How to Apply Exosomes in Clinical?
Exosomes are nanoparticle extracellular vesicles composed of a phospholipid bilayer and are 30-150 nm in diameter. They are released to the extracellular environment when multivesicular bodies fuse with the cell membrane, and they contain bioactive molecules including proteins, lipids and RNA (most often miRNA). These features make exosomes highly attractive for biomedical applications. The major clinical applications of exosomes include biomarkers, cell-free therapeutics, delivery platforms, analytical basis for exosome kinetics, and cancer vaccines. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) and dendritic cells (DC), for example, are two commonly used exosome sources, serving as agents to treat inflammation, deliver drugs, and promote immune responses in cancer patients. Exosomes are progressively exploring therapeutic drug delivery, taking advantage of their natural targeting and biocompatibility, and as a perfect alternative to synthetic nanocarriers, for a growing number of applications around the world.
As Biomarkers
Exosomes are of particular use in biomarker applications - especially for the diagnosis and prognosis of chronic diseases like cancer. Because exosomes are consistently present in biological fluids and can express markers of cell status, including miRNA, proteins and lipids, they can be used to perform low-invasive, liquid biopsies. Research has shown that fluctuations in expression of certain exosomal miRNAs can reflect cancer occurrence and progression. Exosomal miR-21 and miR-1246, for instance, are high in patients with breast cancer, and could be a biomarker for the disease. Exosomal proteins could also be used as biomarkers for early detection of disease. CD26, CD81, S1C3A1, and CD10 may be potential markers for liver damage. Through the use of high-throughput multi-omics, and machine learning, exosomal biomarkers are rapidly emerging that could help stratify diseases and provide targeted treatment individualized to the patient.
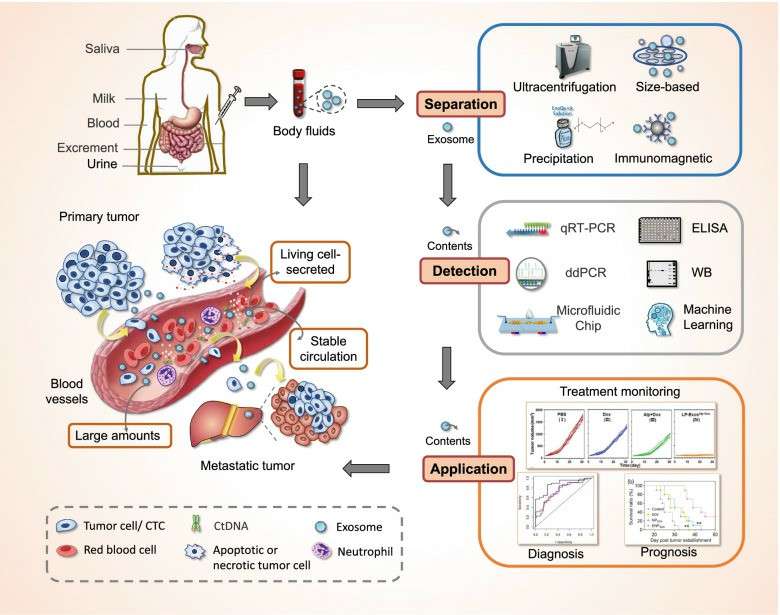 Fig. 1. Exosomes as a new target for liquid biopsy (Yu D, Li Y, et al., 2022).
Fig. 1. Exosomes as a new target for liquid biopsy (Yu D, Li Y, et al., 2022).
As Drug Delivery Vehicles
Exosomes are a promising new alternative to liposomes for drug delivery. Their natural biology - high targeting potential, stability, low toxicity, low immunogenicity - coupled with their natural transport capacity makes them ideal drug carriers. Exosomes can be loaded, by both endogenous and exogenous means, with nucleic acids, proteins and even compounds to optimize pharmacokinetics and minimize off-target effects. Genetic and chemical engineering could further increase the ability of drugs to be directed towards cells or organs, reducing clearance by immune mechanisms and increasing bioavailability. Exosome treatments for many diseases have already been treated in clinical trials. But exosome preparation and optimal production remain in limbo thanks to large-scale production technology and batch-to-batch heterogeneity.
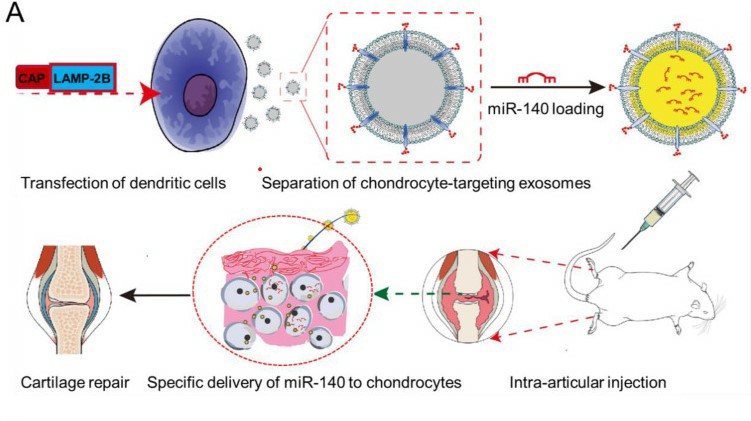 Fig. 2. Genetic engineering of exosomes for targeted delivery of miRNA to chondrocytes (Liang Y, Duan L, et al., 2021).
Fig. 2. Genetic engineering of exosomes for targeted delivery of miRNA to chondrocytes (Liang Y, Duan L, et al., 2021).
Exosome Therapy
Exosome therapy is a new cell-free therapy that uses the bioactive molecules found in exosomes to treat disease. MSC-Exos are another emerging exosome target for treatment. They also contain a broad range of bioactive molecules including proteins and RNAs, that are anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and tissue regenerative, and that have shown promise in diseases such as acute respiratory distress syndrome, kidney disease, graft-versus-host disease, osteoarthritis, stroke, Alzheimer's and type I diabetes. In comparison to stem cell therapy, exosomes are also highly therapeutic, immune-rejection- and tumor-free, which is a big benefit. Nevertheless, there needs to be more research on exosome therapy side effects and safety to ensure clinical application safety.
Exosome-Based Vaccines
Immune vaccines using exosomes are another new strategy involving exosomes as carriers. Adding antigens or immune stimulatory molecules to exosomes allows such vaccines to evoke immune responses to fight germs or tumors. What's different about exosome vaccines is that they replicate the antigen presentation mechanism of a natural infection to induce a strong immune response while still being safely and tolerable. Vaccines containing exosomes have also been tested against cancers and viruses. For instance, researchers delivered HIV-1 inhibitory factors using exosomes to suppres HIV-1 engraftment through epigenetic processes. And exosomes have been used to carry mRNA therapies for cancer vaccines. Evidence from clinical trials is that exosome vaccines can elicit tolerable immune responses.
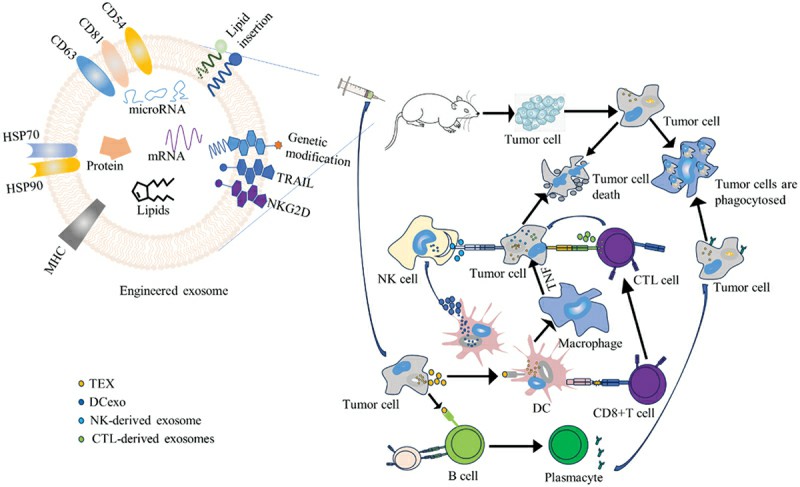 Fig. 3. The mechanism of action of tumor-derived exosomes and immune cell-derived exosomes on tumor cells (Dai Z, Cai R, et al., 202).
Fig. 3. The mechanism of action of tumor-derived exosomes and immune cell-derived exosomes on tumor cells (Dai Z, Cai R, et al., 202).
Aesthetic Medicine
Exosomes offer new approaches in the field of aesthetic medicine for beauty and skincare. As carriers for intercellular signaling, exosomes exhibit significant efficacy in anti-aging, skin repair, and regeneration. They are rich in active substances such as growth factors and cytokines, which can reduce the rate of skin aging and promote elasticity and collagen production, thus widely applied in the development of skincare products like masks and serums. Moreover, the potential of exosomes in weight loss and body sculpting is gradually being explored, achieved by regulating fat metabolism and apoptosis. Therefore, exosomes hold immense potential in beauty applications, attracting attention from both scientific and market perspectives. However, further research and clinical validation are required to ensure their efficacy and safety in aesthetic medicine.
| Products & Services | Description |
| Exosome Applications | Creative Bioarray offers a complete set of services for exosome application including but not limited to exosome transfection, exosome labeling, and exosome targeting. |
| Exosome Analysis | Creative Bioarray provides diverse exosomal species analysis to help you understand your exosome compositions. |
| Exosome Identification | Creative Bioarray provides comprehensive support for your exosome identification by including the morphology assay, purity, and quantity assay, particle size distribution analysis, and exosome-specific markers expression. |
| Exosome Isolation Tools | Creative Bioarray aims to develop the best quality exosome isolation tools with optimized conditions to help our customers obtain pure exosomes with a higher yield. |
References
- Yu D, et al. Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy. Mol Cancer. 2022, 21(1), 56.
- Liang Y, et al. Engineering exosomes for targeted drug delivery. Theranostics. 2021, 11(7), 3183-3195.
- Dai Z, et al. Exosome may be the next generation of promising cell-free vaccines. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024, 20(1), 2345940.

