Calothrixin B Derivatives Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in HEL Cells
Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy. 2024 Feb; 171: 116179.
Authors: Wang B, Wang M, Li K, Wang C, Liu X, Rao Q, Song J, Hang Y, Liu S, Wen M, Huang L, Li Y.
INTRODUCTION
Acute erythroleukemia (AEL) is acute myeloid leukemia characterized by malignant erythroid proliferation. AEL has a low survival rate, which has seriously threatened the health of older adults. Calothrixin B is a carbazole alkaloid isolated from the cyanobacteria Calothrix and exhibits anti-cancer activity. To discover more potential anti-erythroleukemia compounds, we used calothrixin B as the structural skeleton to synthesize a series of new compounds.
METHODS
- To determine the effects of calothrixin B derivatives on the viability of HEL, K562, Jurkat, and HepG2 cells, we treated these cells with the compounds at different concentrations (1-20 μM) for 48 h. Cytotoxicity (IC50) of various concentrations calothrixin B derivatives against indicated cancer cells and HL7702 for 48 h using the MTT Assay.
- To investigate whether the H-107 inhibiting HEL cell growth is caused by apoptosis, we assessed early apoptosis (annexin-V positivity) and late apoptosis (annexin-V/PI positivity) by flow cytometry. To explore the mechanism of apoptosis, we used JC-1 staining to detect the effect of H-107 on mitochondrial membrane potential.
- To elucidate the effect of H-107 on the cell cycle of HEL, we treated HEL cells with different concentrations of H-107. To clarify the role of H-107 in the cell cycle regulation mechanism further, we analyzed proteins related to the cell cycle by Western blot.
- Browse our recommendations
| Product/Service Types | Description |
| Cell Proliferation Assay Services | Creative Bioarray provides cell proliferation assay services for our customers. We are capable of performing different cell proliferation assays based on several concepts, which are measuring the rate of DNA replication, analysis of metabolic activity, cell surface antigen recognitions, detecting proliferation markers, ATP measurement, measures of membrane integrity, and so on. |
| Cell Apoptosis Assays | Creative Bioarray offers a wide array of apoptosis assays for measuring multiple components on a choice of assay platforms to accelerate our customers' research, including but not limited to Annexin V binding assays by flow cytometry analysis, caspase activity assays, mitochondrial membrane potential assays. |
| Cell Apoptosis Assay Kit | Creative Bioarray offers a wide range of assay kits for studying apoptosis including Annexin V apoptosis kit, caspase assay kit, DNA fragmentation assay kit, and mitochondrial apoptosis detection kit. |
| Cell Cycle Assays | Creative Bioarray provides cell cycle analysis services for all of our customers, we use flow cytometry to measure cellular DNA content. Different dyes can be chosen to perform the assays, including propidium iodide (PI), BrdU, 7-amino actinomycin-D (7-AAD), Hoechst 33342 and 33258, and 4'6'-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), based on the customer's applications or requirements. |
| Cell Cycle Analysis Kit | Creative Bioarray's cell cycle analysis kit provides a quick and easy method to detect the number of cells in a cell population, which are at a specific stage of the cell cycle. |
RESULTS
- H-107 has the most potent inhibitory effect on HEL cells, and the IC50 was 3.63 ± 0.33 μM. H-107 inhibited HEL cell proliferation in a significant time and dose-dependent manner. The morphology of HEL cells treated with H-107 gradually shrank and fragmented with the time and concentrations increasing.
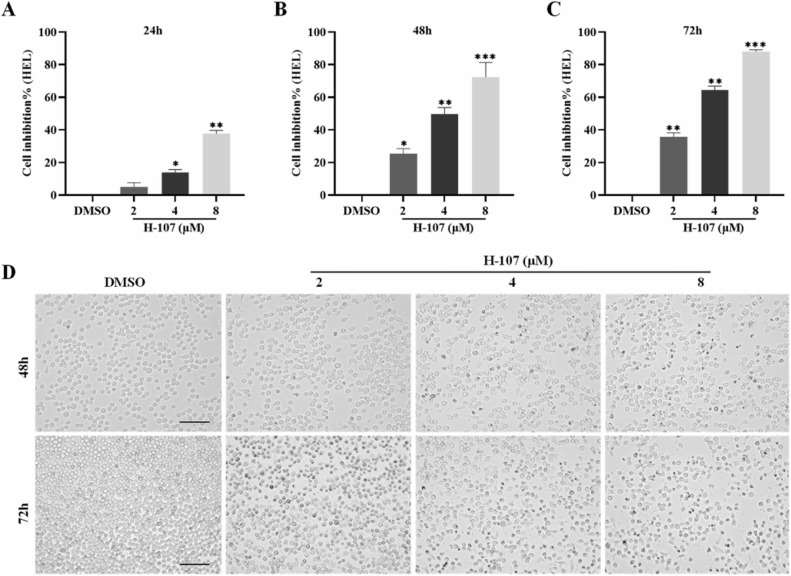 Fig. 1 H-107 inhibited HEL cell proliferation.
Fig. 1 H-107 inhibited HEL cell proliferation.
- The apoptosis rate of HEL cells treated with H-107 (8 μM) for 48 h was 24.58 ± 0.32%, and the apoptosis rate increased to 32.11 ± 0.68% for 72 h. Furthermore, H-107 induced HEL cell apoptosis in a significant time and dose-dependent. The Hoechst 33258 staining indicated that damaged DNA was detected in HEL cells treated with H-107.
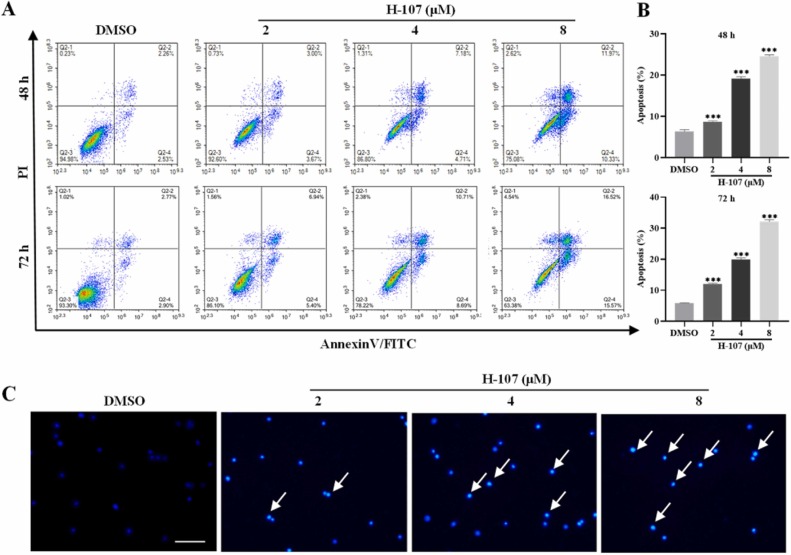 Fig. 2 H-107 induced apoptosis in HEL cells.
Fig. 2 H-107 induced apoptosis in HEL cells.
- The number of JC-1 monomeric cells (green fluorescence) gradually increased, and the red fluorescence gradually decreased with concentration increasing. In addition, the relative value of the JC-1 monomer increased significantly with H-107 concentration accumulation by flow cytometry analysis. Furthermore, cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9, and cleaved PARP protein increased 11-fold, 9-fold, and 3-fold, respectively, in the HEL cells treated with 8 μΜ H-107. However, the anti-apoptosis Bcl-2 level decreased significantly. The results confirmed that H-107 induced apoptosis by impairing mitochondria and activating the caspase cascade.
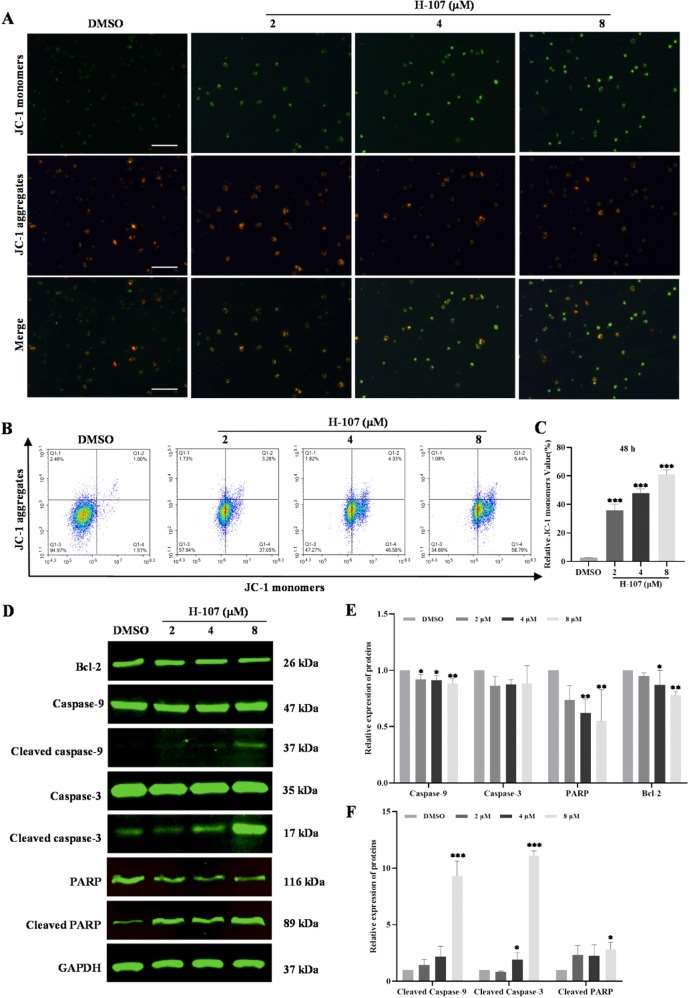 Fig. 3 The damage effect of H-107 on mitochondria of HEL cells.
Fig. 3 The damage effect of H-107 on mitochondria of HEL cells.
- The proportion of G1 phase cells increased from 48.71 ± 0.03% to 73.39 ± 1.91%, indicating that HEL cells arrested in the G0/G1 phase. p53 and p21 protein levels increased significantly, while c-Myc and CDK1 protein levels decreased significantly.
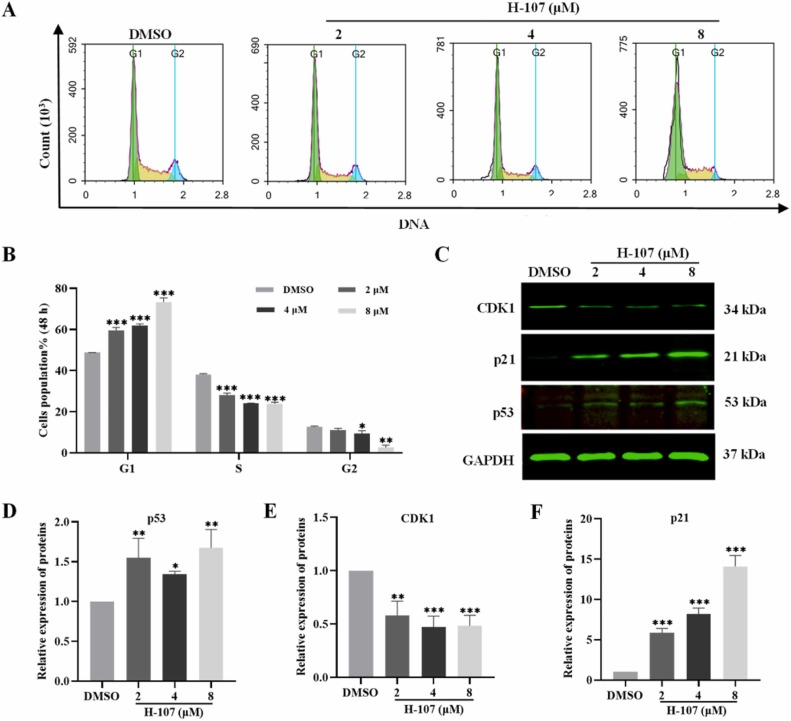 Fig. 4 Effect of H-107 on cell cycle progression of HEL cells.
Fig. 4 Effect of H-107 on cell cycle progression of HEL cells.
SUMMARY
Among the Calothrixin B derivatives, H-107 had the best activity against leukemic cell lines. H-107 significantly inhibited the proliferation of HEL cells with an IC50 value of 3.63 ± 0.33 μM. H-107 induced apoptosis of HEL cells by damaging mitochondria and activating the caspase cascade and arrested HEL cells in the G0/G1 phase. Furthermore, H-107 downregulated the protein levels Ras, p-Raf, p-MEK, p-ERK, and c-Myc. Pretreatment with ERK inhibitor (U0126) increased H-107-induced apoptosis. Thus, H-107 inhibited the proliferation of HEL cells by the ERK /Ras/Raf/MEK signal pathways.
RELATED PRODUCTS & SERVICES
Reference
- Wang B, et al. (2024). "Calothrixin B derivatives induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest on HEL cells through the ERK/Ras/Raf/MEK pathway." Biomed Pharmacother. 171: 116179.