Five hundred μM n-butyrate also significantly inhibited the proliferation of EoL-1 cells (Fig. 3A).
Dead cell counting by Trypan blue showed no significant alteration in the ratio of EoL-1 viable to dead cells from day 1 to day 4 of 10 μM DHA-treated EoL-1 cells. No direct toxic effect was exerted by 10 μM DHA but reflected reduced proliferation (Fig. 3B). On the contrary, for 20 and 50 μM DHA concentrations, the ratio of viable to dead cells decreased significantly on day 3 (Fig. 3B). Similar results were obtained by employing the MTT assay to study the effects of DHA on EoL-1 cell line viability. As shown in Fig. 3C, for treatment with 5 μM DHA the loss in active metabolism was not significant (97%) as compared to control cells. However, cells treated with 10 μM DHA showed a loss of active metabolism (86%), and the effect was dose-dependent (78% for 20 μM and 51% for 50 μM DHA).
The combined effect of DHA and butyrate was also studied at high concentrations. 50 μM DHA caused a similar decrease in EoL-1 cells' viability (51.6% ± 6.2) after 3 days of incubation as 500 μM butyrate (43.7% ± 3.2). When DHA and butyrate were added simultaneously in EoL-1 cell culture, the 3-day viability reached only 17.8% (Fig. 3D). The combination index (CI value) for those two substances was <1, thus indicating a synergistic effect.
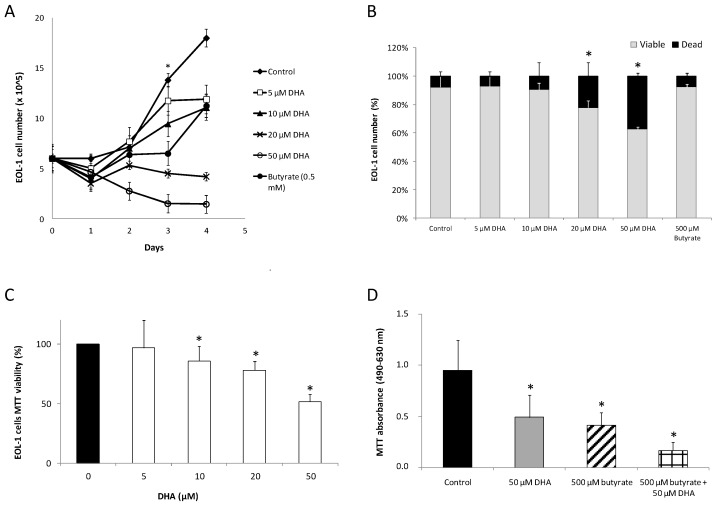 Fig. 3 Effect of DHA on the proliferation of EoL-1 cells. (Moustaka K, et al., 2019)
Fig. 3 Effect of DHA on the proliferation of EoL-1 cells. (Moustaka K, et al., 2019)
Add an appropriate quantity (0.5 mL/10 cm2) of pre-warmed trypsin solution to the side wall of the flask. Gently swirl the contents to cover the cell layer. Incubate the vessel in room temperate for 2-3 minutes. Firmly adherent cells can be detached quickly at 37°C.
The EoL-1 cells can be induced to differentiate into mature eosinophils when treated with n-butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid.
The inducible differentiation capability of EoL-1 cells has made them a valuable tool for researchers investigating the mechanisms underlying eosinophil development and the pathogenesis of eosinophilic leukemias.
The availability of the well-characterized and responsive EoL-1 cell line has been instrumental in advancing our understanding of eosinophilic leukemia and testing potential therapeutic strategies for this challenging disease.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 4.7 | 3 Scientist has reviewed this product
Detailed information
The Creative Bioarray provided detailed information about the origin and provenance of the tumor cell product.
16 Feb 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Excellent quality and purity
The quality and purity of the EoL-1 cells have been excellent, and the detailed documentation provided by Creative Bioarray has been extremely helpful in understanding the cell line's characteristics and handling requirements.
11 Jan 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Helpful troubleshooting support
The customer service at Creative Bioarray has been exceptional, with the team providing detailed instructions and troubleshooting support to ensure I get the most out of these valuable cells.
14 Feb 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need