Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
Lu-165
Cat.No.: CSC-C6403J
Species: Human
Morphology: other
Culture Properties: Suspension cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Store in liquid nitrogen.
A new cancer cell line (Lu‐165) producing a large amount of anti‐diuretic hormone (ADH) was established from a 50‐year‐old small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patient presenting with a syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. These cells grew well in a serum‐supplemented medium and during more than 100 passages they continued producing a large amount of this hormone. This cell line will be a useful tool for studies of the biochemistry and pathology of ADH‐producing cancer.
The Lu-165 cell line exhibits distinct endocrine properties, notably the production of high levels of ADH, also known as vasopressin. This characteristic makes Lu-165 particularly interesting for research into neuroendocrine tumors and their associated hormonal dysregulations. The ability of these cells to synthesize and secrete ADH provides a valuable model for studying the mechanisms of hormone production and secretion in cancer biology. The study of Lu-165 has significant implications for understanding the pathophysiology of paraneoplastic syndromes, where tumors can cause systemic effects through hormone production, leading to various clinical manifestations such as hyponatremia due to excessive ADH secretion.
Effects of Phenytoin on Copeptin Levels in the Medium and AVP mRNA Levels in Lu-165 Cells
Phenytoin, a voltage-gated sodium channel (NaV channel) antagonist, reportedly inhibits arginine vasopressin (AVP) release from an isolated rat neurohypophysis. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction showed high levels of AVP mRNA in Lu-165 cells, but not in Lu-24, Lu-134A, or MS-1 cells (Fig. 1). Copeptin levels in the medium significantly decreased after the 48-h treatment of phenytoin at doses of 25 µg/mL, but not of 5 or 10 µg/mL (Fig. 2A). Copeptin levels in the group without phenytoin were 6.7 ± 0.5 pmol/L, which were significantly different (p < 0.01) from 3.9 ± 0.3 pmol/L in the group with phenytoin at doses of 25 µg/mL (Fig. 2A). Relative AVP mRNA levels in Lu-165 cells also decreased after the 48-h treatment of phenytoin at doses of 25 µg/mL (Fig. 2B). There was a significant difference (p < 0.01) in relative AVP mRNA levels between the group without phenytoin (1.00 ± 0.36) and the group with phenytoin at doses of 25 µg/mL (0.13 ± 0.04) (Fig. 2B).
The sodium challenge with added sodium at 10 and 20 mEq/L increased copeptin levels in the medium in an upward trend. The copeptin levels of 17.7 ± 1.2 pmol/L at added 20 mEq/L were significantly higher (p < 0.05) than those of 9.2 ± 2.3 pmol/L without sodium challenge (added 0 mEq/L). The 48-h treatment of phenytoin at a dose of 25 µg/mL significantly decreased copeptin levels in the medium under the sodium challenge with added sodium at 10 mEq/L (p < 0.01) and at 20 mEq/L (p < 0.05) (Fig. 3A). Although AVP expression levels did not change under the sodium challenges, they significantly decreased in the presence of 25 µg/mL phenytoin under the sodium challenge at added 10 mEq/L (p < 0.05) (Fig. 3B).
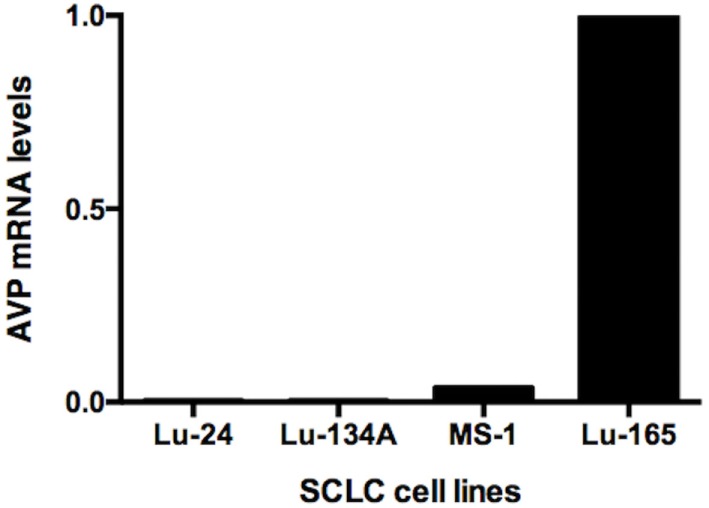 Fig. 1 Comparison of AVP mRNA levels among the four SCLC cell lines Lu-24, Lu-134A, MS-1, and Lu-165. (Ohta T, et al., 2017)
Fig. 1 Comparison of AVP mRNA levels among the four SCLC cell lines Lu-24, Lu-134A, MS-1, and Lu-165. (Ohta T, et al., 2017)
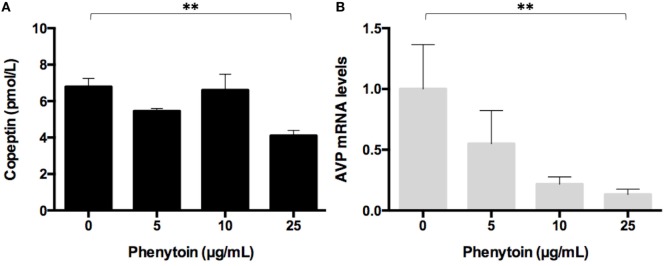 Fig. 2 Effect of three doses of phenytoin treatment (48 h) on copeptin levels in the medium (n = 4) (A) and AVP mRNA levels in Lu-165 cells (n = 5) (B). (Ohta T, et al., 2017)
Fig. 2 Effect of three doses of phenytoin treatment (48 h) on copeptin levels in the medium (n = 4) (A) and AVP mRNA levels in Lu-165 cells (n = 5) (B). (Ohta T, et al., 2017)
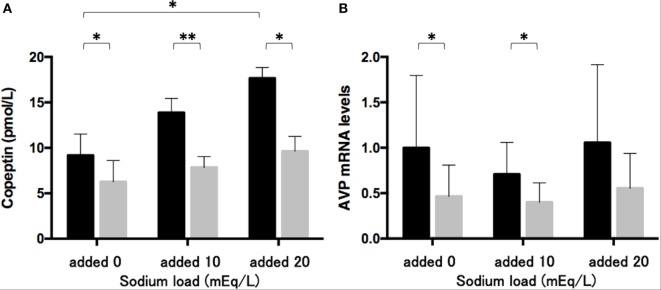 Fig. 3 Effects of phenytoin on copeptin levels in the medium (n = 4) (A) and AVP mRNA levels in Lu-165 cells under the sodium challenge (n = 6) (B). (Ohta T, et al., 2017)
Fig. 3 Effects of phenytoin on copeptin levels in the medium (n = 4) (A) and AVP mRNA levels in Lu-165 cells under the sodium challenge (n = 6) (B). (Ohta T, et al., 2017)
Two common assays for early apoptotic events are the mitochondrial membrane potential assay and the cytochrome c assay. Early in apoptosis, pores open in mitochondrial membranes, making them permeable to ions and other molecules.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Helpful
The tumor cells enable the evaluation of immune cell-tumor interactions and assess the efficacy of novel immune-based interventions.
03 Aug 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need