- You are here: Home
- Resources
- Explore & Learn
- Exosome
- Exosome Quality Control: How to Do It?
Support
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Exosome Quality Control: How to Do It?
Ensuring standardized and scalable production of exosomes, along with a robust quality management system, is essential to advancing their research applications and clinical translation. This is not only related to the stability and reliability of exosome products, but also an important foundation for ensuring their security and effectiveness. At present, for the comprehensive characterization of exosome quality, the industry has formed a set of systematic measurement standards. which are mainly focused on a range of core aspects, including but not limited to particle size analysis, concentration, surface markers, microbial and mycoplasma detection, and so on. The following are examples of commonly used exosome quality control systems and assays.
Exosome Particle Size and Concentration
Currently, the main methods to analyze the particle size and concentration of exosomes are FlowNanoAnalyzer and NTA (Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis). These methods enable precise measurement of exosome size and provide size distribution profiles.
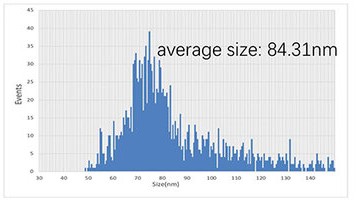 Fig. 1. Particle concentration and size distribution of exosomes measured by NTA (Zhu T, Sun J, et al., 2022).
Fig. 1. Particle concentration and size distribution of exosomes measured by NTA (Zhu T, Sun J, et al., 2022).
Positive Rates of Protein Markers (CD63/CD81/CD9)
Exosomes typically express markers such as CD81, CD63, and CD9, which produce strong fluorescence when incubated with exosomes using fluorescently labeled CD81/CD63/CD9 antibodies that bind to the exosomes, then detected by flow cytometry. This detection technique is quite rapid and suitable for high throughput screening.
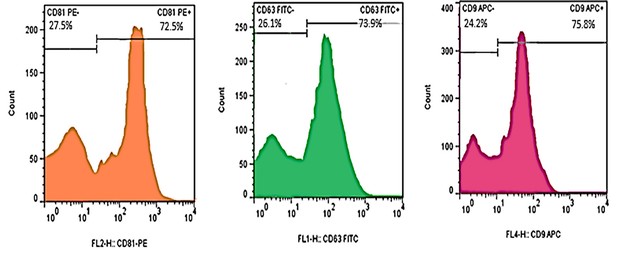 Fig. 2. Flow cytometry showed three positive markers for exosomes: CD81, CD63 and CD9 (Pourhadi M, Zali H, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. Flow cytometry showed three positive markers for exosomes: CD81, CD63 and CD9 (Pourhadi M, Zali H, et al., 2024).
Exosome Morphology
A well-established way to identify the morphology of exosomes is transmission electron microscopy (TEM), which can also identify exosomes by morphology and size and generate TEM images. In contrast to negative staining, we can directly examine the shape, structure and size of individual exosomes through a powerful high-power microscope.
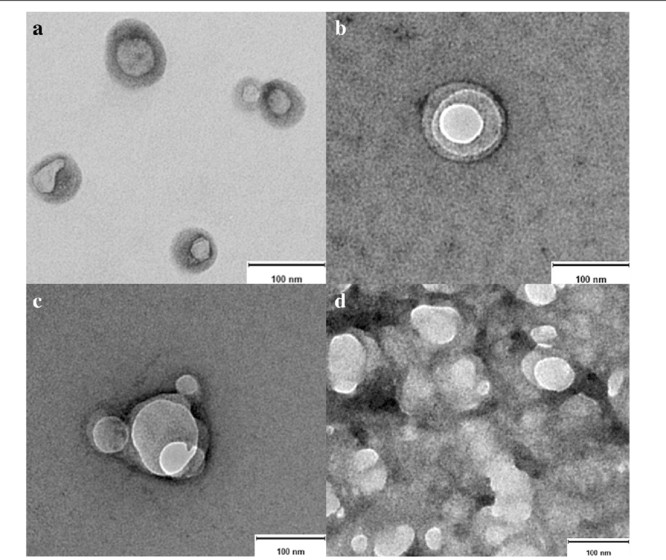 Fig. 3. Transmission electron microscopy of native exosomes (Aguilera-Rojas M, Badewien-Rentzsch B, et al., 2018).
Fig. 3. Transmission electron microscopy of native exosomes (Aguilera-Rojas M, Badewien-Rentzsch B, et al., 2018).
Sterility Testing
Sterility testing ensures that no live bacteria, fungi or viruses get in contact with exosome samples. The test is usually made by culture medium culture method. It is vital that the test is handled under aseptic conditions. Rapid techniques like PCR or enzyme-linked detection kits can also identify specific bacterial or viral DNA/RNA.
Mycoplasma Testing
Mycoplasma contamination is typically detected using specialized test kits, where amplification of conserved mycoplasma DNA sequences induces a visible color change in the reaction solution. Other methods include culture and DNA staining techniques.
Pathogenic Factor Screening
The test for intra- and extracellular pathogenic factors should be negative for HIV antibody, HBsAg, HCV antibody, TP antibody, CMV-IgM, HTLV antibody, HPV antibody, HHV antibody, EBV antibody, Furthermore, nucleic acid tests for HCV, HBV, and HIV should also be negative. Generally, ELISA for antibody level and nucleic acid test for viral nucleic acid are used.
Endotoxin Testing
Common endotoxin detection methods include the Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) test, which detects endotoxins through a colorimetric or turbidity-based gelation reaction. There are alternative methods such as recombinant factor C tests or fluorescence polarization techniques. For example, the endotoxin standard for mesenchymal stem cells requires a value no greater than 0.5 EU/mL.
Abnormal Immune Response Testing
To assess abnormal immune responses, exosome samples should demonstrate no abnormal lymphocyte proliferation. This is measured using CFSE-labeled lymphocyte proliferation inhibition assays, with flow cytometry to assess lymphocyte proliferation rates.
| Products & Services | Description |
| Exosome Analysis | Creative Bioarray provides diverse exosomal species analysis to help you understand your exosome compositions. |
| Exosome Identification | Creative Bioarray provides comprehensive support for your exosome identification by including the morphology assay, purity, and quantity assay, particle size distribution analysis, and exosome-specific markers expression. |
References
- Zhu T, Sun J, et al. Plasma Exosomes from Children with Atopic Dermatitis May Promote Apoptosis of Keratinocytes and Secretion of Inflammatory Factors in vitro. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022. 15:1909-1917.
- Pourhadi M, Zali H, et al. Restoring Synaptic Function: How Intranasal Delivery of 3D-Cultured hUSSC Exosomes Improve Learning and Memory Deficits in Alzheimer's Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. 61(6):3724-3741.
- Aguilera-Rojas M, Badewien-Rentzsch B, et al. Exploration of serum- and cell culture-derived exosomes from dogs. BMC Vet Res. 2018. 14(1):179.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

