Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

ONLINE INQUIRY
HPB-ALL
Cat.No.: CSC-C0497
Species: Human
Source: T cell leukemia
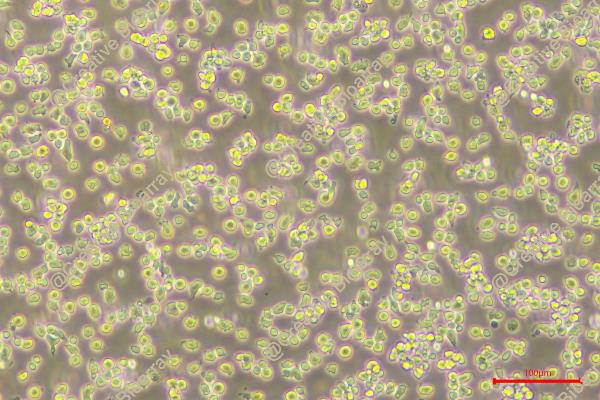
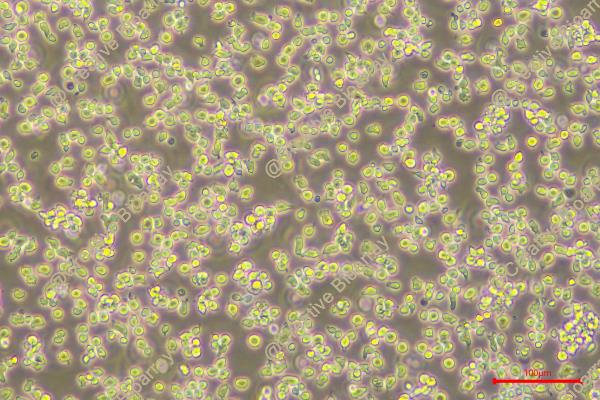
Morphology: round to polymorph cells growing singly or in clusters in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
Immunology: CD2 +, CD3 +, CD4 +, CD5 +, CD6 +, CD7 +, CD8 +, CD13 -, CD19 -, CD34 -, TCRalpha/beta +, TCRgamma/delta -
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, S
The HPB-ALL cell line was established in 1973 from the peripheral blood of a 14-year-old Japanese boy who was diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and thymoma at the time of diagnosis. The cells express markers associated with T-cell development, such as CD2, CD3, CD5, and CD7, but lack expression of more mature T-cell markers like CD4 and CD8. Cytogenetic analysis of the HPB-ALL cells has revealed a complex karyotype, with multiple chromosomal abnormalities typical of T-cell ALL.
The HPB-ALL cell line can be cultured in vitro and maintains its leukemic phenotype, making it a valuable model for investigating the biology and treatment of T-cell ALL. Researchers have utilized this cell line to study various aspects of T-cell transformation, signaling pathways, and drug sensitivity, contributing to the development of more effective treatments for patients with T-cell ALL.
Caspase-Independent Cell Death by FAS Ligation in HPB-ALL Cells
In HPB-ALL cells, a human thymus-derived T-cell line, Fas (CD95)-mediated cell death was inhibited by about only 50% as a result of treatment with an amount of benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-(O-methyl)-CH(2)F (zVAD-fmk) sufficient to block the caspase activity.
The cell death by the anti-human Fas antibody, CH11, was dependent on the concentration of CH-11 by the XTT method in HPB-ALL cells (Fig. 1A). Pretreatment with ZB4, which is known as Fas-neutralizing Abs, completely blocked cell death by CH-11 (Fig. 1B). By the treatment with 20 or 50 µM zVAD-fmk, this cell death was inhibited by about only 50% with CH-11 (Fig. 1A). The treatment of zVAD-fmk did not affect the cell viability in HPB-ALL cells (Fig. 1A). Under these conditions, the activation of caspase-3 by Fas ligation was inhibited completely by the treatment with 20 µM zVAD-fmk (Fig. 1C). By the treatment with 100 µM zIETD-fmk, which is a specific inhibitor of caspase 8, one of the initiator caspases, Fas-mediated cell death was also inhibited to the same extent as in the zVADfmk treatment in HPB-ALL cells (Fig. 1D). Next, the effect of the treatment of zVAD-fmk on Fas-mediated cell death were examined in other human lymphoblast cell lines. In all four cell lines, Fas-mediated cell death was inhibited by the treatment with 20 µM zVAD-fmk, which was different from the results for the HPB-ALL cells (Fig. 1E).
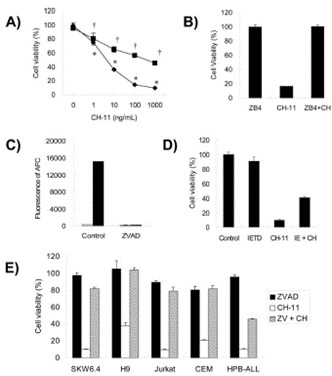 Fig. 1 Effect of zVAD-fmk on Fas-mediated cell death in HPB-ALLs. (Nakayama J, et al., 2007)
Fig. 1 Effect of zVAD-fmk on Fas-mediated cell death in HPB-ALLs. (Nakayama J, et al., 2007)
The Oxidation of EGCG Inhibits HPB-ALL Cell Lines via the Regulation of Notch1 Expression
T-cell ALL (T-ALL) is an aggressive hematological malignancy, and commonly associated with activating mutations in the Notch1 pathway. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) has been shown to regulate Notch signaling. The chemical oxidation of EGCG has been reported under various oxidative conditions. EGCG was reacted with to yield the EGCG oxides 2-4 in 1.3-6.3% yields (Fig. 2).
To investigate the effects of compound 3 on the Notch1 signaling pathway, the expression of Notch1 and the downstream proteins in HPB-ALL cells were examined (Fig. 3). As shown in Fig. 3B-F, HPB-ALL cells were treated with compound 3 at the concentration of 5, 10, 20, 40, 60 μM for 12 h and the expression level of Notch1, cleaved-Notch1, c-Myc, and Hes1 were significantly decreased. Meanwhile, the expression of proliferation marker Ki67 was significantly reduced (Fig. 3B and G). These findings suggest that compound 3 inhibited the proliferation of HPB-ALL cells be through down-regulating the expression of Notch1 and Ki67. Compound 3 significantly induced Annexin V-positive apoptotic cells in HPB-ALL cells (Fig. 4A and B). Moreover, compound 3 induced the expression levels of caspase 3, caspase 9, and PARP 1, and increased the expression levels of cleaved-caspase 3, cleaved-caspase 9, and cleaved-PARP 1 (Fig. 4C-F).
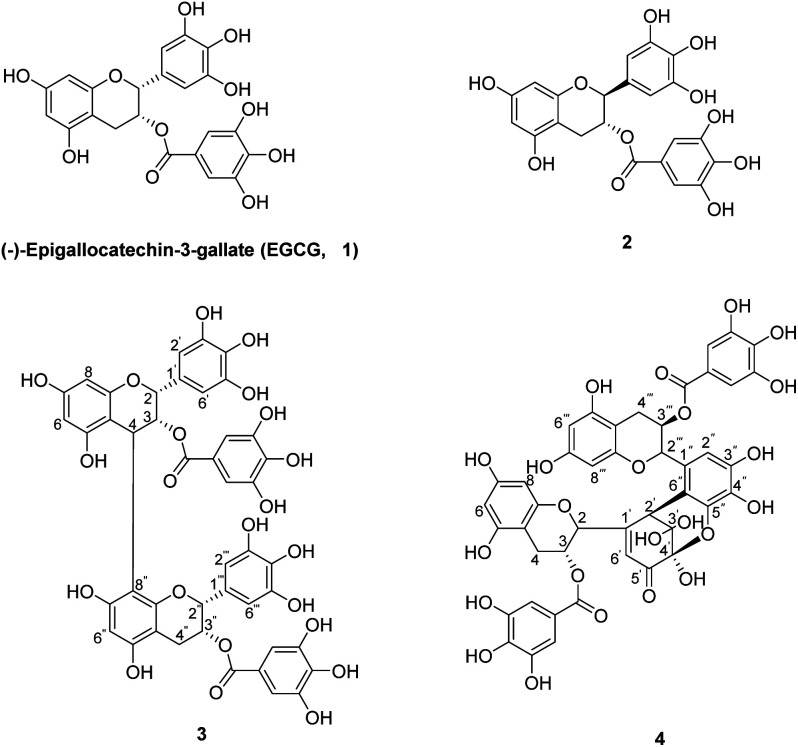 Fig. 2 The chemical structures of EGCG (1) and its oxides (2-4). (Wang YN, et al., 2020)
Fig. 2 The chemical structures of EGCG (1) and its oxides (2-4). (Wang YN, et al., 2020)
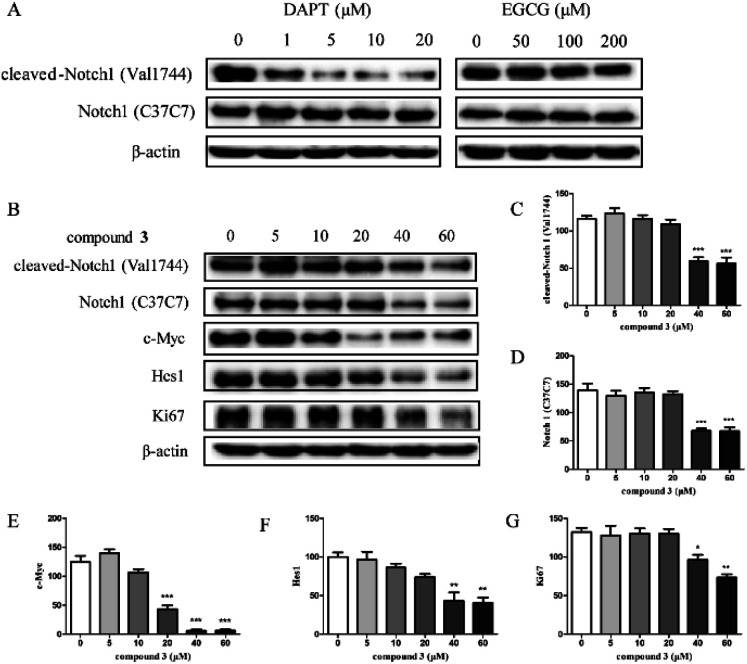 Fig. 3 The effect of compound 3 on Notch1 processing and downstream signaling pathway in HPB-ALL cells. (Wang YN, et al., 2020)
Fig. 3 The effect of compound 3 on Notch1 processing and downstream signaling pathway in HPB-ALL cells. (Wang YN, et al., 2020)
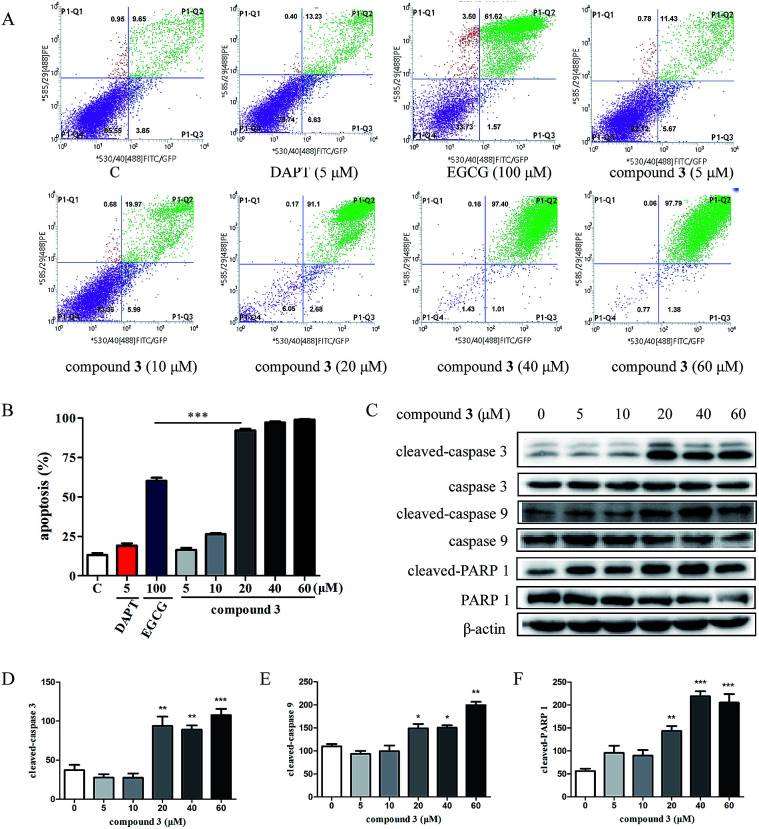 Fig. 4 Compound 3 induces apoptosis in HPB-ALL cells. (Wang YN, et al., 2020)
Fig. 4 Compound 3 induces apoptosis in HPB-ALL cells. (Wang YN, et al., 2020)
In situ hybridization (ISH) is a technique that uses colorimetric or fluorescent probes to target and visualize specific DNA or RNA sequences within tissues. This technology can be broadly applied to study infectious agents, cancer, or developmental biology.
The HPB-ALL cell line was established in 1973 from the peripheral blood of a 14-year-old Japanese boy who was diagnosed with ALL and thymoma.
HPB-ALL cells are of T-cell lineage, exhibiting characteristics of immature T-cells. They express markers associated with T-cell development, such as CD2, CD3, CD5, and CD7, but lack expression of more mature T-cell markers like CD4 and CD8.
The HPB-ALL cell line can be cultured in vitro and maintains its leukemic phenotype, making it a reliable and accessible model system for studying the molecular pathogenesis of T-cell ALL. The availability of this cell line has been instrumental in advancing our understanding of T-cell transformation and the evaluation of novel therapeutic strategies.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 3 Scientist has reviewed this product
Good results
We culture the cells <em>in vitro</em>, which can be used as a reliable model for studying lymphoma and its progression.
11 Apr 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Satisfied
As a researcher studying T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, I have been extremely satisfied with the HPB-ALL cell line from Creative Bioarray.
21 Feb 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Invaluable tools
The ease of ordering and the consistent quality of the HPB-ALL cells have been invaluable for my research.
09 May 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- You May Also Need