Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Publications
- Q & A
- Customer Review
The HuCCT1 cell line is a human cell line derived from bile duct carcinoma, specifically cholangiocarcinoma, which originates in the epithelial cells of the bile ducts. This cell line was established from the tumor of a patient, providing researchers with a vital model to study the biology and pathology of bile duct cancers, which are often aggressive and associated with poor prognoses. Cholangiocarcinoma is relatively rare compared to other types of liver cancers, making the availability of the HuCCT1 cell line particularly important for understanding its unique characteristics and developing targeted therapies.
One of the significant aspects of HuCCT1 is its ability to reflect the histopathological features of cholangiocarcinoma, including its distinctive cellular morphology and growth patterns. This cell line has been characterized to exhibit various markers associated with bile duct cancer, allowing researchers to explore the molecular mechanisms of tumor development, progression, and metastasis. The study of HuCCT1 can provide insights into the genetic alterations that drive cholangiocarcinoma and the microenvironmental factors that contribute to tumor behavior.
Researchers use this cell line to test new chemotherapeutic agents and targeted therapies, assessing their effects on cell proliferation, apoptosis, and overall tumor growth. The adaptability of HuCCT1 in various experimental settings makes it a valuable resource for identifying novel treatment strategies for cholangiocarcinoma, which is often resistant to conventional therapies.
CDH3 Knockdown Reduces HuCCT1 Cell Migration
P-cadherin (CDH3) is a cadherin superfamily member. It is frequently over-expressed in cholangiocarcinoma tissues. Previous reports showed that CDH3 affects cell migration in pancreatic cancer cells and ovarian cancer cells. CDH3 siRNA or scrambled siRNA was transfected into HuCCT1 cells, and cell migration was examined using a wound-healing assay. Fig. 1 shows that down-regulation of CDH3 decreased cell migration rate in HuCCT1, compared to control and scrambled siRNA. To confirm this data, a matrigel invasion assay was conducted, which is a gold standard cancer cell migration and invasion assay. As shown in Fig. 2, the invasion of HuCCT1 cells through the matrigel was significantly reduced when CDH3 was knock-downed. These results are consistent with previous reports and suggest that CDH3 positively affects cell migration in HuCCT1 cells.
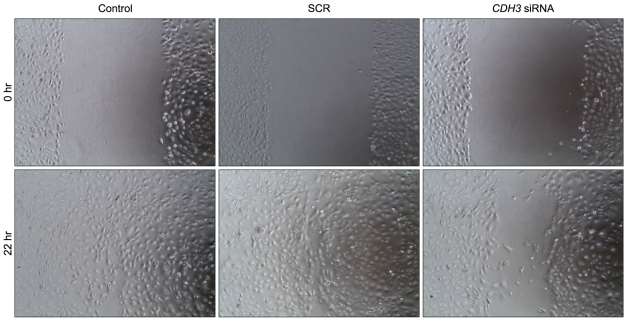 Fig. 1 Down-regulation of CDH3 in HuCCT1 cells reduced migration in wound healing assay. (Baek S, et al., 2010)
Fig. 1 Down-regulation of CDH3 in HuCCT1 cells reduced migration in wound healing assay. (Baek S, et al., 2010)
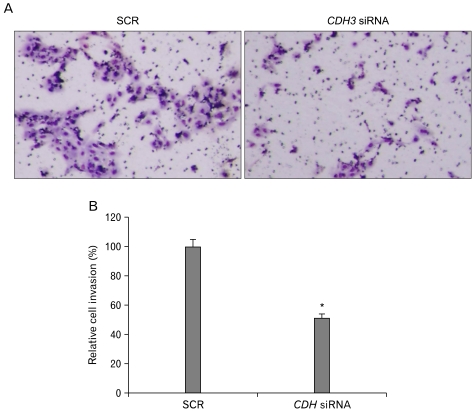 Fig. 2 Down-regulation of CDH3 in HuCCT1 cells reduced invasion in Matrigel invasion assay. (Baek S, et al., 2010)
Fig. 2 Down-regulation of CDH3 in HuCCT1 cells reduced invasion in Matrigel invasion assay. (Baek S, et al., 2010)
Network Analysis Relevant to GRB2-Mediated HuCCT1 Migration
MicroRNA miR-376c was expressed in normal intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells (HIBEpiC) but was significantly suppressed in the HuCCT1 intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) cell line. Proteomic analysis and subsequent validation assays showed that growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (GRB2) was a direct target of miR-376c. To elucidate key molecules in EGF-dependent HuCCT1 migration, in which GRB2 upregulation is caused by abnormal suppression of miR-376c, expression profiles of mRNAs affected by Pre-miR-376c and siGRB2 (siGRB2-2) were compared in EGF-treated HuCCT1 cells. Microarray analysis showed that changes in the expression of 1148 and 2733 genes were induced by Pre-miR-376c and siGRB2-2, respectively. In the microarray data, 85 genes were common to both sets (Fig. 3A). Of these, 41 genes were downregulated by both treatments, and 44 were upregulated by both treatments. A network pathway analysis was conducted, using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) to identify molecules relevant to GRB2-mediated cell migration. A network of 85 genes derived from the microarray data with c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1, also known as MAPK8)-mediated EGFR signaling was generated (Fig. 3B). Ten of the 85 genes were associated with the EGFR pathway. From the viewpoint of the cellular function of miR-376c, two down-regulated genes; i.e., interleukin-1 beta (IL1B) and matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP9), were associated primarily with several cellular-movement networks in the Ingenuity Knowledge Base. These data suggest that IL1B and MMP9 function downstream of GRB2 signaling in EGF-dependent cell migration by HuCCT1. Thus, the gene suppression of IL1B and MMP9 was evaluated in HuCCT1 cells treated with Pre-miR-376c and siGRB2-2. Pre-miR-376c significantly decreased (to 66%) expression of IL1B (Fig. 3C) and MMP9 (to 52%, Fig. 3D), compared to Pre-miR-negative controls. The use of siGRB2-2 also resulted in significant reductions in the expression of these genes, to 83% and 43% relative to controls, respectively (Fig. 3C and 3D).
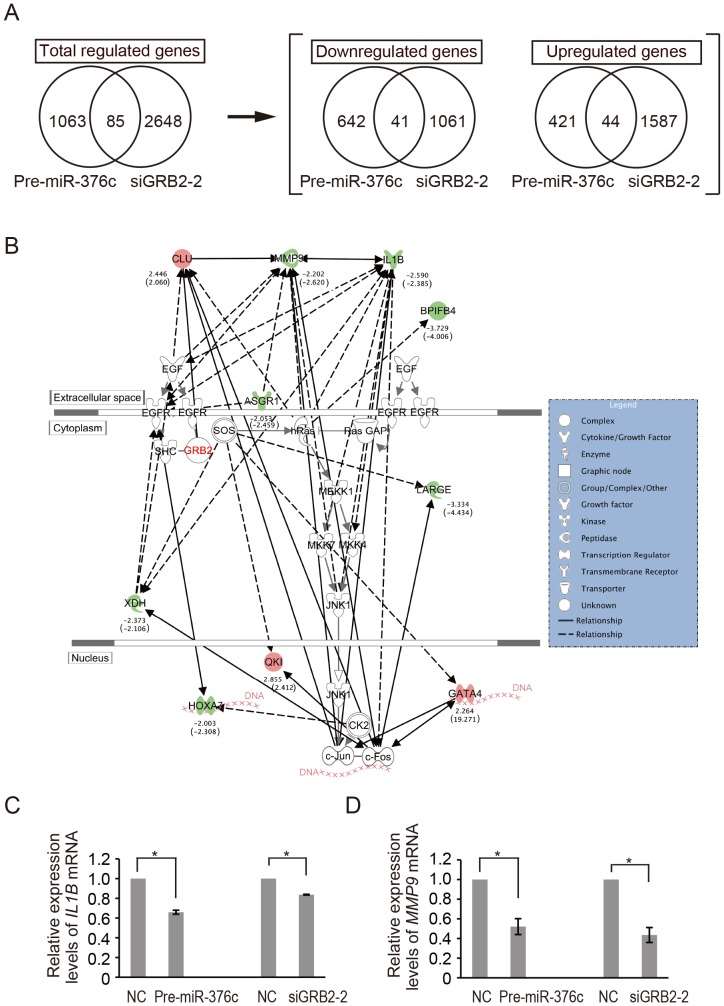 Fig. 3 (A) Venn diagrams showing the significantly different mRNA expression levels of Pre-miR-376c and siGRB2-2 transfectants of HuCCT1 relative to appropriate controls. (B) The network of the identified molecules regulated by both Pre-miR-376c and siGRB2-2 in this study were connected with EGF, EGFR, and GRB2 by IPA analysis. (C and D) Real-time PCR analysis of IL1B (C) and MMP9 (D) expression levels in EGF-treated HuCCT1 cells after transfection with Pre-miR-376c and siGRB2-2. (Iwaki J, et al., 2013)
Fig. 3 (A) Venn diagrams showing the significantly different mRNA expression levels of Pre-miR-376c and siGRB2-2 transfectants of HuCCT1 relative to appropriate controls. (B) The network of the identified molecules regulated by both Pre-miR-376c and siGRB2-2 in this study were connected with EGF, EGFR, and GRB2 by IPA analysis. (C and D) Real-time PCR analysis of IL1B (C) and MMP9 (D) expression levels in EGF-treated HuCCT1 cells after transfection with Pre-miR-376c and siGRB2-2. (Iwaki J, et al., 2013)
Inhibition of HuCCT1 Cell Invasion by Cotargeting Hic-5 and Src
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a malignant neoplasm of the bile ducts, is the second most common type of cancer in the liver, and most patients are diagnosed at a late stage with poor prognosis. It represents a heterogeneous tumor with diverse molecular alterations. As shown in the transwell Matrigel invasion assay (Fig. 4a), dasatinib (50-100 nM) suppressed HuCCT1 cell invasion by 67-80% dose-dependently. Moreover, the depletion of Hic-5 by 25 nM Hic-5siRNA suppressed HuCCT1 cell invasion by 37%. Remarkably, Hic-5 siRNA coupled with 50 nM dasatinib dramatically decreased HuCCT1 cell invasion by 82%, an effect higher than a single treatment of Hic-5 siRNA (by 35%) or 50 nM dasatinib (by 67%) and close to that of 100 nM dasatinib (by 80%) (Fig. 4a). This demonstrated an enhanced effect of knocking down Hic-5 coupled with an inhibition of Src activity on suppressing HuCCT1 cell invasion. To evaluate the possibility that the decrease of cell invasion triggered by Src inhibitor and/or Hic-5 siRNA resulted from the decrease of cell proliferation, an MTT assay in HuCCT1 cells treated by dasatinib or transfected with Hic-5 siRNA was performed. As demonstrated in Fig. 4b, HuCCT1 cell growth was slightly and constantly suppressed by dasatinib by 20% across the concentration range of 10-200 nM, whereas the depletion of Hic-5 did not affect HuCCT1 cell growth). Taken together, it can be estimated that 50-100 nM dasatinib inhibited cell invasion by 48~64%, after excluding the amount of decreased cell growth due to the dasatinib treatment.
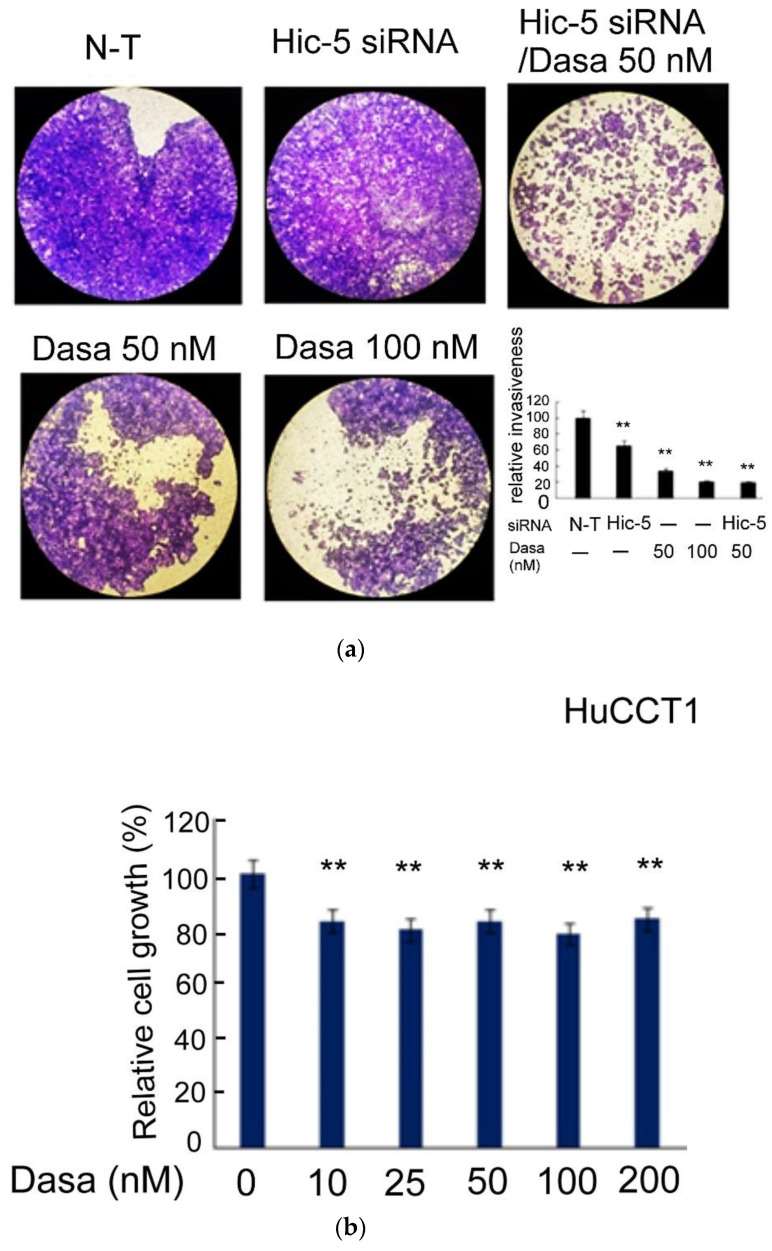 Fig. 4 Src–Hic-5 signal cascade is required for HuCCT1 cell invasion. (Wu WS, et al., 2022)
Fig. 4 Src–Hic-5 signal cascade is required for HuCCT1 cell invasion. (Wu WS, et al., 2022)
Four major liver cell types-hepatocytes (HCs), hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), Kupffer cells (KCs), and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs)-spatiotemporally cooperate to shape and maintain liver functions.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Impressed
We have been impressed with the consistent quality of the liver cancer cells from Creative Bioarray, and have found them to be an essential component of our research.
12 May 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need