Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY

NU-DHL-1
Cat.No.: CSC-C0588
Species: Human
Source: B cell lymphoma
Morphology: single, round to polymorph cells growing in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD3 -, CD10 -, CD13 -, CD19 +, CD20 +, CD34 -, CD37 +, cyCD79a +, CD138 -, HLA-DR +, sm/cyIgG -, sm/cyIgM +, fm/cykappa -, sm/cylambda +
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV
The NU-DHL-1 cell line originates from the left inguinal lymph node of a 73-year-old Caucasian male B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma patient who had diffuse large cell lymphoma of the non-cleaved type when scientists established this B-cell lymphoma cell line in 1982. The NU-DHL-1 cell line maintains a lymphoblastic shape while showing characteristic B-cell surface markers including CD19, CD20, CD37, cytoplasmic CD79a and the immunoglobulin light chain λ. Under microscopic examination these cells present as polymorphic suspension cells which grow either individually or in small groups.
Gene expression profile analysis reveals that NU-DHL-1 belongs to the ABC-like DLBCL cell line category. The NU-DHL-1 cell line shows particular genetic changes at the genomic level including CDKN2A gene deletion and PTEN gene amplification which play a significant role in DLBCL pathogenesis. Therefore, NU-DHL-1 serves as a critical research tool for exploring the molecular mechanisms and treatment approaches of DLBCL. Additionally, the DLBCL cell line NU-DHL-1 possesses unique genetic backgrounds and functional properties which set it apart from other DLBCL cell lines such as OCI-LY1 and SU-DHL-6. The OCI-LY1 cell line displays MYC gene amplification and the SU-DHL-6 cell line demonstrates CD322 gene amplification. The variety of cell lines enables researchers to examine different DLBCL subtypes and their pathogenesis.
High Expression Level of Bcl-2 Predicts Sensitivity to BM-1197
DLBCL and other types of malignant lymphomas frequently become resistant to traditional treatments resulting in negative patient prognoses. Overexpression of Bcl-2 protein contributes to this resistance. Sun's team evaluated BM-1197 as a BH3 domain mimic that targets Bcl-2 to test its effectiveness against DLBCL and Burkitt lymphoma.
Researchers measured Bcl-2 family protein levels across eight B cell-derived lymphoma cell lines including OCI-ly1, OCI-ly8, OCI-ly19, Su-DHL-4, Nu-DHL-1, Raji, Ramos, and Namalwa as well as the T-cell-derived acute T-cell leukemia cell line Jurkat. As illustrated in Fig. 1a Bcl-2 expression levels were high in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell lines but remained low in Burkitt and Jurkat cells as shown in Fig. 1a. The impact of BM-1197 on lymphoma cell growth was measured using a CCK-8 assay following treatment. Figure 2 displays the IC50 values of BM-1197 for each cell line which demonstrates sensitivity in OCI-ly1, OCI-ly8, and OCI-ly19 cells with IC50 values ranging between 0.2 and 0.5 μM (Fig. 1b). A time-dependent reduction in OCI-ly8 cell viability was observed when treated with BM-1197 across 24, 48, and 72-hour intervals (Fig. 1c). To explore potential synergistic effects with chemotherapy, BM-1197 was tested with doxorubicin, vincristine, and gemcitabine in OCI-ly8 cells. The cell growth inhibition observed from the drug combination reached a synergistic effect as demonstrated in the figures. 1d, e, f.
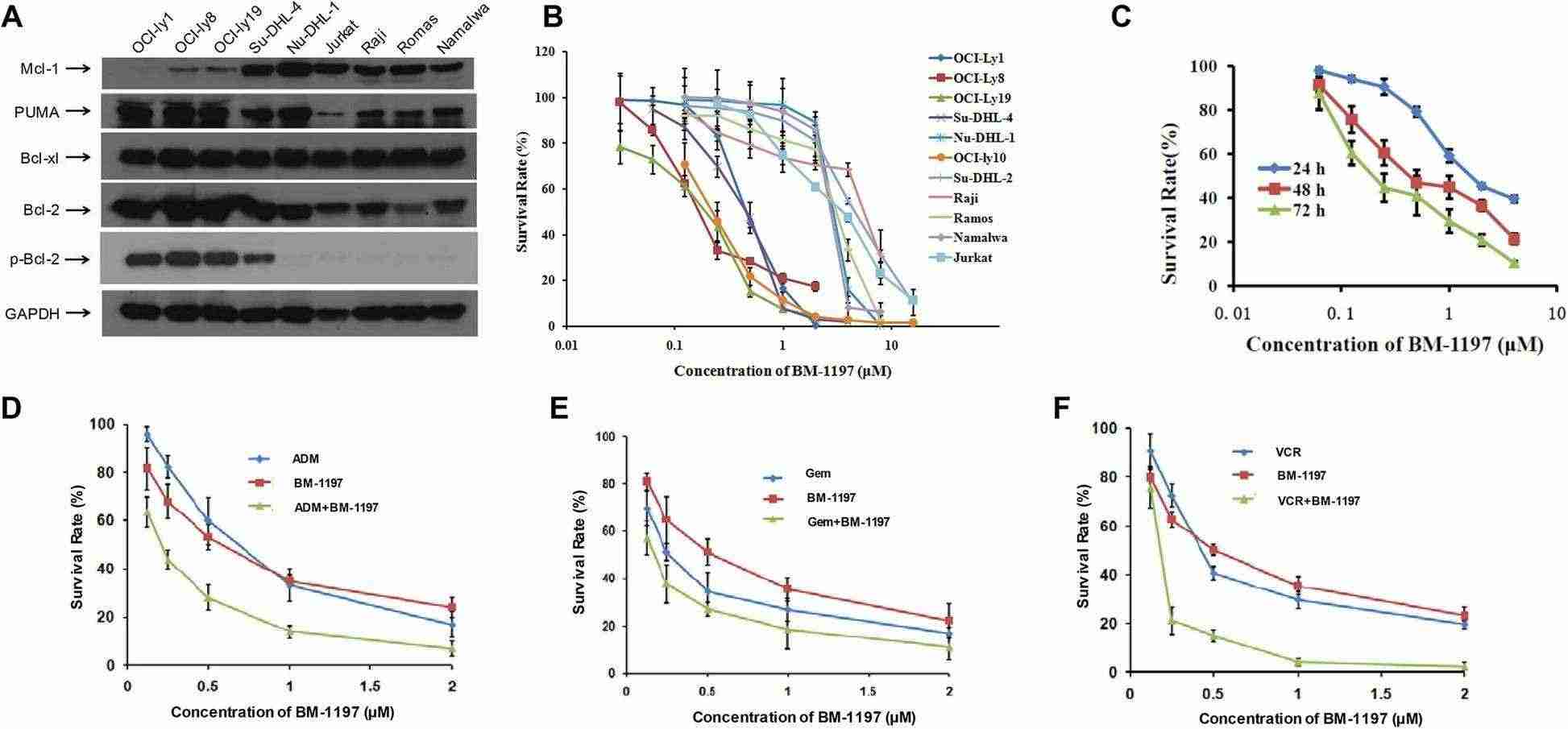 Fig. 1. High expression level of BCL-2 predicts sensitivity to BM1197 (Sun Y, Jiang W, et al., 2020).
Fig. 1. High expression level of BCL-2 predicts sensitivity to BM1197 (Sun Y, Jiang W, et al., 2020).
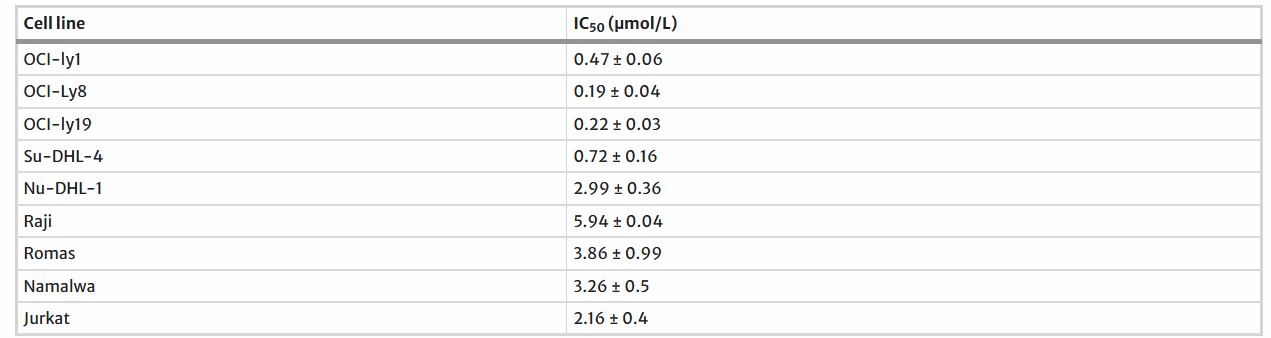 Fig. 2. The IC50 values (μM) of BM-1197 in NHL cell lines (Sun Y, Jiang W, et al., 2020).
Fig. 2. The IC50 values (μM) of BM-1197 in NHL cell lines (Sun Y, Jiang W, et al., 2020).
Downregulation of miR-155 Promotes Vincristine Resistance
DLBCL stands as the most common non-Hodgkin's lymphoma subtype while approximately 40% of patients treated experience disease relapse or develop treatment resistance due to molecular resistance mechanisms including miRNA expression changes. Due et al. Due et al. examined miR-155's function in vincristine resistance within R-CHOP treatment for DLBCL while assessing its predictive biomarker and therapeutic target potential.
Research using lentiviral vectors to modify miR-155 levels demonstrated that elevated miR-155 expression improved vincristine sensitivity in both drug-sensitive and drug-resistant GCB-DLBCL cell lines including SU-DHL-5 and OCI-Ly7. SU-DHL-5 cells showed increased vincristine resistance when miR-155 levels were reduced while OCI-Ly7 cells did not demonstrate this effect. The miR-155 knockout demonstrated its regulatory role through enhanced vincristine resistance. Research shows that miR-155 affects important cellular processes like G2/M checkpoints and spindle assembly which vincristine targets to determine treatment effectiveness. In addition, ABC cell lines RIVA and NU-DHL-1, characterized by intrinsically intermediate response to vincristine and comparably high endogenous expression of miR-155, were similarly analyzed. Applying the TuD model system decreased miR-155 expression in RIVA cells; however, it did not cause unambiguous effect on vincristine sensitivity (Fig. 3BI-BII). Although functionality of the model systems was confirmed (Fig. 4), transduction with LV/miR-155 in RIVA and LV/TuD-155 in NU-DHL-1 did not generate significant changes in intracellular levels of miR-155, and consequently, vincristine dose-response analysis was not performed (Fig. 3AI and DI). Overexpression of miR-155 in NU-DHL-1 cells did not affect vincristine response either (Fig. 3CI-CII), indicating that miR-155 does not play a pivotal role in vincristine response in ABC cells as opposed to GCB cells.
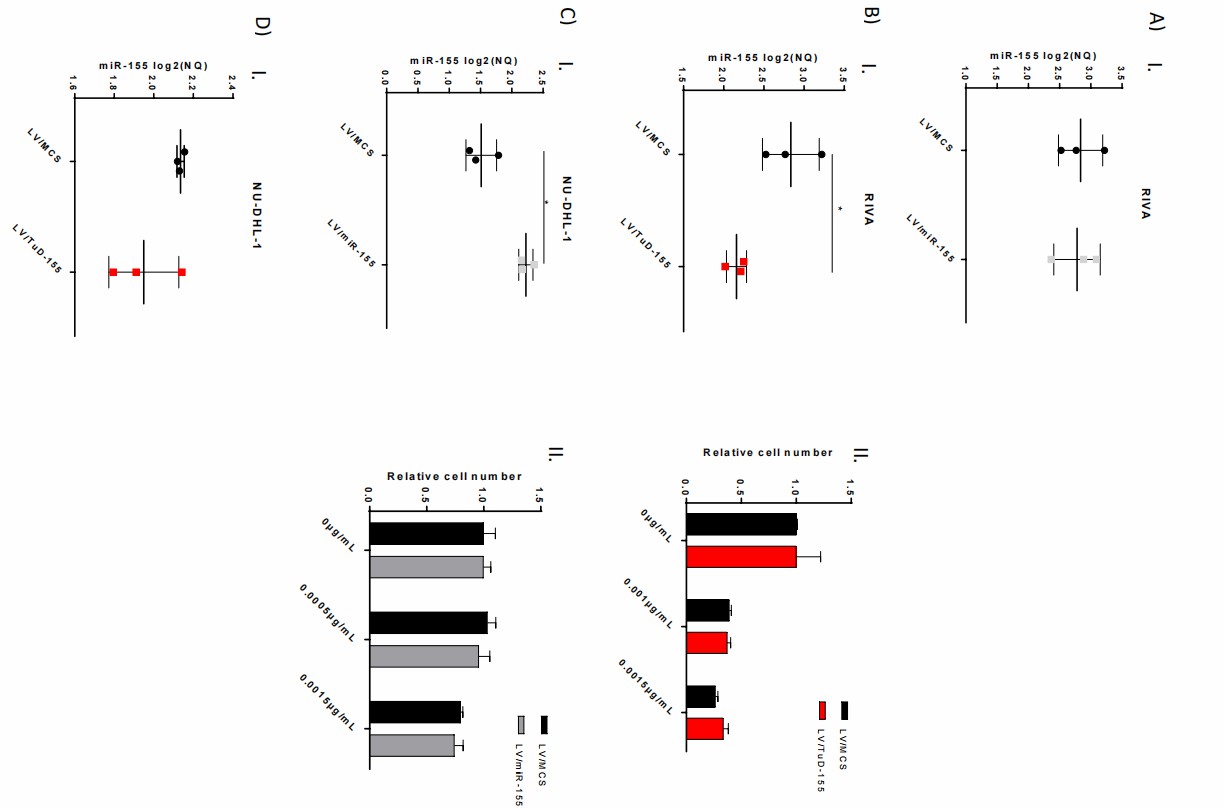 Fig. 3. Manipulation of miR-155 expression in ABC-DLBCL cell lines do not affect
Fig. 3. Manipulation of miR-155 expression in ABC-DLBCL cell lines do not affect
vincristine response (Sun Y, Jiang W, et al., 2020).
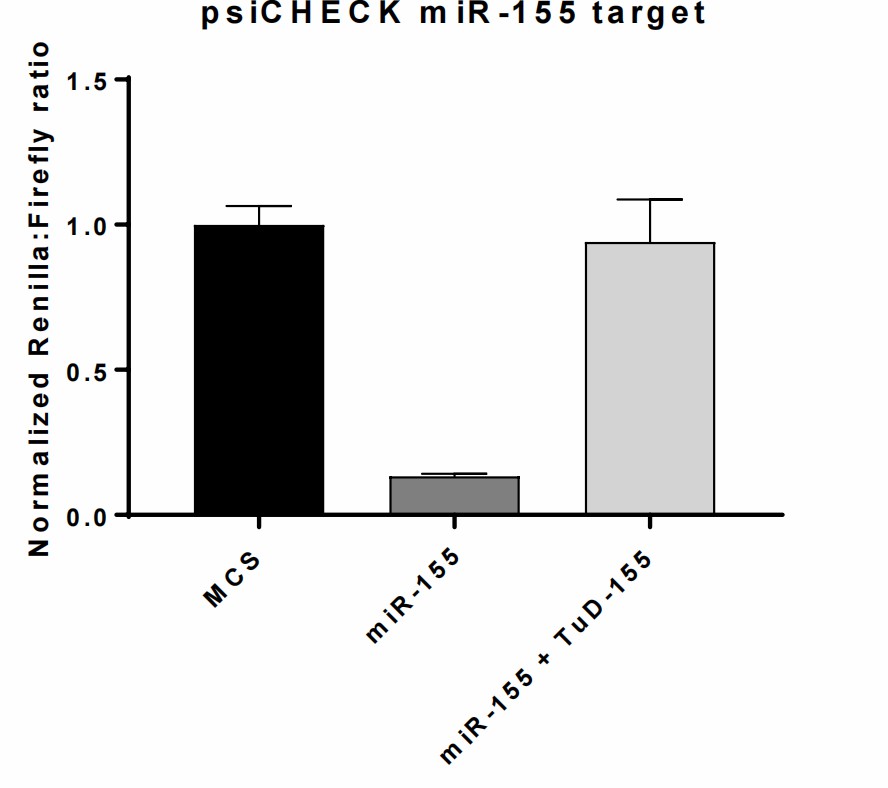 Fig. 4. Suppression of miR-155 by TuD-155 (Sun Y, Jiang W, et al., 2020).
Fig. 4. Suppression of miR-155 by TuD-155 (Sun Y, Jiang W, et al., 2020).
3D cell culture models replicate the natural tumor architecture, thereby presenting an external proliferating zone, an internal quiescent zone with limited oxygen, nutrient, and growth factor distribution, and a necrotic and hypoxic core. All these factors might influence drug response.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Reliable brand
Creative Bioarray is a reliable brand in the field of cells. The company offers international shipping, making it accessible to a broader customer.
27 Sep 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need