SUP-T1
Cat.No.: CSC-C0297
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Pleural Effusion
Morphology: single, round cells in suspension
Culture Properties: Suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
CSF1PO: 10,11
D13S317: 11,12
D16S539: 9,11,12
D5S818: 11,12
D7S820: 11
THO1: 9.3
TPOX: 9
vWA: 16, 18
SUP-T1 is the cell line for human T-lymphoma that is generated from cancerous pleural effusion in an 8-year-old child with T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma. This cell line is predominantly lymphoblastic and carries a spectrum of T-cell markers on its surface: CD1a, CD3, CD4, Cd5, Cd7, Cd8 and CD38. Expression of these T-cell markers on SUP-T1 cells is not only a tool for phenotypic identification, but also important for multiple immune responses. CD3, for example, belongs to the T-cell receptor complex, and is involved in T-cell activation and signalling; CD4 and CD8 recognise helper T-cells and cytotoxic T-cells, respectively; and CD38 mediates cell adhesion and signalling, contributing to the development and function of T-cells.
SUP-T1 cells are widely used in immunology, hematology and oncology. Through the development and differentiation of SUP-T1 cells, researchers can better understand how T-cells develop, mature and function within the immune system. Furthermore, this cell line provides a valuable model to investigate the molecular and genetic pathways of T-cell lymphomas to better understand how the disease develops and which drugs can be used. When it comes to developing new anti-cancer drugs, specifically for treatments of T-cell lymphomas, SUP-T1 cells are key to the ability to measure drug activity and optimise therapy regimens.
MHA Enhances Apoptosis and Disrupts Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) of SUP-T1
Clinacanthus nutans has potential anti-cancer properties, with its chloroform extract showing significant cytotoxicity against leukemia K562 and lymphoma Raji cells. However, the specific anti-cancer mechanisms and chemical characteristics of Clinacanthus nutans remain to be fully explored. Lu's team investigated the anti-cancer effects and mechanisms of its acetone extract (MHA) in human leukemia MOLT-4 and lymphoma SUP-T1 cells. Data on cell viability indicate that MHA effectively inhibits SUP-T1 lymphoma cells (Fig. 1A). MHA treatment induced morphological changes and DNA condensation (Fig. 1B). Cell cycle arrest, one of the hallmarks of apoptosis, was assessed by flow cytometry to determine whether MHA treatment causes cell cycle arrest in SUP-T1 cells. The results showed that MHA treatment increased sub-G1 and G2/M cell numbers, indicating that MHA treatment kills SUP-T1 lymphoma cells and does not arrest G2/M phase cell cycle (Fig. 1C and D). The mitochondrial membrane potential was measured using the fluorescent marker JC-1 that resides on the mitochondrial membrane and (Fig. 5B, mitochondrial membrane potential dropped drastically in SUP-T1 cells upon MHA treatment (Fig. 2A and B). This loss of mitochondrial membrane potential could lead to mitochondrial-based apoptotic death. As a result, flow cytometry revealed the presence of annexin V-FITC protein (a calcium-binding protein on the cell membrane) and showed that MHA treatment increases the expression of annexin V protein in SUP-T1 lymphoma cells (Fig. 2C and D). These findings demonstrate that MHA increases apoptosis and disrupts SUP-T1 mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP).
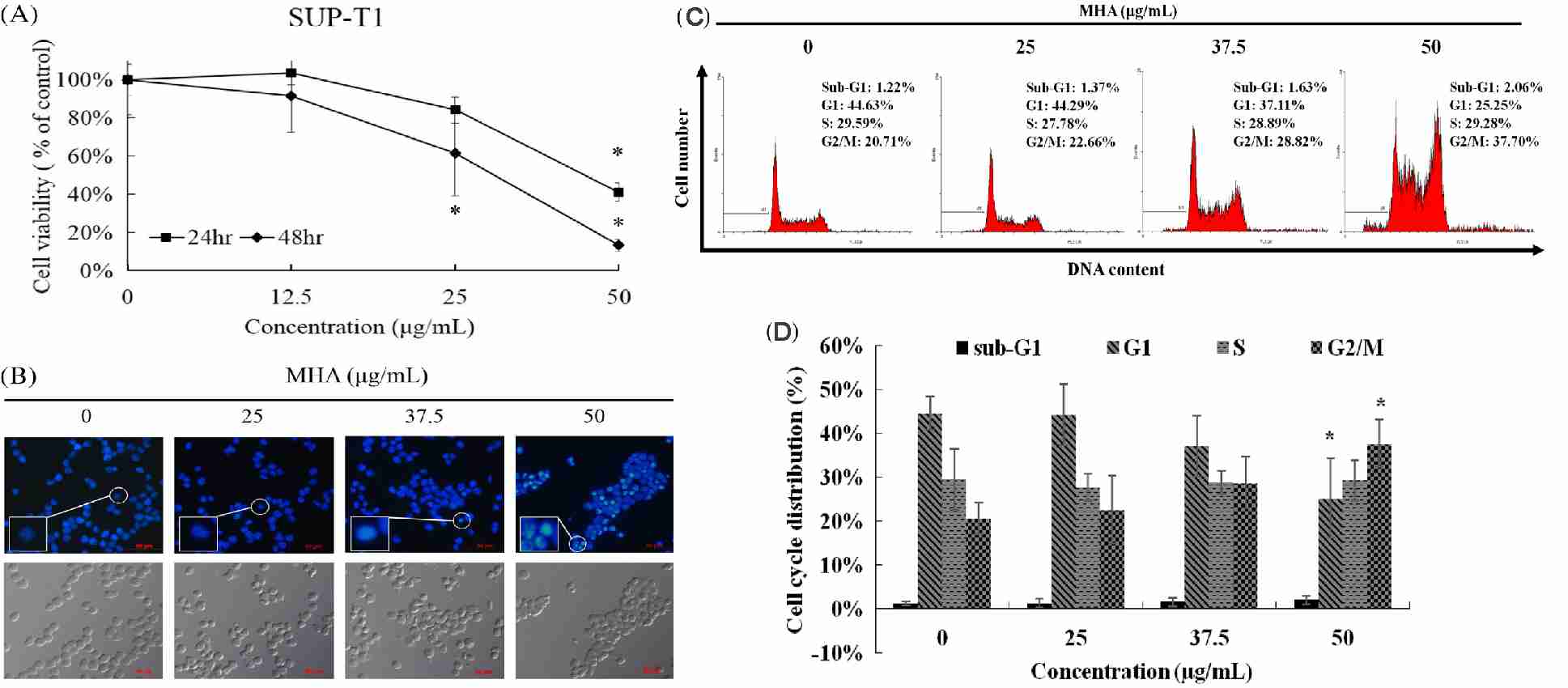 Fig. 1. MHA treatment inhibited SUP-T1 cell proliferation (Lu M C., Li T Y., et al., 2018).
Fig. 1. MHA treatment inhibited SUP-T1 cell proliferation (Lu M C., Li T Y., et al., 2018).
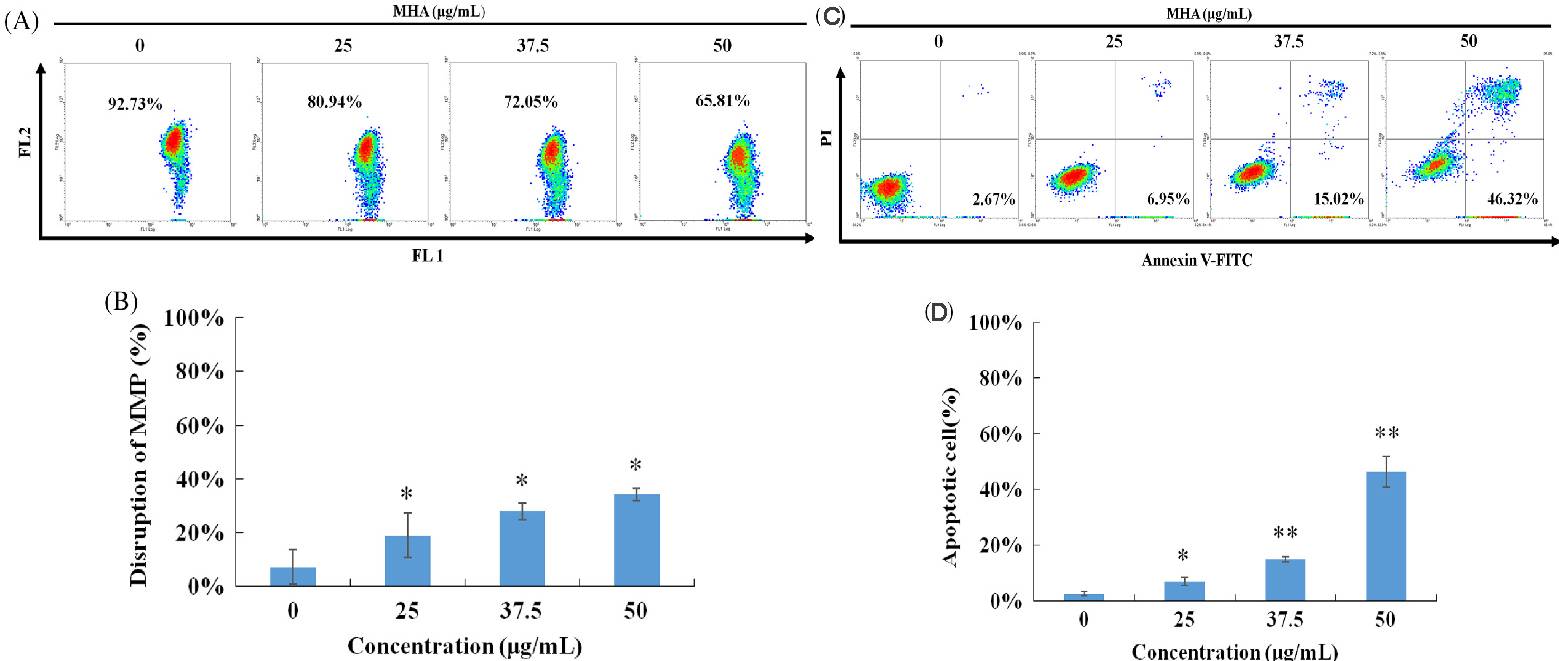 Fig. 2. MHA treatment resulted in disruption of the mitochondrial membrane potential in SUP-T1 (Lu M C., Li T Y., et al., 2018).
Fig. 2. MHA treatment resulted in disruption of the mitochondrial membrane potential in SUP-T1 (Lu M C., Li T Y., et al., 2018).
Assessment of the Effects of AV25R on Proliferation Activity in Four Cancer Cell Lines
Thiazolopyridines are a very important small-molecule group that has several biological functions including anti-tuberculosis, antimicrobial, antiviral, and anticancer. Ladwing tested the bioactivity and anticancer activity of a new thiazolopyridine derivative, AV25R, in lymphoma (SUP-T1, SU-DHL-4), and B-acute leukemia cell lines (RS4;11, SEM). They evaluated the early biological response of four human tumour cell lines by comparing their metabolism and growth at 48 and 72 hours after administration of AV25R. These indicated that the AV25R treatment effectively inhibited cell proliferation in B-ALL RS4;11 cells at all tested concentrations after 48 hours, with percentages dropping to 60.53%5.32% at 1 M, 34.34% 18.27% at 5 M, and 15.91% 6.26% at 10 M (Fig. 3). The B-ALL cell line SEM showed a slight, but significant, reduction in cell count. For the lymphoma cell line SUP-T1, the cell count decreased significantly in 5 µM and 10 µM, whereas the cell count of SU-DHL-4 just decreased significantly for the highest concentration. After 48 hours, they calculated the IC50 values for AV25R in each cell line. SEM had the highest IC50 at 20.98 µM. SUP-T1 and SU-DHL-4 had similar IC50 values of 12.17 µM and 12.72 µM. The RS4;11 cell line had the lowest IC50 at 1.95 µM, which is significantly lower than both the lymphoma cell lines and the B-ALL cell line SEM.
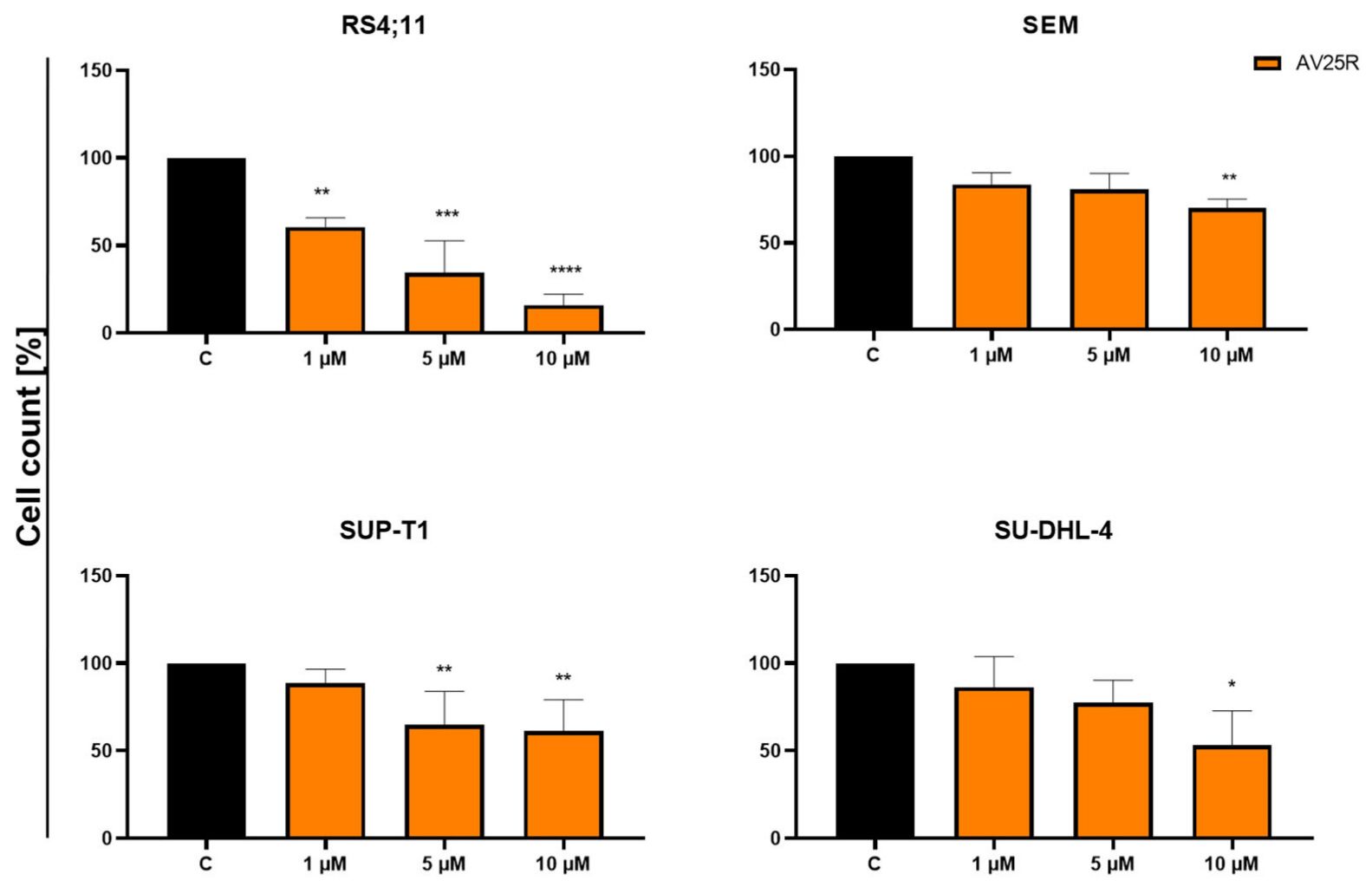 Fig. 3. Results of cell count after 48 h of concentration-dependent AV25R exposure on B-ALL cell lines RS4;11 and SEM, as well as lymphoma cell lines SUP-T1 and SU-DHL-4 (Ladwig, A., Gupta, S., et al., 2023).
Fig. 3. Results of cell count after 48 h of concentration-dependent AV25R exposure on B-ALL cell lines RS4;11 and SEM, as well as lymphoma cell lines SUP-T1 and SU-DHL-4 (Ladwig, A., Gupta, S., et al., 2023).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells