- You are here: Home
- Resources
- Explore & Learn
- Exosome
- Exosomes as Emerging Biomarker Tools for Diseases
Support
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Exosomes as Emerging Biomarker Tools for Diseases
Exosomes have emerged as a fascinating class of extracellular vesicles that hold immense potential as biomarker tools for diagnosing, prognosticating, and treating various diseases. These tiny vesicles, released by cells into the extracellular space, carry a cargo of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and other biomolecules, reflecting the physiological and pathological states of their parent cells.
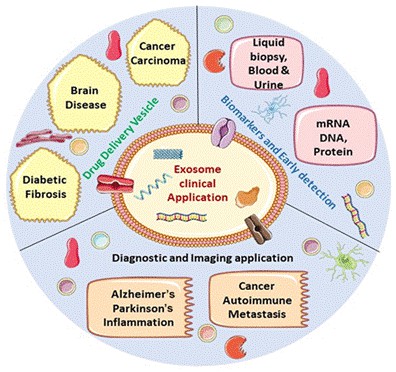 Fig. 1 Exosomes as biomarkers for diseases. (Huda MN, et al., 2021)
Fig. 1 Exosomes as biomarkers for diseases. (Huda MN, et al., 2021)
Exosomes as Diagnostic Biomarkers
Exosomes have demonstrated significant promise as diagnostic biomarkers across a range of diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and infectious diseases. These vesicles offer several advantages over traditional diagnostic methods, such as their non-invasive nature and the ability to provide real-time information about disease status.
- In cancer, exosomes derived from tumor cells can be isolated from various biofluids, including blood, urine, and saliva. By analyzing the content of these exosomes, specific tumor-derived nucleic acids, proteins, and other biomolecules can be identified, enabling the early detection and monitoring of cancer. For example, in breast cancer, exosomal microRNAs have been identified as potential diagnostic markers due to their differential expression patterns in patients compared to healthy individuals. Similarly, in neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's disease, exosomal amyloid-beta peptides and tau proteins have shown promise as diagnostic biomarkers.
- Cardiovascular diseases, such as myocardial infarction and heart failure, can also be diagnosed using exosomal biomarkers. Exosomes derived from cardiac cells contain specific cardiac microRNAs, proteins, and lipids that can indicate myocardial injury or dysfunction. For instance, elevated levels of cardiac-specific miR-208a in exosomes have been associated with heart failure.
- In infectious diseases, exosomes can carry pathogen-derived nucleic acids or proteins, providing valuable insights into the presence and progression of infections. For instance, exosomal microRNAs from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages have been identified as potential diagnostic markers for tuberculosis.
Exosomes as Prognostic Biomarkers
Exosomal biomarkers also hold promise as prognostic indicators, providing valuable information about disease progression, treatment response, and patient outcomes. By analyzing the cargo of exosomes, researchers can gain insights into the molecular changes occurring within cells and their microenvironment, enabling the prediction of disease aggressiveness and therapeutic efficacy.
- In cancer, exosomal biomarkers have been identified as prognostic indicators, aiding in predicting patient survival and treatment response. For example, in prostate cancer, the presence of exosomal prostate-specific antigen (PSA) has been correlated with disease progression and poor prognosis. Similarly, in lung cancer, exosomal expression of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) has been associated with resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors and reduced patient survival.
- Exosomal biomarkers have also demonstrated prognostic value in cardiovascular diseases. In heart failure patients, the levels of certain cardiac-specific microRNAs, such as miR-133a and miR-208b, in circulating exosomes have been linked to disease severity and prognosis. These biomarkers can provide valuable information for tailoring treatment strategies and predicting patient outcomes.
Creative Bioarray Relevant Recommendations
Creative Bioarray provides a complete set of services for exosome research and resolves your issues quickly and efficiently. We also offer comprehensive support for customized services to meet your needs. We provide various exosome-related assays, including but not limited to:
| Service Types | Description |
| Exosome Isolation and Purification | Creative Bioarray provides reliable techniques for exosome isolation from different sample matrices. We also provide exosome isolation using specified techniques if required by customers. |
| Exosome Identification | Creative Bioarray provides comprehensive support for your exosome identification by including the morphology assay, purity, and quantity assay, particle size distribution analysis, and exosome-specific markers expression. |
| Exosome Quantification | Creative Bioarray offers a range of options to meet most exosome quantitation demands. We provide reliable, and optimized tools at the most competitive price for quantitative analysis of exosomes in diverse biological samples such as plasma, urine, etc. |
| Exosome Analysis | Creative Bioarray provides diverse exosomal species analysis to help you understand your exosome compositions. |
Reference
- Huda MN, et al. (2021). "Potential Use of Exosomes as Diagnostic Biomarkers and in Targeted Drug Delivery: Progress in Clinical and Preclinical Applications." ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 7 (6), 2106-2149.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

