Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
U-2932
Cat.No.: CSC-C0624
Species: Human
Source: B cell lymphoma
Morphology: small round cells growing singly and in clusters in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD3 -, CD10 +, CD13 -, CD19 +, CD20 +, CD37 +, CD38 +, cyCD79a +, CD80 +, CD138 +, HLA-DR +, sm/cyIgG -, sm/cyIgM +, sm/cykappa +, sm/cylambda -
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV
The U-2932 cell line was established in 1996 from the ascites (abdominal fluid) of a 29-year-old woman with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). The U-2932 cells were described as overexpressing the BCL2, BCL6, and p53 genes. This genetic profile assigned the cell line to the activated B-cell (ABC)-like subtype of DLBCL. The ABC subtype is one of the two main molecular classifications of DLBCL, the other being the germinal center B-cell (GCB) subtype. Patients with the ABC subtype generally have a poorer prognosis compared to those with the GCB subtype.
The establishment of the U-2932 cell line provides a valuable model system for studying the biology and treatment of this aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which arises from mature B cells. This cell line has been widely used in lymphoma research to elucidate the molecular mechanisms driving disease pathogenesis and to evaluate novel therapeutic approaches.
In Vitro Efficacy of Tirabrutinib and Downstream Signaling Analysis in U-2932 Cells
Tirabrutinib is a highly selective Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor used to treat hematological malignancies. In vitro analyses of the anti-tumor mechanisms were conducted in ABC-DLBCL cells followed by phosphoproteomic and transcriptomic analyses.
Tirabrutinib was shown to inhibit the growth of U-2932 cells (Fig. 1A). For U-2932 cells, the IC50 was 27.6 nM, and the maximum growth inhibition rate was 30.8% at 100 nM. Tirabrutinib inhibited BTK autophosphorylation at Tyr-223 in both cells in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 1B), with the IC50 values (12.0 nM) being comparable to the IC50 for growth inhibition. Thus, proliferation appears to be inhibited by tirabrutinib via inhibition of BTK phosphorylation.
Next, a phosphoproteomic analysis was conducted to investigate phosphoregulation induced by 1-h treatment with tirabrutinib in U-2932 cells, which would result in anti-tumor efficacy. In U-2932 cells, more than 5,563 distinct phosphoproteins and 11,493 distinct phosphorylation sites (class I phosphosites) were identified with high confidence (P ≥ 0.75). The overall abundances of Ser(P), Thr(P), and Tyr(P) were 84.6%, 14.8%, and 0.7%, respectively. Only 30 phosphorylation sites from 28 distinct phosphoproteins were suppressed (0.3% of all quantified sites) and four phosphorylation sites from four phosphoproteins were induced (0.04% of all quantified sites). Regarding the downregulated phosphorylation sites, five site-specific phosphorylation events that underwent significant regulation in U-2932 cell lines were identified (Table 1).
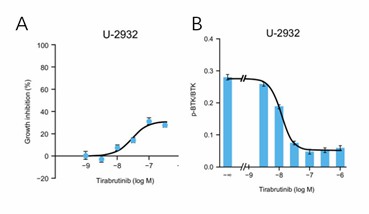 Fig. 1 Antiproliferative activity (A) and BTK autophosphorylation inhibitory effects (B) of tirabrutinib. (Kozaki R, et al., 2023)
Fig. 1 Antiproliferative activity (A) and BTK autophosphorylation inhibitory effects (B) of tirabrutinib. (Kozaki R, et al., 2023)
Table 1. Significantly downregulated phosphosites in U-2932 cells. (Kozaki R, et al., 2023)
| Protein | Gene | Position | Sequence window | Tirabrutinib/ctrl. U-2932 rep. 1 | Tirabrutinib/ctrl. U-2932 rep. 2 |
| Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase B | ITPKB | S43 | PRRAVLSPGSVFS | 0.57 | 0.58 |
| Golgi vesicular membrane-trafficking protein p18 | BET1 | S50 | TAIKSLSIEIGHE | 0.57 | 0.61 |
| Vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B/C | VAPB | S158 | IVSKSLSSSLDDT | 0.66 | 0.60 |
| Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 | MAPK1 | Y187 | TGFLTEYVATRWY | 0.23 | 0.41 |
| Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | ADRBK1 | S685 | PLVQRGSANGL | 0.61 | 0.64 |
Activity of miR-1244, miR-193b-5p, and miR-1231 on U-2932 Cells In Vitro
Around 30-40% of patients with DLBCL suffer an early relapse after standard chemotherapy, but today no prediction of whether a patient belongs to this group is possible. MicroRNA is small nucleotide sequences that regulate cellular functions via post-transcriptional modification of gene expression and can serve as prognostic biomarkers.
Reverse transfection of U-2932 cells with reagent achieved a high percentage of 89.6 ± 0.7% of transfected cells after 48 h. The miRNA negative control (100 nM) (miR control (−)) did not change the viability of U-2932 cells for non-transfected (NT) cells after 48 h of transfection, discarding an adverse effect of the transfection method itself on cell viability (Fig. 2). Transfection of miR-1244, miR-193b-5p or miR-1231 (100 nM) mimics did not significantly change the viability of U-2932 (Fig. 2A) for miR control (−)-transfected cells. However, the inhibition of these three miRNAs of endogenous origin with their respective inhibitors significantly decreased U-2932 cell viability after 48 h by 24.1 ± 5.7%, 28.9 ± 6.5%, and 30.9 ± 3.3%, respectively (Fig. 2B), supporting the idea that these miRNAs are involved in the survival of these tumor cells.
The effect of miR-1244, miR-193b-5p, or miR-1231 on the response of DLBCL cells to CHOP treatment was then evaluated. Transfection of U-2932 with miR control (−) did not change cell sensitivity to CHOP and reduced viability dose-dependently with an IC50 of 1.45 μg/mL in non-transfected and miR control (−)-transfected cells. Transfection of U-2932 cells with miR-1244 or miR-193b-5p mimics increased cell viability in the presence of vehicle (1% DMSO) by 27.4 ± 6.4% and 27.9 ± 8.4% (Fig. 3), respectively. Even more importantly, these miRNAs completely blocked the reduction of cell viability by CHOP (0.3 μg/mL) after 48 h of treatment. On the contrary, the miR-1231 mimic did not significantly change the inhibitory effect of CHOP on U-2932 cell viability at any of the concentrations studied (0.3, 1, and 3 μg/mL).
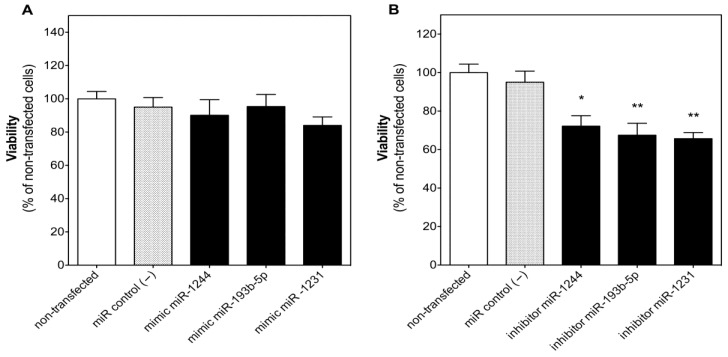 Fig. 2 Inhibition, but not expression, of miR-1244, miR-193b-5p, or miR-1231 reduced cell viability in U-2932 cells. (Bento L, et al., 2022)
Fig. 2 Inhibition, but not expression, of miR-1244, miR-193b-5p, or miR-1231 reduced cell viability in U-2932 cells. (Bento L, et al., 2022)
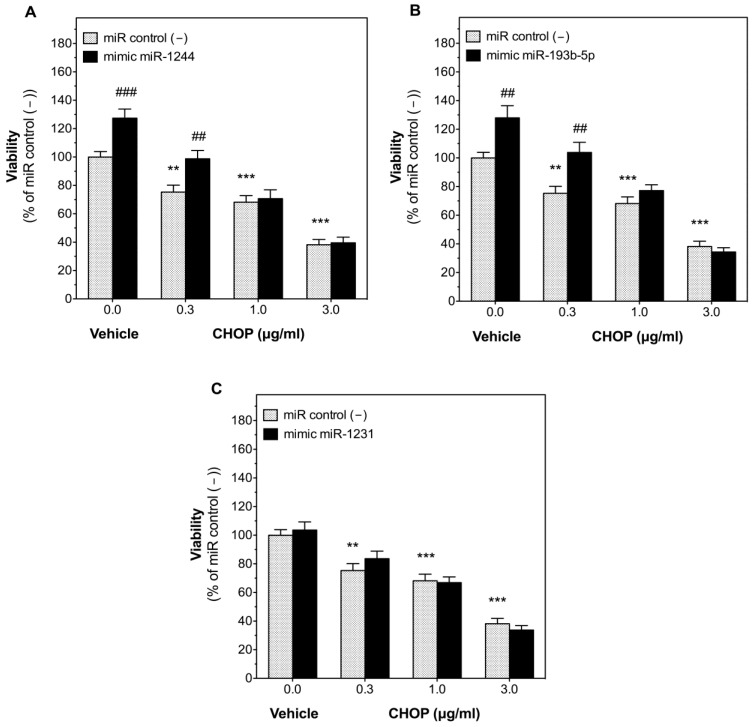 Fig. 3 Expression of miR-1244 and miR-193b-5p, but not miR-1231, blocked the antitumoral effect of CHOP in U-2932 cells. (Bento L, et al., 2022)
Fig. 3 Expression of miR-1244 and miR-193b-5p, but not miR-1231, blocked the antitumoral effect of CHOP in U-2932 cells. (Bento L, et al., 2022)
The complete process for STR typing includes sample collection, DNA extraction, DNA quantitation, PCR amplification of multiple STR loci, STR allele separation and sizing, STR typing and profile interpretation, and a report of the statistical significance of a match (if observed).
The U-2932 cells were described as overexpressing the BCL2, BCL6, and p53 genes, which assigned the cell line to the ABC-like subtype of DLBCL.
Patients with the ABC subtype of DLBCL generally have a poorer prognosis compared to those with the GCB subtype.
The establishment of the U-2932 cell line provides a valuable model system for studying the biology and treatment of this aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which arises from mature B cells.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 3 Scientist has reviewed this product
High reproducibility
The high reproducibility of Creative Bioarray's products ensures reliable experimental results.
16 July 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Detailed documentation
I appreciate the detailed documentation provided with the cells, which has been helpful in understanding their characteristics and background.
01 Feb 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Well-characterized U-2932 cells
I am confident in the reproducibility of my results thanks to the reliable and well-characterized U-2932 cells I have obtained from this provider.
14 Nov 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need