CARD-FISH: Illuminating Microbial Diversity
Catalyzed reporter deposition-fluorescence in situ hybridization (CARD-FISH) is a powerful technique that enables the visualization and identification of microbial cells in their natural environment. It has revolutionized the field of microbial ecology by providing insights into the diversity, spatial distribution, and metabolic activities of microorganisms.
What Is CARD-FISH?
CARD-FISH combines the principles of FISH and the catalytic deposition of reporter molecules. The technique involves the hybridization of fluorescently labeled nucleic acid probes to specific microbial RNA or DNA targets. These probes are designed to be complementary to the target sequences, allowing for precise detection and identification of microbial cells.
The unique aspect of CARD-FISH lies in the catalytic signal amplification and reporter deposition steps. Enzymes, such as horseradish peroxidase (HRP), are conjugated to the probes. When the probe binds to its target, the HRP enzyme catalyzes the deposition of fluorescent reporter molecules onto the probe-target complex. This amplification step enhances the signal, enabling the visualization of individual microbial cells with high sensitivity and specificity.
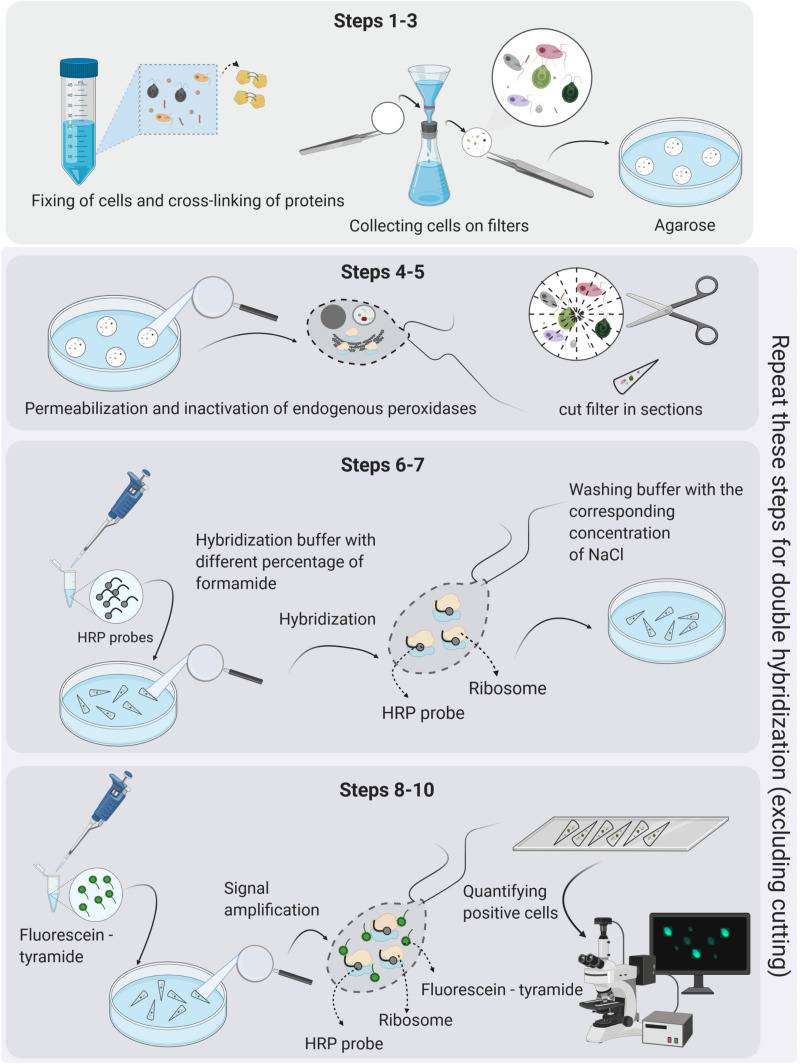 Fig.1 The key steps in the CARD-FISH and double CARD-FISH procedures. (Piwosz K, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 The key steps in the CARD-FISH and double CARD-FISH procedures. (Piwosz K, et al., 2021)
Types of CARD-FISH Probes
CARD-FISH probes can be designed to target different microbial groups, allowing for the identification of specific taxa or functional genes. Each probe can be labeled with a specific fluorochrome, enabling multiplex CARD-FISH, where multiple probes with distinct fluorescence signals can be used simultaneously to detect different microbial groups within a sample. Some commonly used CARD-FISH probes include:
- 16S rRNA probes. These probes target the conserved regions of the 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene, enabling the identification and quantification of bacterial and archaeal cells. They provide valuable insights into the microbial composition and diversity of various environments.
- 18S rRNA probes. Designed to target the 18S rRNA gene, these probes are used to detect and classify eukaryotic microorganisms, such as protists and fungi. They contribute to our understanding of the role of eukaryotes in different ecosystems.
- Functional gene probes. These probes target specific functional genes, such as amoA for ammonia-oxidizing bacteria or nirS for denitrifying bacteria. By detecting these genes, CARD-FISH allows researchers to study the distribution and activity of microbial groups involved in key biogeochemical processes.
Advantages and Limitations of CARD-FISH
| Advantages | Limitations |
|
|
CARD-FISH in Environmental Microbiology
CARD-FISH has made significant contributions to the field of environmental microbiology, providing valuable insights into microbial diversity, ecological functions, and ecosystem dynamics. Some key applications of CARD-FISH in this field include:
- Study of microbial communities in aquatic ecosystems. CARD-FISH allows researchers to investigate the composition and spatial distribution of microbial communities in marine and freshwater environments. It has provided insights into the roles of microorganisms in nutrient cycling, carbon sequestration, and the degradation of pollutants.
- Soil microbiology. By employing CARD-FISH, scientists have explored the diversity and function of microbial communities in soil ecosystems. This has enhanced our understanding of soil fertility, nutrient cycling, and the impacts of land management practices on soil microbial communities.
- Extreme environments. CARD-FISH has been instrumental in studying microbial life in extreme environments such as deep-sea hydrothermal vents, polar regions, and deserts. It has shed light on the adaptations and interactions of microorganisms in these challenging habitats.
- Bioremediation and waste management. Understanding the microbial communities involved in bioremediation processes is crucial for effective waste management strategies. CARD-FISH has been used to identify and quantify specific microbial groups involved in pollutant degradation, aiding in the development of targeted bioremediation approaches.
Creative Bioarray Relevant Recommendations
| Product/Service Types | Description |
| Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Service | Creative Bioarray offers a full line of FISH services, from standardized testing of validated assays to custom development of new assays. |
| FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service | Creative Bioarray frequently receives requests for custom synthesized probes, for novel, rare, and specialized applications. |
| ISH/FISH Probes | Creative Bioarray provides the most comprehensive list of FISH probes for the rapid identification of a wide range of chromosomal aberrations across the genome. |
Reference
- Piwosz K, et al. (2021). "CARD-FISH in the Sequencing Era: Opening a New Universe of Protistan Ecology." Front Microbiol. 12: 640066.

