- You are here: Home
- Disease Models
- Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Human PBMCs Transplantation-Induced GvHD Model
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Pain Models
- Metabolic Disease Models
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
Human PBMCs Transplantation-Induced GvHD Model
Creative Bioarray has developed a sophisticated GvHD model induced by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) to deepen our understanding of the complex pathophysiological mechanisms underlying GvHD. This model serves as a critical tool for rigorously evaluating the efficacy of potential therapeutic interventions and for optimizing treatment strategies. By leveraging both in vitro and in vivo platforms, Creative Bioarray aims to bridge the gap between preclinical research and clinical application, thereby accelerating the translation of scientific discoveries into effective clinical treatments for GvHD.
Human PBMCs can induce GvHD in humanized mouse models due to the presence of human T cells, which possess the ability to recognize and respond to foreign antigens presented by the mouse's cells. This recognition triggers an immune reaction that culminates in GvHD, a potentially severe complication of bone marrow transplantation characterized by the donated cells attacking the recipient's body. The use of human PBMCs in this model offers a unique opportunity to study GvHD mechanisms in a setting that closely mimics the human immune system, thereby facilitating the testing and development of therapeutic strategies that can be directly translated to human patients. This approach not only enhances our understanding of the complex interactions between the donor's immune cells and the recipient's tissues but also accelerates the discovery of novel treatments for GvHD, ultimately improving patient outcomes following bone marrow transplantation.
Our Human PBMCs Transplantation-Induced GvHD Model
- Available Animal
- Mouse (immunodeficient mouse)
- Modeling Method
Mice are infused with hPBMCs to induce GvHD on day 0.
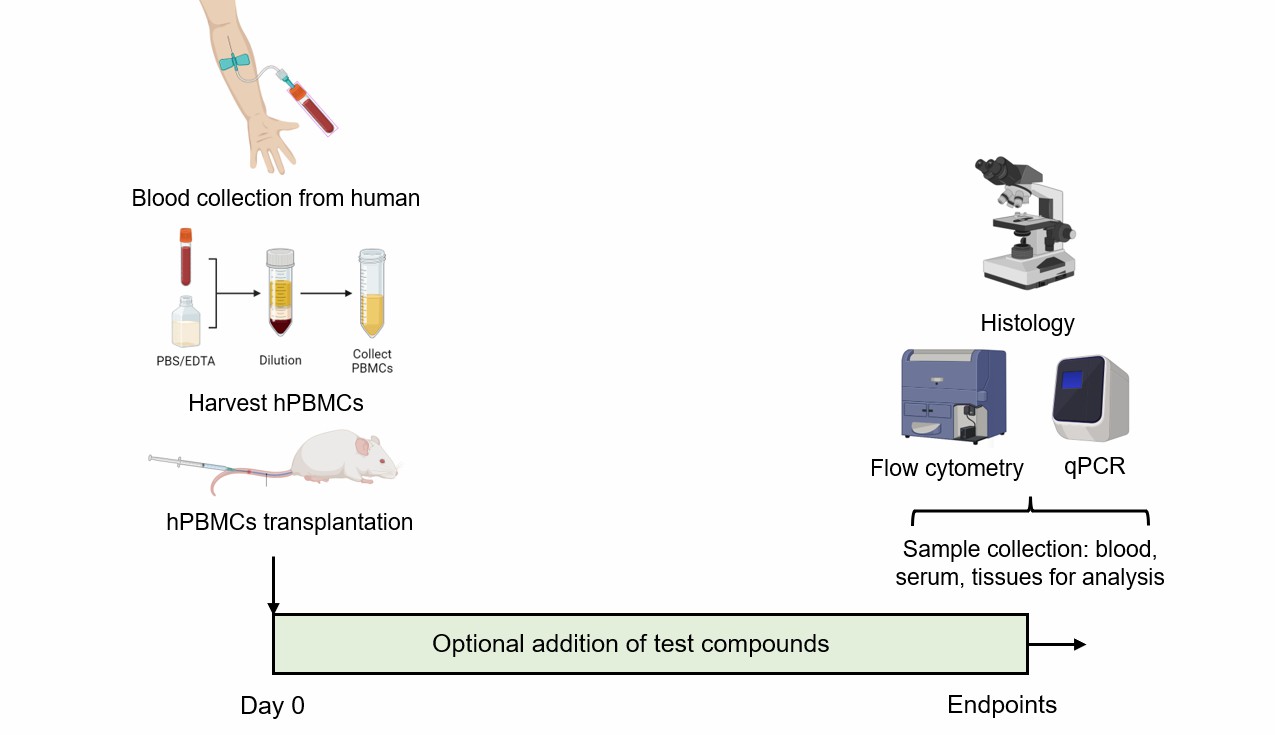 Fig. 1 Modeling method of human PBMCs transplantation-induced GvHD model
Fig. 1 Modeling method of human PBMCs transplantation-induced GvHD model
- Endpoints
- Body weight
- Clinical score
- Cytokine analysis
- Survival rate
- Flow cytometry
- Histology analysis
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
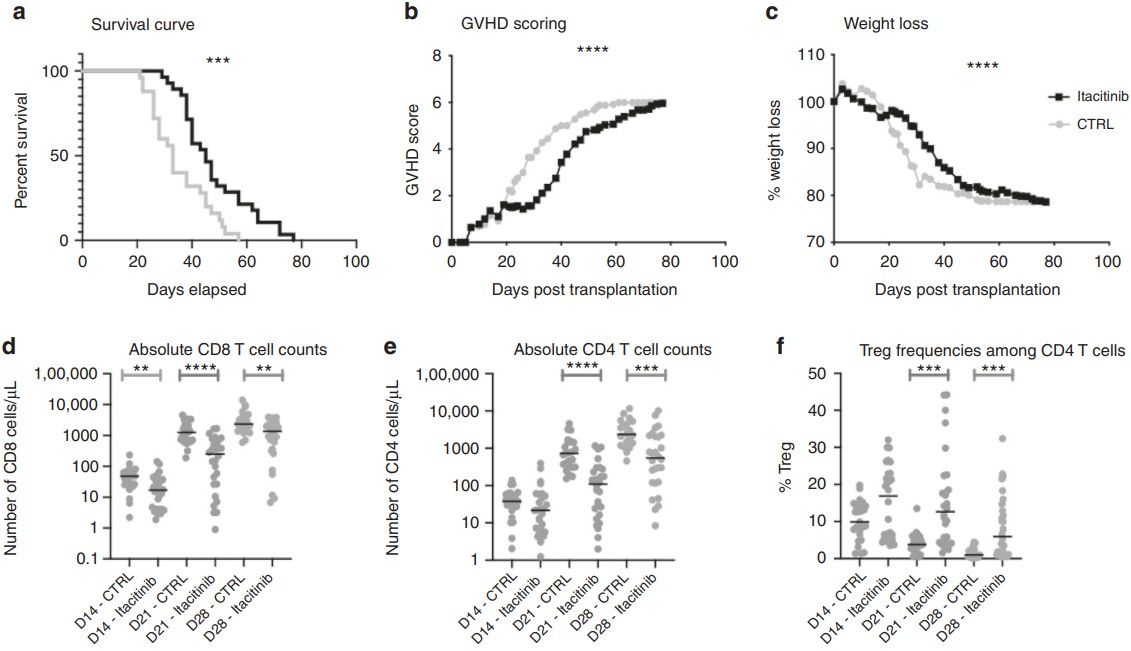 Fig 2. Impact of itacitinib on xGVHD. Survival (a), GVHD scoring (b) and weight loss (c) in the three cohorts (with three different PBMC donors) combined. Gray line with circles shows control mice (n = 25) while black line with squares shows itacitinib mice (n = 28). Absolute CD8 T-cell counts (d), absolute CD4 T-cell counts (e) and Treg frequencies among CD4 T-cells (f) in the three cohorts combined. (Courtois et al. 2021)
Fig 2. Impact of itacitinib on xGVHD. Survival (a), GVHD scoring (b) and weight loss (c) in the three cohorts (with three different PBMC donors) combined. Gray line with circles shows control mice (n = 25) while black line with squares shows itacitinib mice (n = 28). Absolute CD8 T-cell counts (d), absolute CD4 T-cell counts (e) and Treg frequencies among CD4 T-cells (f) in the three cohorts combined. (Courtois et al. 2021)
Furthermore, we also provide another GvHD model that maybe you are interested in:
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray has a team of scientists with deep expertise in therapeutics and extensive experience in disease modeling. We are dedicated to providing our clients with reliable services at competitive prices. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
Reference
- Courtois, J., et al. Itacitinib prevents xenogeneic GVHD in humanized mice. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2021;56(11):2672-2681.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.

