Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
A2780/ADR
Cat.No.: CSC-C9487J
Species: Human
Source: Reproductive: Ovary
Morphology: Epithelial
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Never can cryopreserved cells be kept at -20 °C.
The A2780 cell line was originally isolated and cultured from the tumor tissue of an untreated ovarian cancer patient. A2780/ADR is a drug-resistant cell line created by subjecting the A2780 cell line to Adriamycin (Doxorubicin) over multiple induction cultures. The cells of the A2780 cell line are typically epithelial-like, polygonal or spindle-shaped, and will often stick to the substrate in culture, which can be tumorigenic in immunodeficient mice. In addition, the A2780/ADR cell line also shows cross-resistance to melphalan and vinblastine.
This cell line, A2780/ADR, inherited many of the same biological features as ovarian cancer cells, including proliferation, migration, invasion and drug resistance. It is therefore an important resource for examining the pathogenesis and treatment of ovarian cancer. It is used in toxicity testing, cancer gene research, and the creation of new drugs. Furthermore, the A2780 cell line is used for drug sensitivity and resistance research, particularly in studying multidrug resistance (MDR).
Effect of the Sonodynamic Activation of Doxorubicin on ROS Production, Cell-Cycle, Gene Expression and Cell Death
Ovarian cancer (OC) remains the leading cause of death from gynecological malignancies due to late-stage diagnoses and drug resistance. Traditional treatments often fail to significantly reduce mortality. Doxorubicin (Doxo), while potent, has notable side effects and can trigger drug resistance. Sonodynamic therapy (SDT), which combines Doxo with low-intensity ultrasound (US), seeks to enhance effectiveness. Foglietta's team aims to determine if low-concentration Doxo can be used as a sonosensitizer in SDT to kill OC cells effectively, both in Doxo non-resistant (A2780/WT) and Doxo resistant (A2780/ADR) cell lines, and to assess its potential in inducing immunogenic cell death (ICD) to reduce recurrence.
Doxo's ability to produce ROS is one of its principal actions inside cells. Therefore, they analysed ROS production after SDT with Doxo using flow cytometry. In A2780/WT cells treated with Doxo and US, ROS production increased significantly, peaking at 5 minutes, then decreased (Fig. 1A). A2780/ADR cells did not show significant ROS changes (Fig. 1B). To deeply explore the effect of SDT with Doxo, a cell-cycle analysis was performed. After 36 hours of treatment, cell-cycle analysis with Vybrant dye revealed a G2/M phase arrest in both cell lines (Fig. 2A and B). A2780/WT cells had an increased G2/M phase percentage (55.80 ± 11.80%) and decreased G0/G1 phase percentage (25.30 ± 4.80%). Similarly, A2780/ADR cells showed a G2/M phase increase (71.50 ± 17.80%) and G0/G1 phase decrease (10.70 ± 4.20%). These results conclude that SDT with Doxo induces cell-cycle arrest in G2/M phase in both cell lines. Gene expression analysis indicated a significant increase in CDKN1A (cell-cycle related genes) expression for both cell lines after SDT with Doxo (15.05 ± 3.30 in A2780/WT, Fig. 2C; 6.07 ± 1.49 in A2780/ADR, Fig. 2D), suggesting a p53-independent pathway. Flow cytometry 36 hours post-treatment showed increased early apoptotic and late apoptotic/necrotic cells in A2780/WT (early: 28.76 ± 3.40; late: 12.56 ± 1.32) and A2780/ADR cells (early: 24.96 ± 1.78; late: 30.50 ± 5.25), with decreased live cells (A2780/WT: 58.68 ± 5.67; A2780/ADR: 44.70 ± 5.80) after SDT with Doxo (Fig. 2E-H).
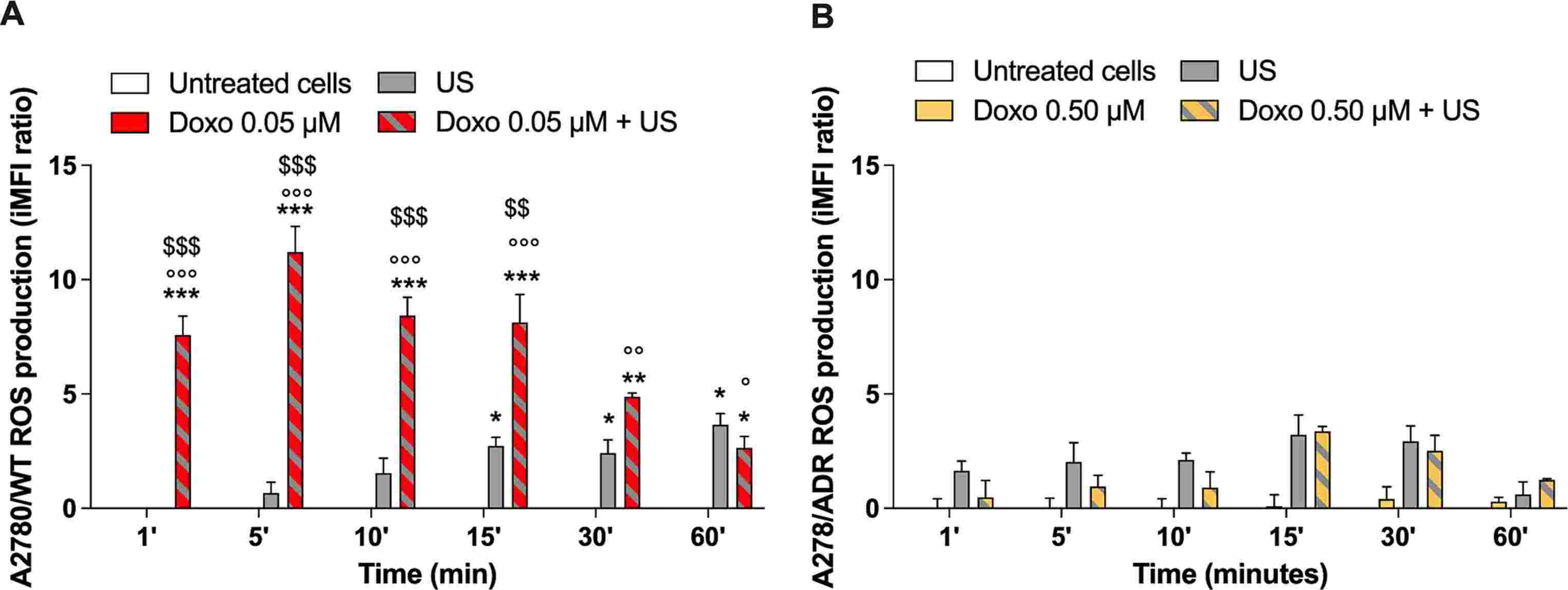 Fig. 1. Effects on ROS production of SDT with Doxo in A2780/WT and A2780/ADR cells (Foglietta F, Macrì M, et al., 2023).
Fig. 1. Effects on ROS production of SDT with Doxo in A2780/WT and A2780/ADR cells (Foglietta F, Macrì M, et al., 2023).
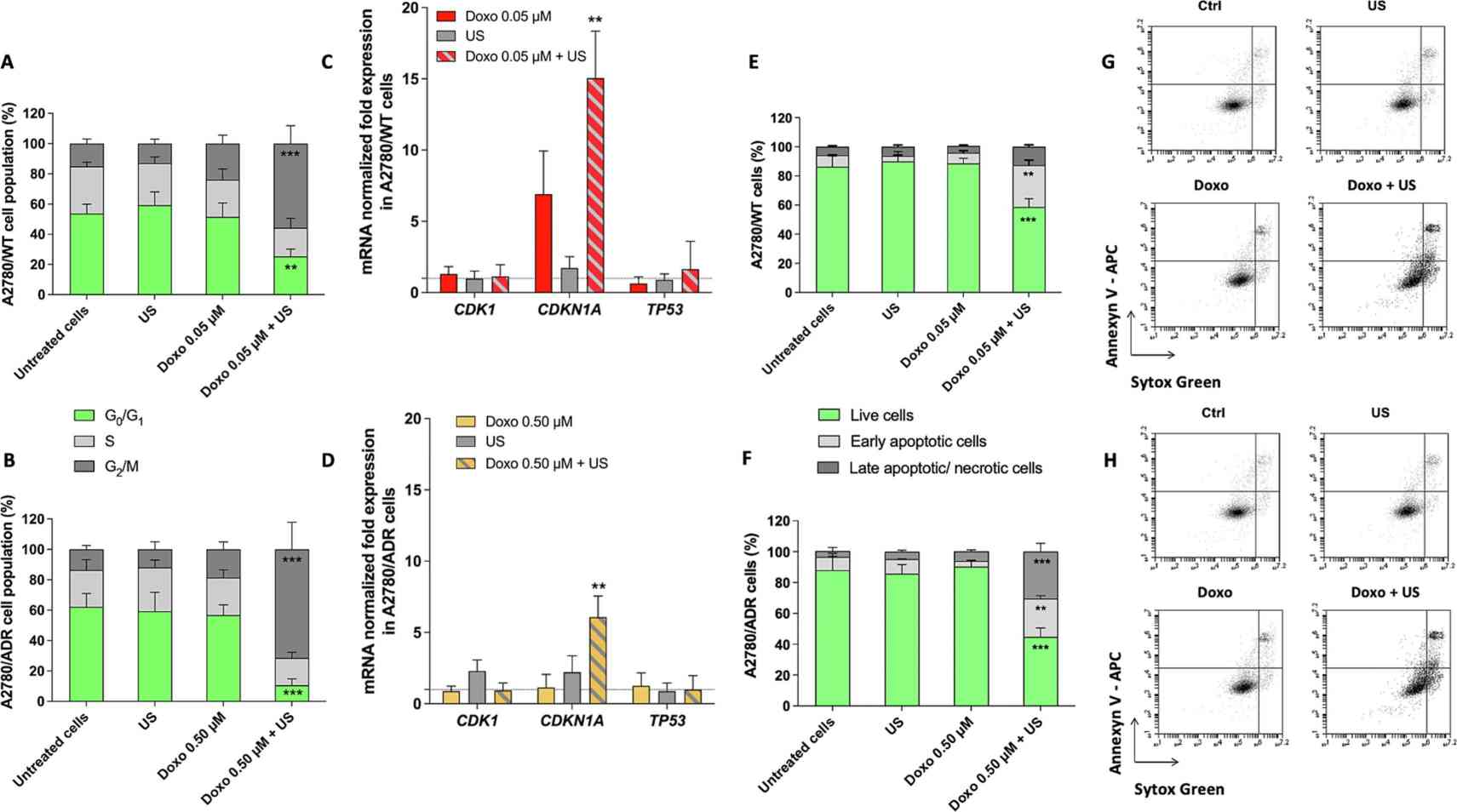 Fig. 2. Effect of SDT with Doxo on cell-cycle distribution, gene expression and cell death in A2780/WT and A2780/ADR cells (Foglietta F, Macrì M, et al., 2023).
Fig. 2. Effect of SDT with Doxo on cell-cycle distribution, gene expression and cell death in A2780/WT and A2780/ADR cells (Foglietta F, Macrì M, et al., 2023).
Terfenadine Restores Doxorubicin Activity to MDR Ovarian Cancer Cells
Ovarian cancer treatment is challenged by chemoresistance and recurrence, largely due to ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 1 (ABCB1) overexpression. Current ABCB1 inhibitors face limitations due to low binding affinities and high toxicity. Terfenadine is an antihistamine originally used to treat allergies, but recent studies have shown its potential in inhibiting cancer cell growth and inducing apoptosis by altering calcium signaling pathways. Huang's team aims to understand the role of the CAMKIID/CREB1 pathway in ABCB1 overexpression and how terfenadine can restore doxorubicin sensitivity in MDR ovarian cancer cells by inhibiting this pathway. To explore new therapies for ABCB1-mediated MDR ovarian cancer, a quantitative high-throughput combinational screening (qHTCS) was conducted on the ABCB1-overexpressing cell line A2780-ADR. Compared to A2780 cells, A2780-ADR showed higher ABCB1 expression and activity, as seen in increased protein levels and decreased Rho123 accumulation (Fig. 3A, B and Fig. 4A). IC50 values for ABCB1 substrates like doxorubicin were higher in A2780-ADR cells but decreased in the presence of the ABCB1 inhibitor tariquidar (Fig. 3D and Fig. 4D–F). The qHTCS included 6,016 drugs, identifying 246 that inhibited A2780-ADR cell growth (IC50 < 10 µM, Fig. 3E). Further testing with doxorubicin revealed 24 synergistic compounds (Fig. 3F). Terfenadine was chosen for further study due to its unknown mechanism with doxorubicin and its noted anticancer activity (Fig. 3G).
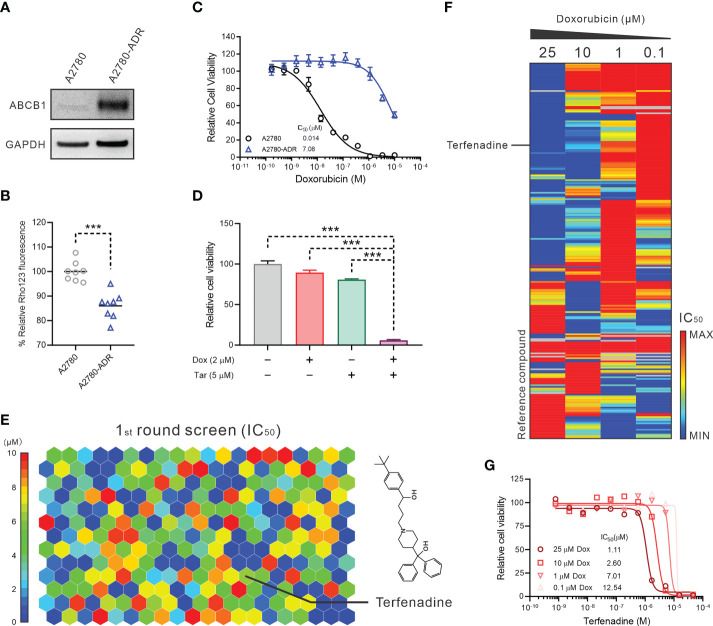 Fig. 3. Terfenadine restores the activity of doxorubicin in MDR ovarian cancer cells (Huang W, Yang S, et al., 2022).
Fig. 3. Terfenadine restores the activity of doxorubicin in MDR ovarian cancer cells (Huang W, Yang S, et al., 2022).
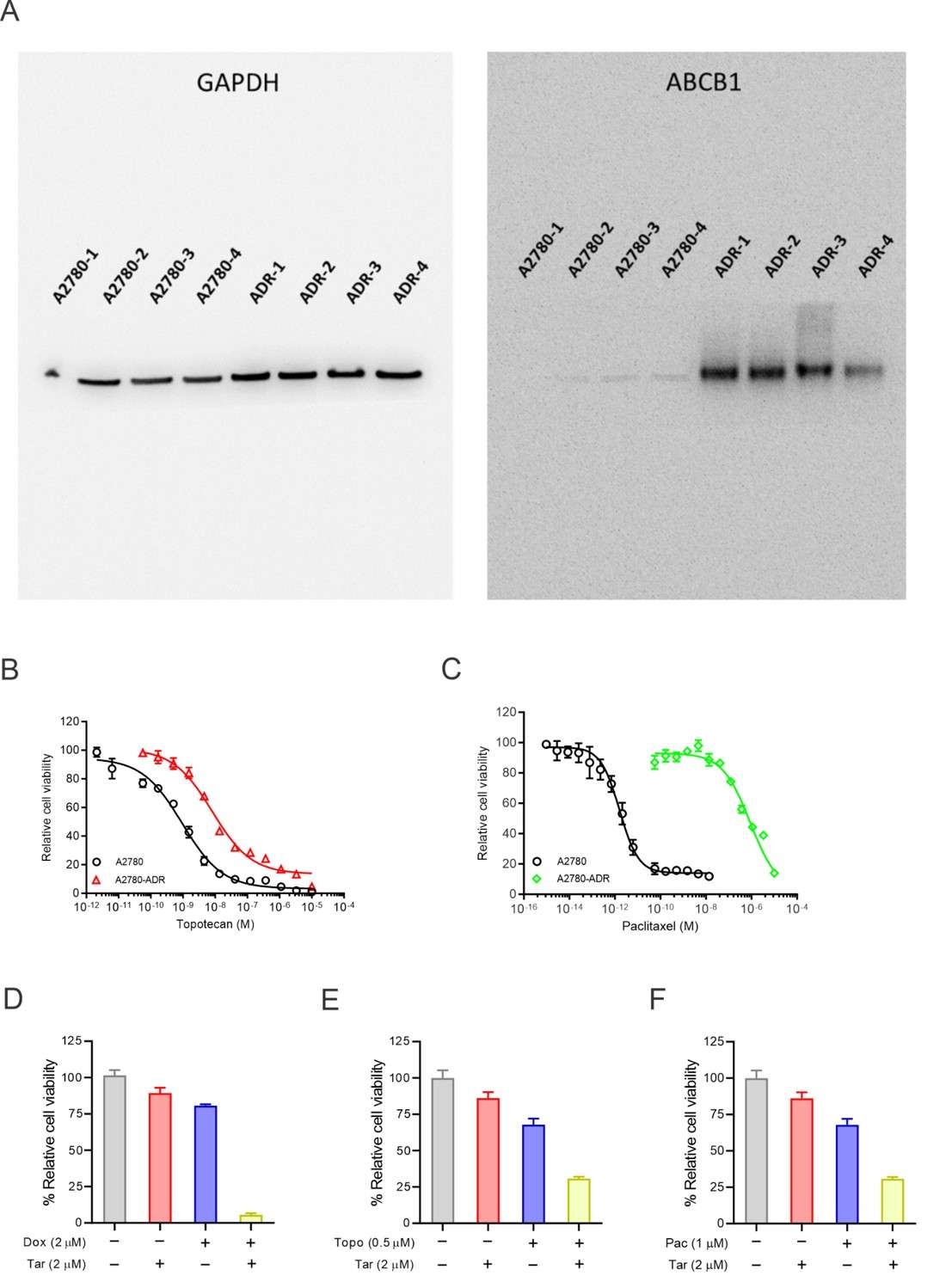 Fig. 4. Terfenadine restores the doxorubicin in MDR ovarian cancer cells' activity (Huang W, Yang S, et al., 2022).
Fig. 4. Terfenadine restores the doxorubicin in MDR ovarian cancer cells' activity (Huang W, Yang S, et al., 2022).
Although various family members are expressed by the major ovarian cell types (i.e., oocytes, granulosa cells, and thecal cells), many of their effects center on the control of granulosa cell growth and differentiation, both of which affect folliculogenesis and oocyte development.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Reliable
The resources from Creative Bioarray have been extremely helpful in optimizing our experimental techniques and ensuring consistent and reliable results.
12 Mar 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review