- You are here: Home
- Resources
- Life Science Articles
- Immortalization of Horse-Derived Fibroblast by Cell Cycle Regulator
Resources
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Toxicology Assay
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Custom Cell & Tissue Lysate Service
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
ISH/FISH Services
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope Service
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- FISH Probe Design, Synthesis and Testing Service
-
FISH Applications
- Multicolor FISH (M-FISH) Analysis
- Chromosome Analysis of ES and iPS Cells
- RNA FISH in Plant Service
- Mouse Model and PDX Analysis (FISH)
- Cell Transplantation Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of CAR-T Cells & Oncolytic Viruses
- CAR-T/CAR-NK Target Assessment Service (ISH)
- ImmunoFISH Analysis (FISH+IHC)
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- FISH Analysis of Microorganisms
- Neoplasms FISH Analysis
- CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms (FISH)
- FISH Quality Control Services
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) FISH
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- In Situ Detection of Chemokines/Cytokines
- In Situ Detection of Virus
- Transgene Mapping (FISH)
- Transgene Mapping (Locus Amplification & Sequencing)
- Stable Cell Line Genetic Stability Testing
- Genetic Stability Testing (Locus Amplification & Sequencing + ddPCR)
- Clonality Analysis Service (FISH)
- Karyotyping (G-banded) Service
- Animal Chromosome Analysis (G-banded) Service
- I-FISH Service
- AAV Biodistribution Analysis (RNA ISH)
- Molecular Karyotyping (aCGH)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Service
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- SCE (Sister Chromatid Exchange) Analysis
- Biosample Services
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- In Vitro DMPK Services
-
In Vivo DMPK Services
- Pharmacokinetic and Toxicokinetic
- PK/PD Biomarker Analysis
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence
- Bioanalytical Package
- Metabolite Profiling and Identification
- In Vivo Toxicity Study
- Mass Balance, Excretion and Expired Air Collection
- Administration Routes and Biofluid Sampling
- Quantitative Tissue Distribution
- Target Tissue Exposure
- In Vivo Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
- Drug Toxicity Services
Immortalization of Horse-Derived Fibroblast by Cell Cycle Regulator
PeerJ Life & Environment. 2024 Jan 26; 12: e16832.
Authors: Tani T.
INTRODUCTION
Immortalized cells serve as a crucial research tool that capitalizes on their robust proliferative properties for functional investigations of an organism. Establishing an immortalized American miniature horse cell line could yield valuable insights into these animals' genetic and physiological characteristics and susceptibility to health issues. To date, immortalized small horse cells with normal karyotypes have not been established.
METHODS
- A tissue sample was obtained from an American miniature horse. Muscle fragments were obtained from a syringe injected into the hind leg muscles and primary cells were established by explant culture in high glucose DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin-amphotericin mixture and 1% Zellshield at 37°C in a CO2 incubator for 10 days.
- To immortalize American miniature horse fibroblasts, primary cells were transduced with a lentivirus composed of K4D-EGFP with or without TERT and SV40T. The efficiency of transduction was monitored via the expression of EGFP, which was confirmed 5 days after transduction.
- The established cells by K4D, K4D plus TERT, and SV40T were named as K4D, K4DT and SV40T cells respectively. To detect the introduced gene cassette, I performed genomic PCR using the genomic DNA obtained from the primary, K4D, K4DT, SV40T, and TERT cells derived from two individuals.
- Browse our recommendations
| Product/Service Types | Description |
| Immortalized Cell Lines | With years of experience in cell immortalization, Creative Bioarray has developed the most comprehensive immortalized cell lines comprising human-immortalized cells, mouse-immortalized cells, and other immortalized cells. |
| Cell Immortalization kit | To surpass senescence, Creative Bioarray has developed several Cell Immortalization Kit for immortalizing mammalian cells in culture. |
| Cell Immortalization Service | Creative Bioarray is offering cell immortalization services. Based on our experienced scientist team and elaborate technical platforms, we have been able to successfully immortalize cells from any species and any tissue with the function you need. |
RESULTS
- Under standard culture conditions, the primary cells exhibited a fibroblast-like morphology (Figs. 1A, B, and C). To confirm the cell type of the primary cells, primary antibodies against vimentin were used to stain the cells. As shown in Fig. 1D, the primary cells were found to be vimentin-positive. The primary American miniature horse fibroblasts were efficiently infected with the K4D-EGFP-expressing virus, resulting in a high percentage of green fluorescence-positive cells (Fig. 2A). The expression of TERT and SV40T was selected by multiple passages in the presence of blasticidin or puromycin. As shown in Fig. 2B, the expected size of CDK4-2A-CyclinD1 fragments in K4D and K4DT cells, TERT fragments in K4DT cells, and SV40T fragments in SV40T cells were detected. These results indicate that the target genes were successfully introduced into the transduced cells.
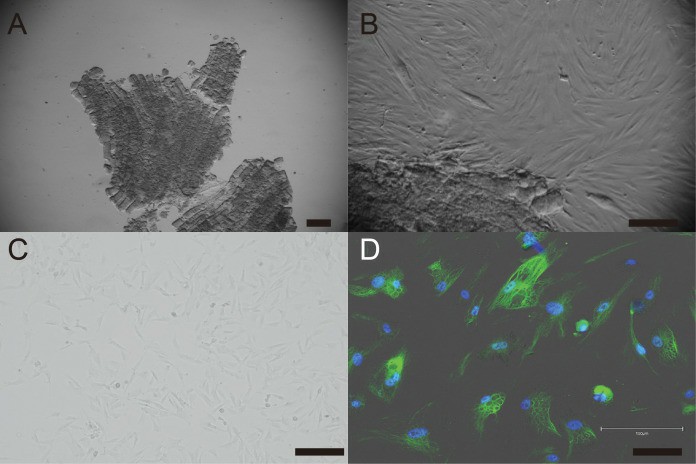 Fig. 1 Establishment of fibroblast from American miniature horse muscle fragments.
Fig. 1 Establishment of fibroblast from American miniature horse muscle fragments.
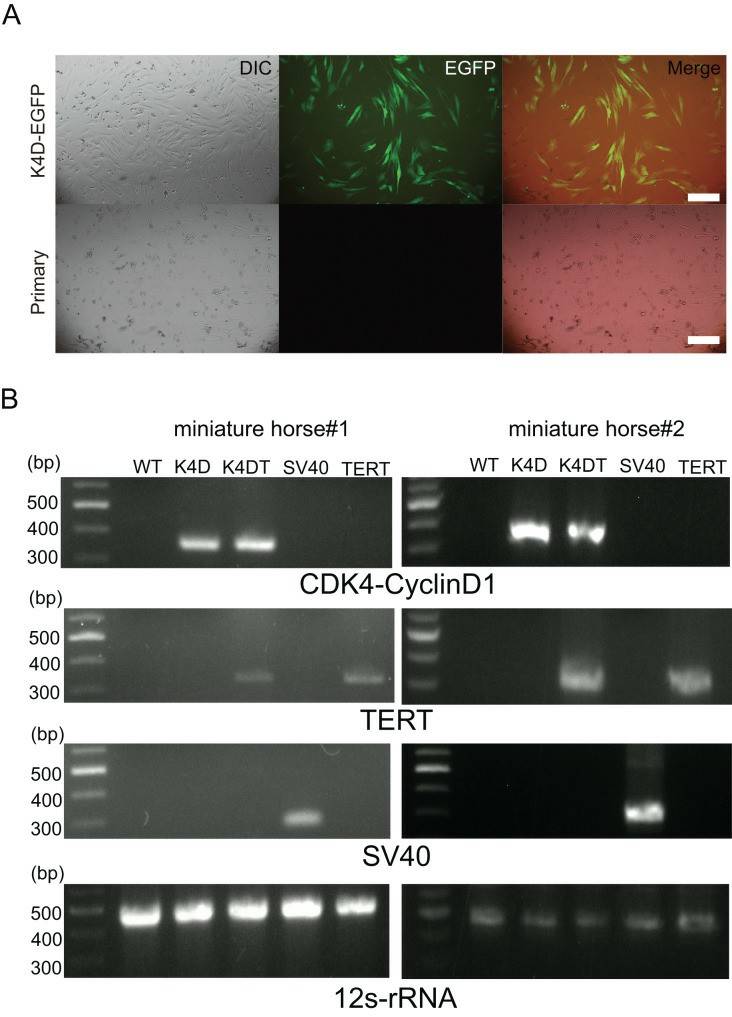 Fig. 2 Detection of K4D-EGFP expression and genomic integration of introduced genes cassette in American miniature horse-derived cell.
Fig. 2 Detection of K4D-EGFP expression and genomic integration of introduced genes cassette in American miniature horse-derived cell.
- As shown in Fig. 3A, sequential passages of primary, K4D, K4DT, SV40T, and TERT transduced cells derived from two individuals were carried out for 6-7 months. Although the primary and TERT cells of two individuals could not continue cell proliferation beyond 15 passages (25 PD value). Both K4D and SV40T cells stop cell proliferation around 65 PD and 80 PD.
- While both K4DT cells showed cell proliferation of more than 100 PD values. The doubling time at passages 10 was 32.1 h (miniature horse #1) and 34.4h (miniature horse #2) for primary when compared to K4D, K4DT, and SV40T cells significantly (Fig. 3B). Additionally, the BrdU incorporation rate for both primary cells was significantly lower when compared to K4D, K4DT, SV40T and TERT cells (Fig. 3C). To assess the degree of cellular senescence, SA-β-gal staining was performed at passage 15. Both primary and TERT cells almost stopped proliferating and stained positive for SA-β-gal. However, K4D, K4DT, and SV40T cells did not stain for SA-β-gal (Fig. 3D). These data showed that K4D, K4DT, and SV40T expressing cells from two individuals dramatically prolonged the proliferation up to 65 PD values of American miniature horse-derived cells. While both K4DT cells did not stop proliferation over 100 PD.
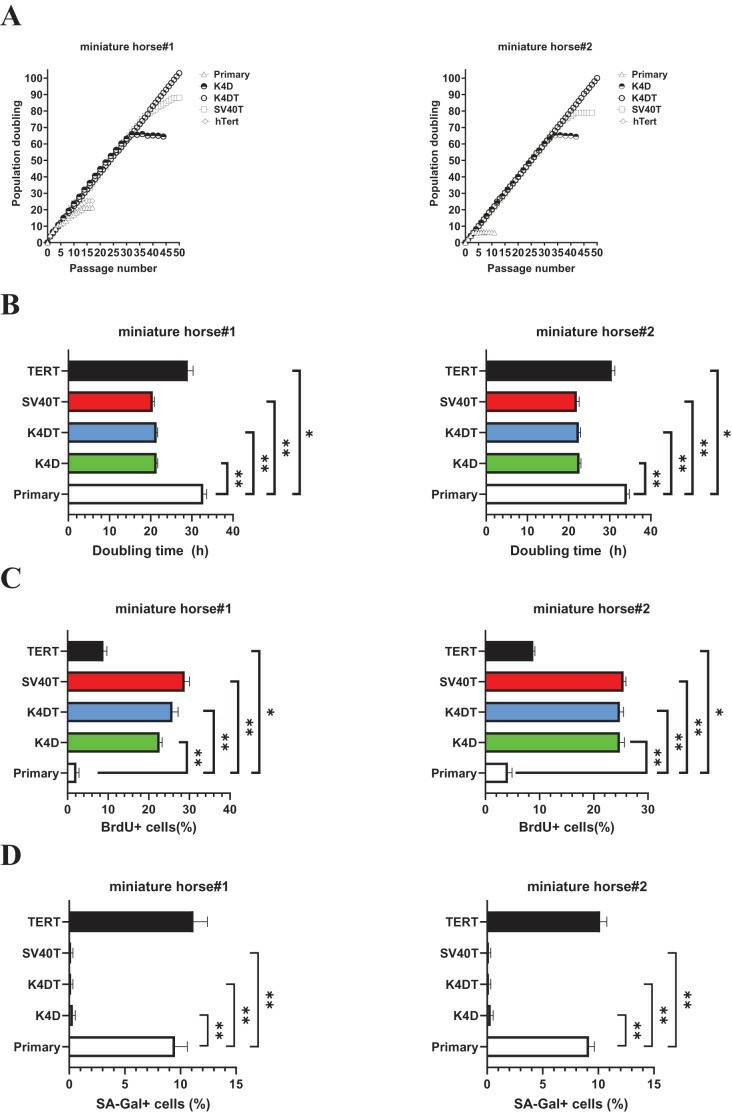 Fig. 3 Biological analysis of proliferation in American miniature horse-derived cells.
Fig. 3 Biological analysis of proliferation in American miniature horse-derived cells.
SUMMARY
In this study, primary and immortalized fibroblast cell lines were successfully established through the combined expression of human-derived mutant cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4R24C), cyclin D1, and telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), although CDK4R24C and cyclin D1, SV40T and TERT did not result in successful immortalization.
RELATED PRODUCTS & SERVICES
Reference
- Tani T. (2024). "Immortalization of American miniature horse-derived fibroblast by cell cycle regulator with normal karyotype." PeerJ. 12: e16832.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.