Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY

RPMI-1788
Cat.No.: CSC-C8930H
Species: Homo sapiens ,human
Source: blood, peripheral; leukocyte; B lymphocyte
Morphology: lymphoblast
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
The RPMI-1788 cell line, established in the 1970s, is a human B-lymphoblastoid cell line derived from peripheral blood and transformed by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). As an immortalized B-cell model, it exhibits characteristics typical of activated B-lymphocytes, including expression of surface markers like CD19 and CD20, secretion of immunoglobulins, and robust growth in suspension culture using media such as RPMI-1640. Moreover, RPMI-1788 cells express CD80 and CD86, which are thought to contribute to their stimulatory capacity for T cells.
Its EBV transformation enables sustained proliferation, making it a valuable tool for studying B-cell biology, viral latency, and oncogenic pathways. Recent research leverages RPMI-1788's immunological properties to investigate B-cell receptor signaling, cytokine networks, and interactions in autoimmune diseases and lymphomas. Its utility in high-throughput drug screening is enhanced by its scalability, particularly in evaluating inhibitors targeting B-cell-specific proteins or EBV-related oncogenes. Additionally, the cell line aids in developing immunotherapies, such as optimizing chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies and monoclonal antibodies, by serving as a target for cytotoxicity assays. RPMI-1788's combination of genetic stability, antigen-presenting capacity, and responsiveness to experimental manipulation underscores its ongoing relevance in advancing translational immunology and oncology research.
BCP Reduces Cancer Cells Viability
Cannabinoid type 2 receptors (CB2Rs) belong to the G protein-coupled receptor family and are mainly expressed in hematopoietic and immune cells, such as B-cells, T-cells, and macrophages; thus, CB2R activation might be useful for treating cancers affecting plasma cells, such as multiple myeloma (MM). Previous studies have shown that CB2R stimulation may have anti-proliferative effects; therefore, the purpose of the present study was to explore the antitumor effect of beta-caryophyllene (BCP), a CB2R agonist, in an in vitro model of MM.
Cell viability was evaluated by incubating MM.1S, MM.1R, and RPMI 1788 cell lines with increasing concentrations of BCP, ranging from 6.25 μM to 200 μM. The results of the MTT assay showed that BCP had a selective antiproliferative effect on MM cells (Fig. 1).
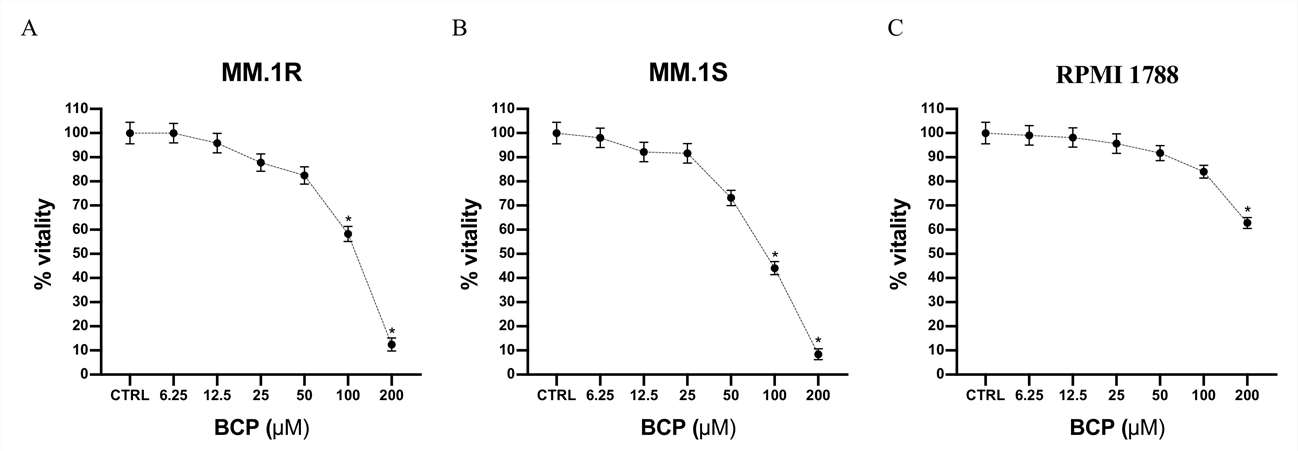 Fig. 1. Cell viability evaluated in MM.1R, MM.1S, and RPMI 1788 cell lines (Mannino, Federica, et al. 2021).
Fig. 1. Cell viability evaluated in MM.1R, MM.1S, and RPMI 1788 cell lines (Mannino, Federica, et al. 2021).
In addition, a trypan blue assay was performed to confirm the selective antiproliferative effect of BCP on the MM.1S and MM.1R cell lines. The RPMI 1788 cell line, used as normal cells, was treated with BCP at concentrations of 50 and 100 μM for 24 h, thus demonstrating that BCP did not affect the proliferation of normal cells (Fig. 2) and confirming the MTT results and BCP-selective effect in the MM cell lines.
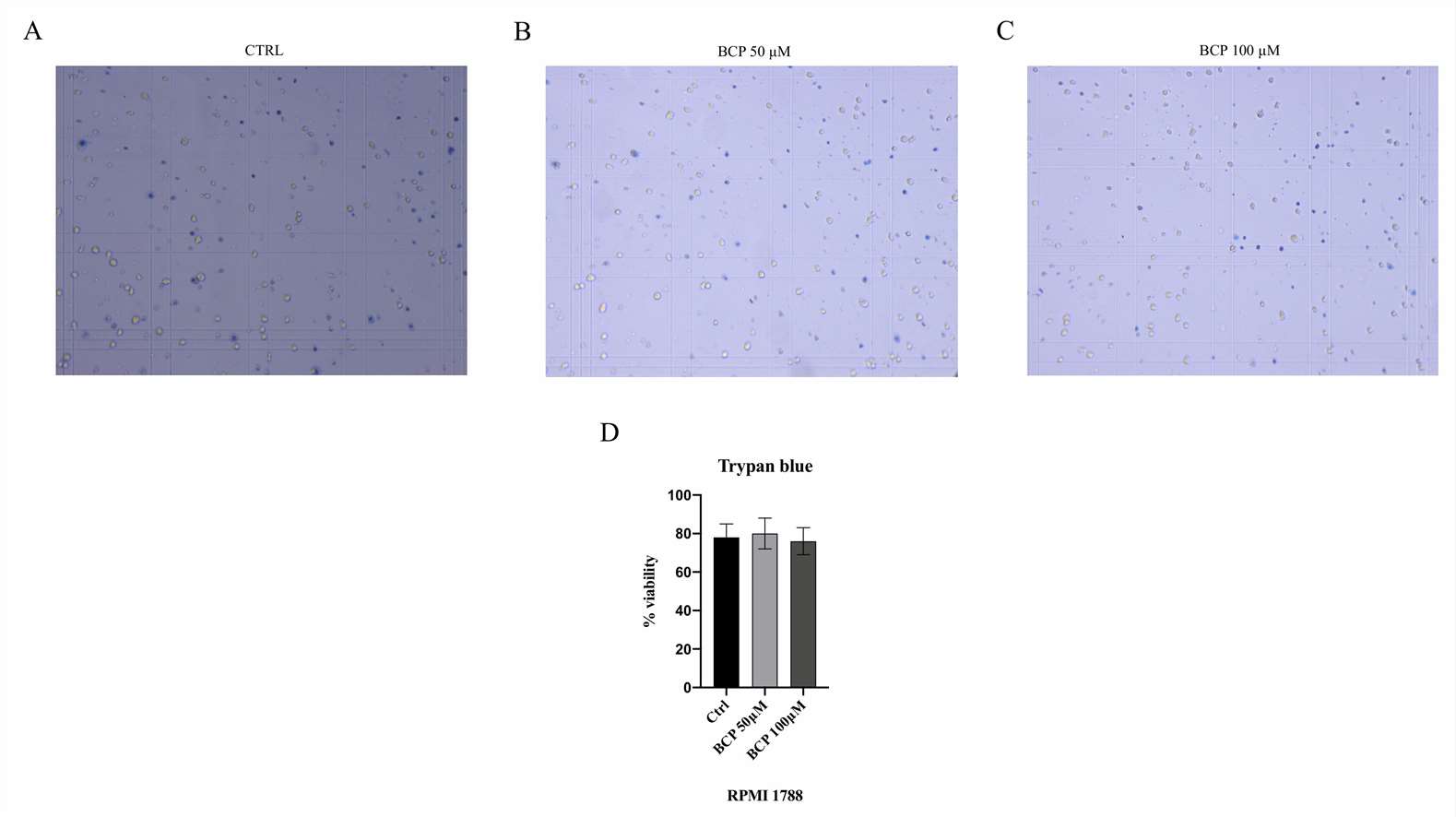 Fig. 2. The figure represents the trypan blue staining in RPMI 1788 cells treated with BCP (Mannino, Federica, et al. 2021).
Fig. 2. The figure represents the trypan blue staining in RPMI 1788 cells treated with BCP (Mannino, Federica, et al. 2021).
Aronia melanocarpa Flavonol Extracts' Effect on Lymphoblast Normal Cells
In order to assess the toxicity of the extract and black chokeberry flavonol extract, the researches investigated the cytotoxicity using a human lymphoblastic RPMI-1788 cell line (Fig. 3).
Analysis of the number of viable cells in each sample showed that incubating cells with Aronia ethanol extract at relatively low concentrations in combination with cyclophosphamide (1.25 mg/mL) caused a significant cytotoxic effect on normal human cells for 24 h in the culture medium. At 0.25 mg/mL and lower concentrations, the Aronia flavonol fraction had a protective effect on the viability of the lymphoblast cells under the stress induced by cyclophosphamide.
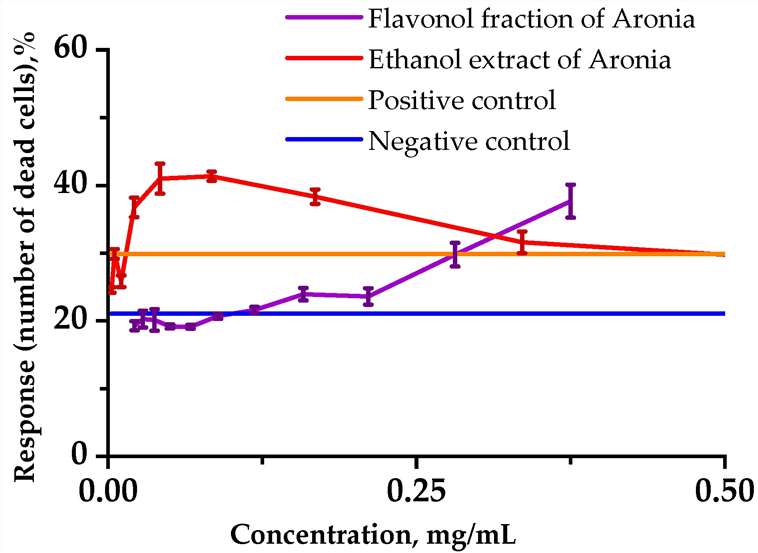 Fig. 3. Influences of the analyzed substances on the viability of RPMI-1788 cells (Bushmeleva, Kseniya, et al. 2023).
Fig. 3. Influences of the analyzed substances on the viability of RPMI-1788 cells (Bushmeleva, Kseniya, et al. 2023).
Trypsin is a serine protease enzyme helps to detach the adherent cells from tissue culture flask. EDTA as a chelating agent, will helps to trigger the activity of the trypsin, without EDTA trypsin will not detach the cells.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 4.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
High-quality
The gallbladder tumor cells I purchased from Creative Bioarray were of high purity and showed excellent growth and proliferation in my experiments.
18 Apr 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need