Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY

RPMI-8402
Cat.No.: CSC-C0376
Species: Human
Source: T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Morphology: round single cells in suspenson, growing partly in clumps
Culture Properties: suspenson
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD2 +, CD3 -, CD4 -, CD5 +, CD6 +, CD7 +, CD8 -, CD13 -, CD19 -, CD34 +, TCRalpha/beta -, TCRg
Scientists established the RPMI-8402 cell line in 1972 from the peripheral blood of a female ALL patient who was 16 years old. The RPMI-8402 cell line displays common T-cell characteristics while expressing both genetic and phenotypic properties typical of acute T-lymphoblastic leukemia. Researchers rely on this cell line for experimental studies into leukemia pathogenesis alongside drug screening and immunotherapy development. RPMI-8402 cells display a round morphology and grow in suspension either as isolated cells or small clusters that resemble myeloblast-like cells. The cell line demonstrates expression of CD5 and CD7 markers while lacking CD3, CD4, CD8, CD19, and TCRαβ markers. The cell line displays a human hypotriplid karyotype which features multiple chromosomal abnormalities such as the t(11;14)(p15;q11) translocation and an R273C mutation in the TP53 gene along with genetic heterogeneity among cells.
The RPMI-8402 cell line serves as a key model to study the pathogenesis and genetic alterations in acute T-lymphoblastic leukemia. The cell line also functions as a leukemia model which facilitates anti-leukemia drug efficacy testing along with the study of T-cell immune responses and signaling pathways.
The Constitutive Expression of EPHB6 Receptor in Human T-ALL Promotes In Vitro Proliferation and In Vivo Cell Expansion
T-cell lymphoblastic acute leukemia (T-ALL) is a highly aggressive form of blood cancer marked by cellular subsets with abundant leukemia-initiating cells (LICs). Recent findings indicate that Ephrin receptors (Eph) are highly expressed in cancer stem cells. Investigations revealed that EphB6 is uniquely overexpressed among the Eph family in T-ALL samples, especially in a minor yet significant subpopulation with increased LIC activity. To explore EphB6's role in T-ALL, PF382 and RPMI-8402 cells were transduced with lentivectors encoding the EPHB6 gene or an empty vector as a control. Interestingly, EPHB6 expression enhanced cell expansion (Fig. 1C) and increased cell cycling, evidenced by higher Ki67 protein levels (Fig. 1D-E) and BrdU incorporation. To verify these findings in primary T-ALLs, two clones of patient-derived xenografts (PDX) were analyzed using flow cytometry, identifying a cell cluster with high EphB6 levels (Fig. 1F). EphB6 positive and negative PDX fractions were FACS sorted and tested for leukemogenic capacity via transplantation into NSG mice (Fig. 1G). Mice with EphB6+ cells died sooner than those with EphB6- cells, confirming EphB6's link to LIC. Consistent with this, LIC frequency was higher in EphB6+ populations.
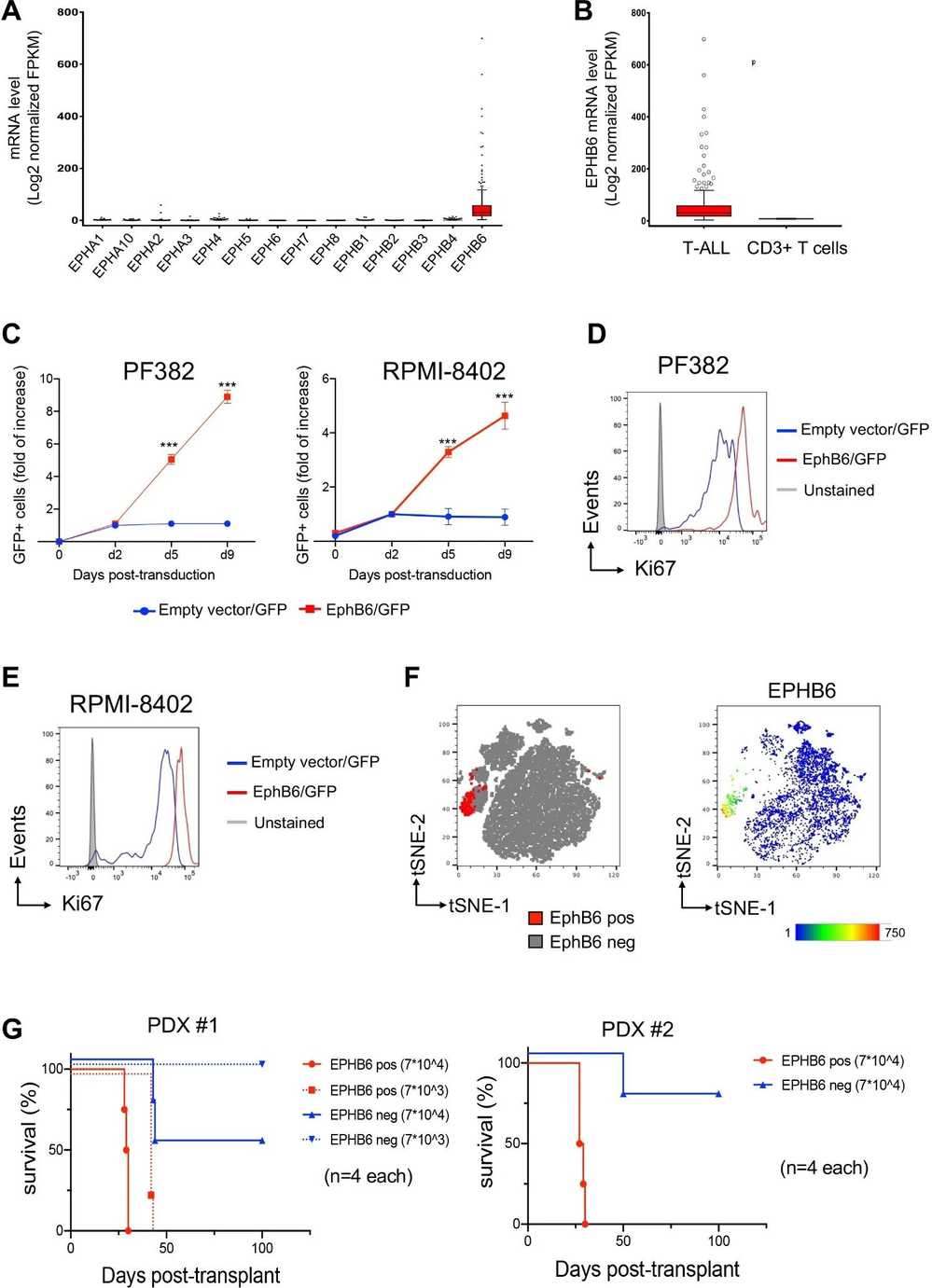 Fig. 1. The constitutive expression of EPHB6 receptor in human T-ALL promotes in vitro proliferation and in vivo cell expansion (Colucci M, Trivieri N, et al., 2023).
Fig. 1. The constitutive expression of EPHB6 receptor in human T-ALL promotes in vitro proliferation and in vivo cell expansion (Colucci M, Trivieri N, et al., 2023).
CircFBXW7 is Depleted in T-ALL Patients and its Silencing has Functional Impact in T-ALL In Vitro
CircRNAs have emerged as significant factors in leukemogenic mechanisms, especially in T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (T-ALL), showing notable dysregulation. Buratin et al. investigated circFBXW7, highly expressed in T-cells and abundant compared to its linear counterpart. They conducted a loss-of-function study in T-ALL using RPMI-8402 and ALL-SIL cell lines, both with high circFBXW7 expression (Fig. 2B). Knocking down circFBXW7, while keeping FBXW7 mRNA unchanged, led to increased cell viability and proliferation (MTT and EdU assays; Fig. 2C-D). Microarray analysis revealed 2265 differentially expressed genes, with downregulated chemokines and pro-apoptotic genes (Fig. 2E-F). Key activated pathways included cell-cycle processes and mTOR signaling due to upregulation of pro-survival genes. MYC target genes and the NOTCH signaling pathway were significantly upregulated (Fig. 2G-H), with increased MYC and NOTCH1 proteins observed (Fig. 2I), suggesting a feedback loop involving MYC (Fig. 2J).
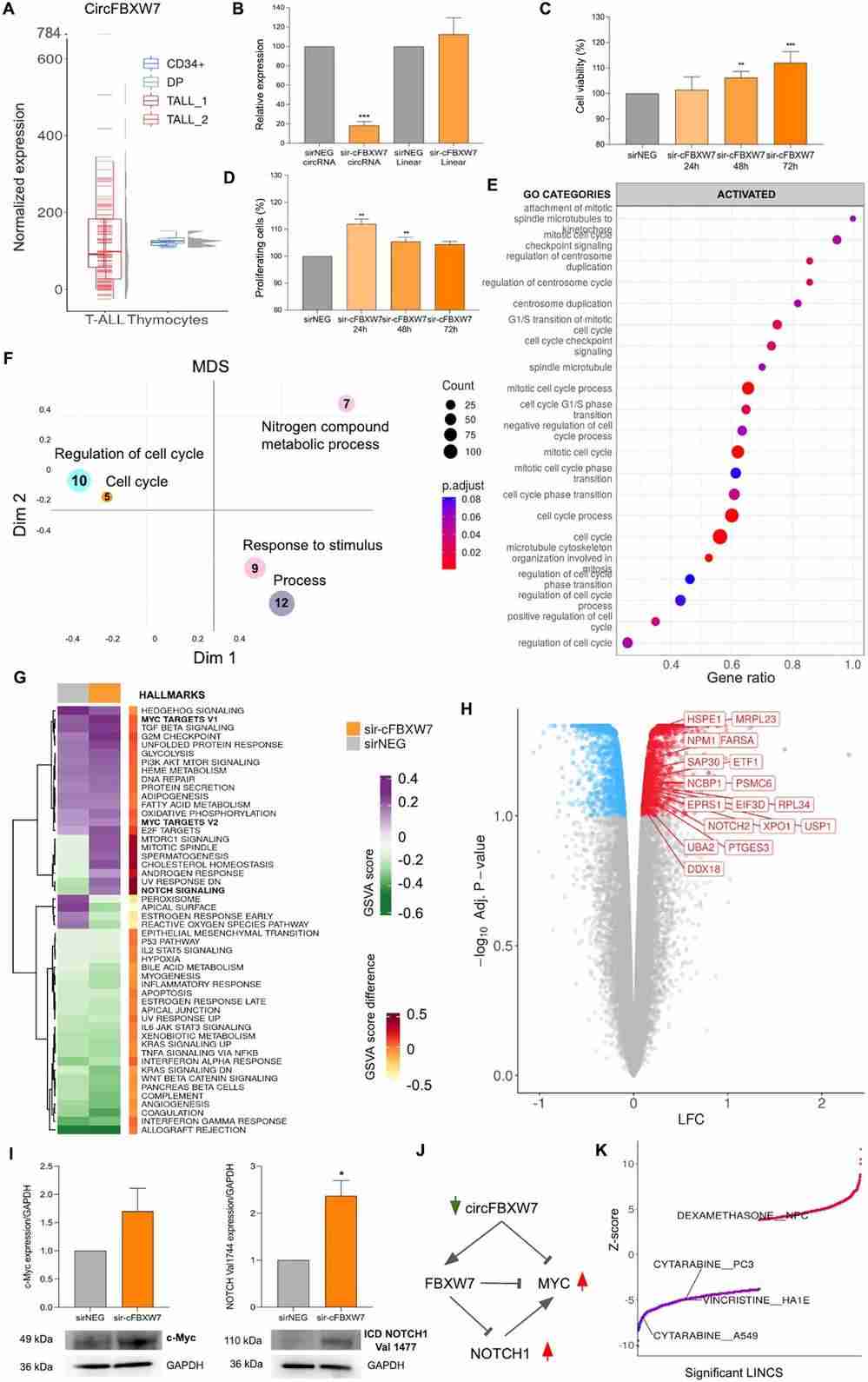 Fig. 2. CircFBXW7 is depleted in T-ALL patients and its silencing had functional impact in T-ALL in vitro (Buratin A, Borin C, et al., 2023).
Fig. 2. CircFBXW7 is depleted in T-ALL patients and its silencing had functional impact in T-ALL in vitro (Buratin A, Borin C, et al., 2023).
The major differences between DMEM and MEM include the use of lower concentrations of amino acids, vitamins, and inorganic phosphate and the inclusion of lactate and glutamine in the medium.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 4.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Easy to culture
These cells are easy to culture, which greatly facilitates our experiments.
12 June 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need