Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
SUP-M2
Cat.No.: CSC-C0518
Species: Human
Source: anaplastic large cell lymphoma
Morphology: round cells growing singly or in clumps in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
Immunology: CD2 +, CD3 -, CD4 +, CD13 -, CD14 -, CD19 -, CD21 -, CD25 +, CD30 +, CD34 -, CD71 +, HLA-DR +
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, SMRV -
SUP-M2 cells are a human cell line derived from the cerebrospinal fluid of a 5-year-old girl with refractory malignant histiocytosis. These cells are characterized by specific genetic and phenotypic features, making them an important model for studying a particular type of cancer known as anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL).
The SUP-M2 cell line is notable for carrying the characteristic translocation t (2; 5) (p23; q35). This translocation leads to the fusion of two genes, NPM1 and ALK, resulting in the formation of the NPM1-ALK fusion gene. The NPM1-ALK fusion gene is a hallmark genetic alteration in a subset of ALCL cases and plays a crucial role in the development and progression of this disease.
In addition to the genetic abnormality, SUP-M2 cells also express the CD30 antigen. CD30 is a cell surface marker that is commonly observed on ALCL cells. The presence of CD30 further defines SUP-M2 cells as anaplastic large-cell lymphoma and contributes to their phenotypic characteristics.
The SUP-M2 cell line has been widely used in research to investigate the biological and molecular aspects of ALCL, including the role of the NPM1-ALK fusion gene, cellular signaling pathways, therapeutic targets, and drug testing. By studying SUP-M2 cells, researchers aim to gain insights into the pathogenesis of ALCL and develop more effective treatment strategies for this type of lymphoma.
B7-H3 Redirected CAR-T Cells Control ALCLs In Vitro
B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3), also named CD276, is a member of the B7 family of immune regulatory proteins. B7-H3 CAR-T cells showed strong cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion against target ALCL cells (SUP-M2, SU-DHL-1, and Karpas 299) in vitro. Cytotoxicity was measured using two different approaches LDH release cytotoxic assay and luciferase-based assay in various E: T ratios. Increased cytotoxicity along with an increased E: T ratio was observed in B7-H3 CAR-T cells to target ALCL cell lines in both approaches. Furthermore, >60% specific lysis was reached when the E: T ratio was 5:1 for all targets in the LDH release cytotoxic assay (Fig. 1A).
To confirm this effect, stable expressing luciferase cell lines were generated from parental SUP-M2, Karpas299, and SU-DHL-1 cell lines as well as the performed luciferase-based assay. This was consistent with data from the LDH release cytotoxic assay, and B7-H3 CAR-T cells showed their potency in controlling SUP-M2, Karpas299, and SU-DHL-1 (Fig. 1B). The secreting of IL-2 and IFNγ was observed at a high level when B7-H3 T cells were co-cultured with ALCLs. In contrast, UTD and CD19 CAR-T control cells showed minimal secretion of both cytokines (Fig. 1C and D).
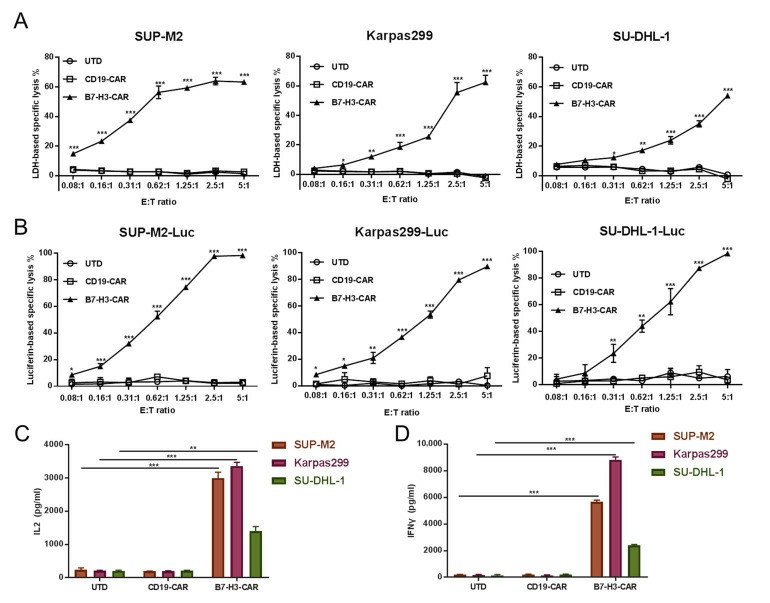 Fig. 1 B7-H3 T cell effects on B7-H3-expressing ALCL cells (SUP-M2, SU-DHL-1, and Karpas 299). (Slupianek A and Skorski T, 2004)
Fig. 1 B7-H3 T cell effects on B7-H3-expressing ALCL cells (SUP-M2, SU-DHL-1, and Karpas 299). (Slupianek A and Skorski T, 2004)
According to educational materials provided by the National Institutes of Health, monoclonal tumor origin means that tumors are derived from a single ancestral cell that underwent conversion from a normal to a cancerous state.
The t(2;5)(p23;q35) translocation in SUP-M2 cells leads to the formation of the NPM1-ALK fusion gene. This genetic alteration is characteristic of a subset of ALCL cases and is crucial in the development and progression of this type of lymphoma.
CD30 is a cell surface marker expressed by SUP-M2 cells. It is commonly observed on ALCL cells and aids in defining SUP-M2 cells as anaplastic large cell lymphoma. CD30 is involved in various signaling pathways and is a target for therapeutic interventions in ALCL.
Yes, apart from ALCL-related research, SUP-M2 cells can be utilized to investigate broader aspects of cancer biology, including cellular signaling pathways, genetic alterations, and drug response mechanisms. They provide a valuable resource for studying malignant histiocytosis and other relevant diseases.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 4.7 | 3 Scientist has reviewed this product
Excellent results
The tumor cells are easy to culture and have provided excellent results in our experiments.
03 Nov 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Satisfied
I recently purchased SUP-M2 cell products from Creative Bioarray, and I am extremely satisfied with the quality and performance of their cells.
29 Jan 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
In excellent condition
The SUP-M2 cells were delivered in excellent condition, exhibiting the expected phenotypic characteristics of ALCL. The documentation provided, including certificates of analysis and handling instructions, was comprehensive and helpful for my research.
23 Aug 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need