- You are here: Home
- Akt Kinase Phosphorylation Assay by Immunoprecipitation
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Akt Kinase Phosphorylation Assay by Immunoprecipitation
- Service Details
- Workflow
- Features
- Case Studies
- FAQ
Akt, also known as protein kinase B (PKB), is a serine/threonine kinase that belongs to the AGC kinase family. Mammalian Akt exists in three forms: Akt1, Akt2, and Akt3. This kinase functions as a signaling molecule that orchestrates several critical biological processes, including cell division, proliferation, and survival. Activation of Akt is typically triggered by receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which subsequently activate specific isoforms of class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks). Malfunctioning or excessive Akt activation has been associated with a range of disorders, including certain types of cancer and type 2 diabetes. Consequently, Akt is a significant focus for scientists aiming to develop targeted treatments, and specific inhibitors are available to mitigate its hyperactive conditions.
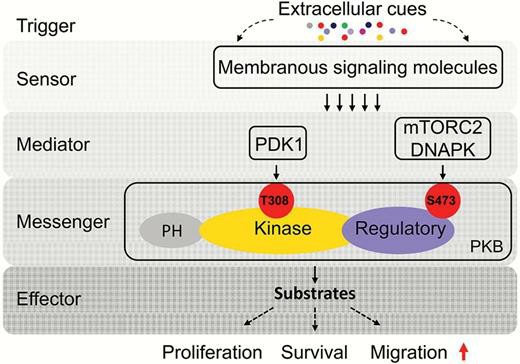 Fig. 1. Molecular mechanism of protein kinase B (PKB) signaling transduction. (Xue G, Zippelius A, Wicki A, et al., 2015)
Fig. 1. Molecular mechanism of protein kinase B (PKB) signaling transduction. (Xue G, Zippelius A, Wicki A, et al., 2015)
Creative bioarray utilizes a sophisticated approach that combines immunoprecipitation (IP) with kinase activity assays. Specific antibodies are used to bind to Akt kinases, effectively isolating these enzymes from complex mixtures of cellular extracts. After isolation, the phosphorylation status of Akt kinases within the immunoprecipitated complexes is assessed and quantified using immunoblotting techniques, such as Western blot analysis.
Workflow
1
Cell lysis and protein purification
Cells are lysed using a soft and efficient cell lysis buffer to extract intracellular proteins.
2
Immunoprecipitation
The cell lysate is pre-conjugated with an approved Akt kinase antibody to form an immune complex with the target protein. Immediately following immunoprecipitation, a specific antibody affinity buffer (such as Protein A/G-Sepharose beads) is added. The immune complexes are then centrifuged and washed, resulting in an immunoprecipitated, pure Akt kinase complex.
3
Kinase assay
After immunoprecipitation, an in vitro kinase assay is performed with a recombinant substrate to measure Akt kinase activity.
4
Western immunoblotting
Akt kinase and its phosphorylated form in the immunoprecipitated complexes are detected by immunoblotting.
Features

High sensitivity and specificity
Our assay provides a high level of sensitivity, allowing for the detection of even low levels of Akt kinase activity.

Species reactivity
The assay is compatible with multiple species, expanding its utility for various research models.
Technical expertise
Our team has extensive experience in performing and interpreting Akt kinase assays, ensuring accurate and reliable results.
Case Studies
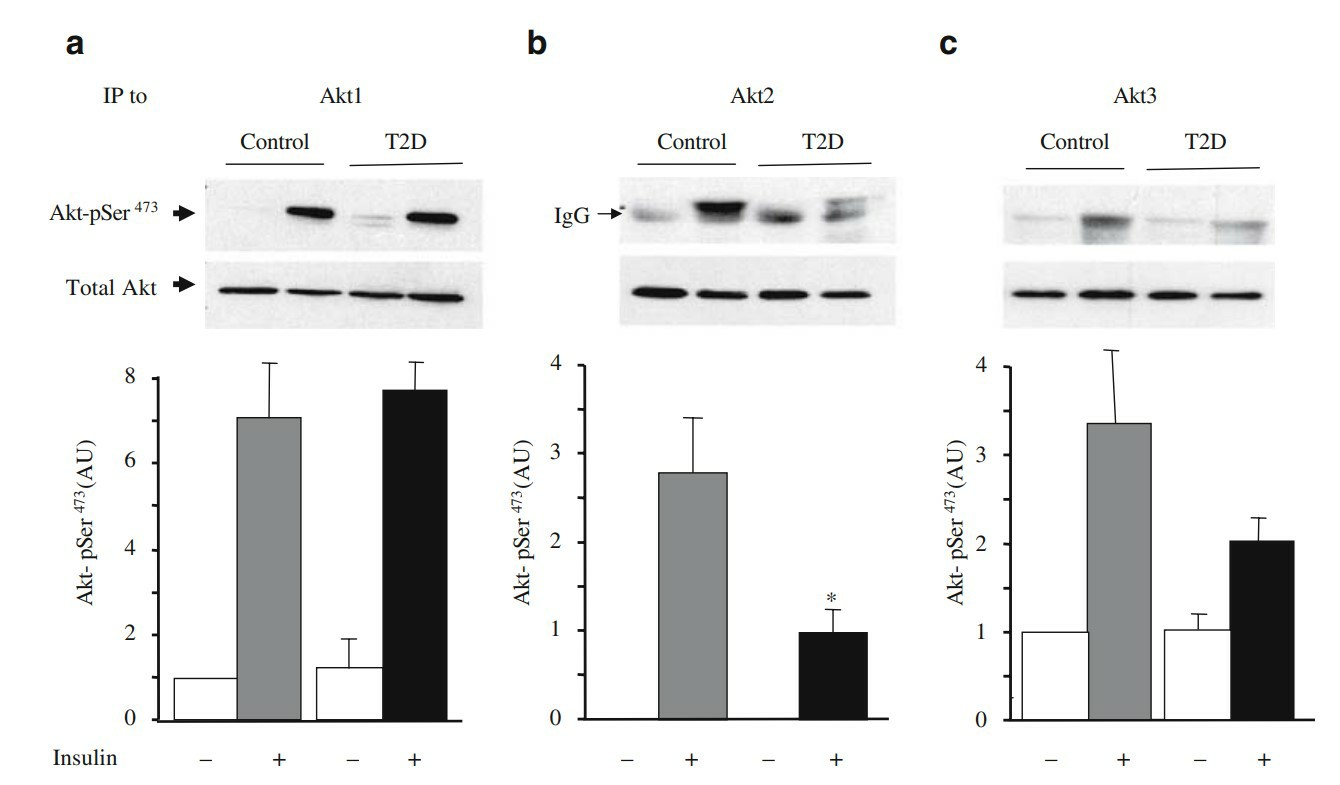 Fig .2. Insulin-stimulated Ser473 phosphorylation of the specific Akt isoforms in myotubes from type 2 diabetic patients. Protein lysates (400 µg) from myotubes treated (grey and black bars) or not (white bars) with 100 nmol/l insulin for 20 min, were immunoprecipitated (IP) with specific antibodies to Akt1, Akt2 or Akt3. (Cozzone D, Fröjdö S, Disse E, et al., 2008)
Fig .2. Insulin-stimulated Ser473 phosphorylation of the specific Akt isoforms in myotubes from type 2 diabetic patients. Protein lysates (400 µg) from myotubes treated (grey and black bars) or not (white bars) with 100 nmol/l insulin for 20 min, were immunoprecipitated (IP) with specific antibodies to Akt1, Akt2 or Akt3. (Cozzone D, Fröjdö S, Disse E, et al., 2008)
FAQ
1. How do I prepare the sample?
If sending cell samples, ensure to submit enough cells, and be sure that the cells are in good condition. Cells need to be handled properly prior to pick-up and liquid nitrogen snap-frozen or refrigerated at - 80°C, straight after pick-up to avoid refreezing and thawing. Tissues should be as fresh as possible, and should be kept immediately after being collected in liquid nitrogen to prevent protein loss during long-term storage.
2. How long will the assay take?
We usually have a full test report within 2-3 weeks of receiving the sample.
3. What is the benefit of immunoprecipitation in the assay?
Immunoprecipitation permits the selective enrichment of Akt, lowering noise and increasing sensitivity and specificity of the test.
Quotations and Ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
References
- Xue G, Zippelius A, Wicki A, et al. Integrated Akt/PKB signaling in immunomodulation and its potential role in cancer immunotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015. 107(7):djv171.
- Cozzone D, Fröjdö S, Disse E, et al. Isoform-specific defects of insulin stimulation of Akt/protein kinase B (PKB) in skeletal muscle cells from type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2008. 51(3):512-521.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

